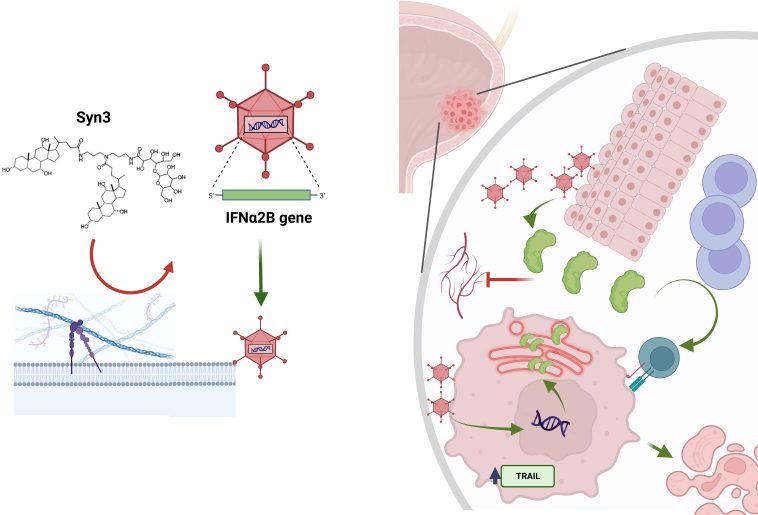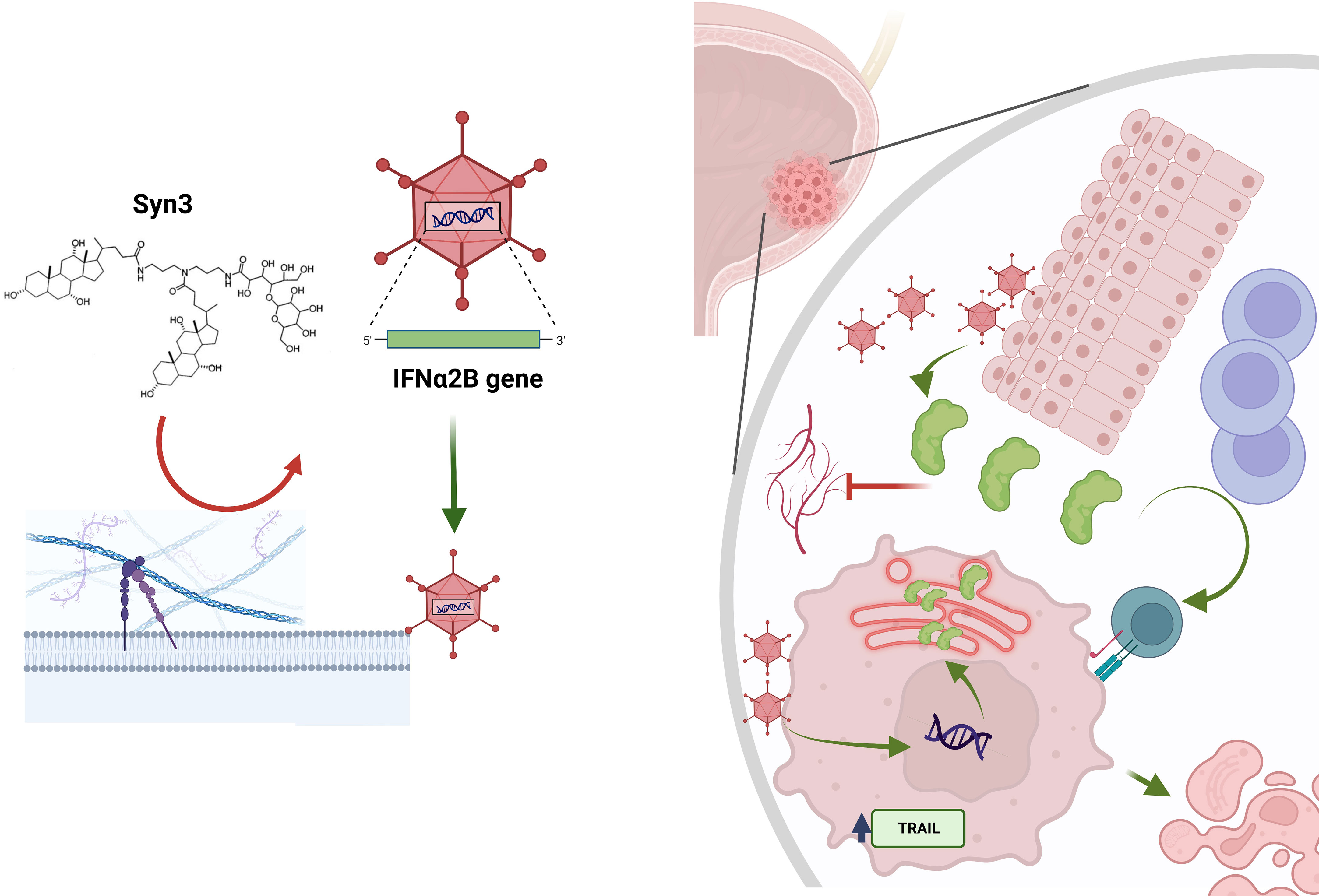
Understanding BCG-Unresponsive Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
The treatment landscape for BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer has changed dramatically over the past few years. For patients who experience high-grade recurrences after an adequate course of BCG therapy, the available options have expanded, offering alternatives that avoid the need for radical cystectomy. This opinion editorial takes a closer look at one such alternative—nadofaragene firadenovec—and explores its role, real-world implementation, and the challenges that come with integrating new treatments into everyday clinical practice.
Patients with BCG-unresponsive bladder cancer previously faced limited choices. Radical cystectomy, although considered the gold standard, is an intimidating procedure that many find overwhelming or simply cannot tolerate due to age, comorbidities, or personal preferences. As medical professionals and patient advocates, we must acknowledge the tangled issues involved when addressing a disease where treatment decisions affect both survival and quality of life.
In this editorial, we will dig into the key areas of patient selection, the logistical advantages of a quarterly dosing schedule, and the subtle parts of integrating this new therapy into established practices. By sharing expert insights and highlighting real-world experiences, we aim to provide a balanced view of where nadofaragene firadenovec fits into the current treatment paradigm.
Nadofaragene Firadenovec and Its Quarterly Dosing Advantage
One of the standout features of nadofaragene firadenovec is its quarterly dosing schedule. Unlike traditional intravesical agents that require more frequent instillations, this therapy, given only once every three months, eases many of the practical burdens for both patients and clinicians. This may become an essential advantage for elderly patients and those living far from treatment centers.
The quarterly dosing schedule offers several key benefits:
- Reduced Visits: Fewer treatments mean less travel time and fewer disruptions to daily life.
- Simpler Coordination: With appointments spread out over three months, scheduling can be easier and less nerve-racking.
- Less Invasive: Minimizing the frequency of catheterizations helps reduce the chance of discomfort and local side effects.
For many patients, especially those who have already endured multiple BCG instillations which can be both physically and emotionally draining, the promise of an approach that offers both continued treatment efficacy and improved quality of life is truly promising. Logistical ease is a defining factor in treatment adherence and overall satisfaction in care delivery.
Identifying the Ideal Candidates for Nadofaragene Firadenovec
One of the crucial challenges in any emerging therapy is determining which patients stand to benefit the most. In the realm of BCG-unresponsive bladder cancer, candidate selection is critical, and it is important to figure a path through the tangled issues of treatment eligibility.
According to clinical experts, including the insights shared by Dr. Fed Ghali in recent discussions, the ideal recipient for nadofaragene firadenovec is a patient who meets the following criteria:
- High-Grade Recurrence Status: The patient must have undergone an adequate BCG treatment regimen—often defined as a minimum of seven doses—with subsequent high-grade recurrence.
- Ineligibility for Radical Cystectomy: Candidates typically are those who either refuse cystectomy due to its intimidating nature or who are not medically fit for such a radical intervention.
- Retention Capability: The therapy relies on maintaining the agent in the bladder long enough for it to exert its effect, so patients must have the capacity to retain the therapeutic solution without immediate voiding.
In essence, the fine points of candidate selection often come down to careful patient history and personal circumstances. By integrating comprehensive evaluations into clinical practice, practitioners can better steer through the potential benefits and ensure that each patient is matched with the most suitable therapeutic option. This decision-making process is super important both from a clinical outcome perspective and for maintaining quality of life.
Practical Implementation in Clinical Settings
Introducing a new therapy like nadofaragene firadenovec into a busy urology clinic involves tackling several practical, and sometimes complicated, pieces. As reported by clinicians who have started using the therapy, the steps to successfully incorporate this treatment have been manageable, though not without a few initial bumps.
A summary of the implementation process includes:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Pharmacy Coordination | Since nadofaragene firadenovec is an adenovirus-based therapy, coordination with the pharmacy becomes essential to ensure safety protocols are met and proper handling procedures are established. |
| Staff Training | Nursing and support staff need to be familiarized with the unique handling and administration of this agent compared to traditional therapies like BCG or chemotherapy. |
| Patient Scheduling | The quarterly dosing schedule requires a revamp of patient calendar planning. This less frequent schedule, however, can boost patient adherence as it reduces the number of required visits. |
| Managing Expectations | Clinicians must set realistic expectations regarding potential side effects, such as increased urinary urgency and bladder spasms, and how these will be managed. |
By following these steps, many practices have reported a smooth transition into using nadofaragene firadenovec, noting that early logistic challenges are typically overcome with a bit of teamwork and clear communication. Importantly, these practical measures highlight the need to consider the subtle differences that new therapies bring into the clinical workflow.
Managing Side Effects: Bladder Spasms and Urinary Symptoms
Introducing new treatment options always comes with the responsibility of managing unpredictable side effects. In the case of nadofaragene firadenovec, clinicians have noted that patients may experience more pronounced bladder spasms and urinary symptoms than those treated with traditional BCG or the gemcitabine-docetaxel regimen. Though these side effects are generally manageable, they do present their own set of tricky parts.
Strategies to address these challenges include:
- Anticholinergic Medications: The pre- and post-treatment use of anticholinergics can help minimize or prevent the overactivity of the bladder muscles.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about the likelihood of urinary symptoms helps reduce anxiety when these effects occur. Understanding that these are expected reactions rather than signs of treatment failure is crucial.
- Close Monitoring: Regular follow-ups and symptom tracking can identify individuals who are experiencing more severe side effects, allowing for timely intervention.
While these tricky parts might appear intimidating at first, many clinicians find that they are well worth managing if the alternative means continuing with a potentially more effective treatment option without the need for radical surgery.
Real-World Experiences and Clinical Trial Comparisons
It is one thing to discuss data from tightly controlled clinical trials, and another to see how that data translates into everyday practice. Dr. Ghali’s experience with approximately 20 patients so far offers a glimpse into the real-world experience with nadofaragene firadenovec and illustrates important differences between clinical trial cohorts and patients seen in most clinics.
Some of the observations from these early experiences include:
- Enhanced Bladder Activity: Patients consistently show a more active bladder response, which is beneficial if it indicates that the therapy is engaging the target area. However, it can also be associated with increased discomfort.
- Cumulative Effects: The timing of nadofaragene firadenovec administration relative to previous salvage therapies appears to impact its effectiveness. Anecdotal evidence suggests that whether the therapy is given immediately after BCG or after additional salvage treatments might make a difference in outcomes.
- Pharmacy and Process Adaptations: Early adopters noted that once the initial coordination with the pharmacy was streamlined, the therapy was quickly adopted into regular practice. This real-world implementation shows that while there are some tangled issues at the outset, they can be overcome with proper planning and teamwork.
It is important to note that many of these findings are still considered preliminary. While head-to-head comparisons with other agents in similar settings remain limited, early feedback encourages further investigation and larger prospective trials to refine treatment sequences and optimize patient outcomes.
Evaluating the Role of Comparative Clinical Trials and Sequencing Strategies
One of the key challenges in adopting new therapies in a busy clinical setting is making sense of how they stack up against established treatments. Right now, most data on nadofaragene firadenovec come from single-arm trials. This means that direct comparisons with other agents are limited, making it tricky to understand where this new intervention fits within the broader treatment paradigm.
Here are a few of the subtle details and fine shades involved in the sequencing of therapies in bladder cancer:
- The Need for Head-to-Head Studies: Ideally, robust comparative trials would answer the question of whether nadofaragene firadenovec offers superior outcomes compared to other salvage therapies.
- Patient Subgroups: Future trials should aim to identify biomarkers or clinical characteristics that predict which patients might derive the greatest benefit. This could help in fine-tuning treatment plans for different populations.
- Sequential Benefits: Understanding whether previous salvage therapies diminish or enhance the response to nadofaragene firadenovec remains an open question. Anecdotally, the response rate might be different if the agent is administered directly after BCG versus later after further treatments.
In many ways, figuring out the best sequence of treatments is like trying to find your way through a maze: every step needs to be carefully evaluated so the optimal path becomes clear. The current data remind us that treatment decisions are rarely black and white, and that a patient’s journey often includes many small twists and turns that must be taken into account.
Balancing Radical Cystectomy with Conservative Management
Radical cystectomy has long been considered the gold standard for patients with high-grade bladder cancer who are unresponsive to BCG. However, this surgical option is known to be a nerve-racking undertaking, especially for older patients or those with other significant health concerns. It is essential to balance the recognized benefits of surgery with the potential quality-of-life advantages offered by newer, less invasive therapies.
Some of the factors to consider when weighing these options include:
- Surgical Risks: Radical cystectomy carries with it the risk of significant complications, extended recovery time, and changes in urinary function. For some patients, these risks can be both overwhelming and off-putting.
- Quality of Life: Many patients prefer treatments that allow them to maintain their lifestyle with minimal disruption. The quarterly dosing schedule of nadofaragene firadenovec and its non-invasive administration may offer an attractive alternative.
- Long-Term Outcomes: Despite the promise of new therapies, long-term cure rates remain a critical factor in treatment decisions. Clinicians must ensure that patients clearly understand that radical cystectomy remains the most definitive treatment in many cases.
This balancing act between radical surgery and conservative management requires an honest conversation between clinicians and patients. It is essential that patients are given all the necessary information about the potential benefits and limitations of newer treatments, while also recognizing that surgery, in many cases, continues to offer the best chance for cure.
Expert Opinions and Real-World Insight from Urological Oncologists
Feedback from practicing urological oncologists has been instrumental in painting a realistic picture of how new therapies are being received. Experts like Dr. Fed Ghali and Dr. Zachary Klaassen have contributed valuable insights, highlighting not only the promising aspects of treatments like nadofaragene firadenovec but also the need for continued research and evidence-based refinements.
Key takeaways from expert opinions include:
- Ease of Incorporation: Many clinicians report that, after overcoming initial hurdles with pharmacy coordination, the therapy was easily integrated into routine practice.
- Patient-Centric Approaches: The choice of therapy must take the patient’s overall condition, previous treatment history, and lifestyle into account. In many cases, the new therapy provides a welcome alternative for those reluctant or unable to undergo surgery.
- A Call for More Data: While the current real-world feedback is promising, there is a strong desire for head-on trial data. More studies are needed to determine the subtle differences in efficacy among various salvage therapies.
The collective opinion of experts seems to be that while new therapies like nadofaragene firadenovec represent a significant step forward, the journey toward fully optimizing treatment for BCG-unresponsive bladder cancer is still evolving. With more comparative research and long-term data, the medical community will be better equipped to fine-tune treatment algorithms and improve patient outcomes.
The Future of Bladder Cancer Treatment: Biomarkers and Personalized Therapy
Looking ahead, one of the most exciting prospects in the treatment of bladder cancer is the development of personalized therapy guided by biomarkers. As our understanding of the threatening twists and turns within the disease’s progression improves, researchers hope to identify specific markers that can predict treatment responses with greater accuracy.
The potential benefits of a biomarker-driven approach include:
- Customized Treatment Plans: Patients could receive therapies that are tailored to their individual disease profiles, increasing effectiveness and reducing unnecessary side effects.
- Early Identification of Non-Responders: Biomarkers may help clinicians determine early on which patients are unlikely to respond to standard therapies, thereby allowing a quicker switch to alternative treatments.
- Refined Patient Stratification: Understanding subtle details in tumor biology could lead to better stratification of patients into subgroups, allowing for more targeted trials and improved therapeutic outcomes.
While these advances remain in the research phase for now, ongoing studies and collaborative efforts across institutions are paving the way for a future where therapy is as individualized as the patient. This could eventually transform the landscape of bladder cancer treatment, making it possible to steer through the complicated pieces of treatment selection with far greater confidence.
Logistical Considerations and the Role of the Multidisciplinary Team
Introducing advanced therapies into clinical practice is not solely about the therapeutic agent itself. It is also about the entire healthcare ecosystem that supports patient care—from the pharmacy and nursing teams to scheduling systems and patient education. The successful implementation of nadofaragene firadenovec highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach and a coordinated plan.
Key logistical challenges and solutions include:
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Coordination between departments is essential for managing new therapies. Pharmacists and clinical staff must become familiar with handling adenovirus-based agents, which differ from traditional intravesical therapies.
- Staff Training and Adaptation: It is important that staff members are trained and comfortable with the new protocols. This reduces the likelihood of errors and helps ensure patient safety.
- Patient Scheduling and Follow-Up: With treatments scheduled every three months, patient tracking systems need an update. Effective scheduling software and appointment reminders can help both patients and clinicians manage long-term care more effectively.
The role of the multidisciplinary team cannot be overstated. When everyone from the laboratory team to the clinical support staff is working together, patients reap the benefits of a seamless, well-organized treatment process.
Comparative Advantages and the Need for Further Investigation
Although current findings are promising, there remain several nerve-racking unanswered questions in the realm of bladder cancer treatment. The differences between immediate post-BCG treatment versus after additional salvage therapies, for instance, are still being explored by researchers. Even as clinicians report good early outcomes, many subtle details remain to be sorted out.
Key areas where further investigation is essential include:
- Treatment Sequencing: More head-to-head studies are necessary to compare the efficacy of nadofaragene firadenovec with traditional therapies. Only through direct comparisons can clinicians figure a path toward the most effective treatment algorithms.
- Response Durability: Long-term data regarding the durability of responses with this new agent are still emerging. Clinicians will benefit from knowing how long the therapeutic benefits last and whether additional regimens are needed over time.
- Patient-Specific Factors: Ongoing research into patient demographics, genetic markers, and prior treatment responses will further refine how candidates for this therapy are selected.
Comparative research should also extend to quality-of-life outcomes. While the lower frequency of instillations is attractive, understanding how side effects and long-term bladder function compare across treatment modalities is equally important. These are the kind of fine details that, when clarified, can greatly enhance shared decision-making between doctors and their patients.
Balancing Treatment Efficacy with Patient Quality of Life
Ultimately, all new treatments must be evaluated not only by their ability to control cancer but also by their impact on patient quality of life. Therapies like nadofaragene firadenovec show promise in reducing the treatment burden by limiting the number of required visits and avoiding some of the more invasive aspects of traditional therapies. However, no treatment can be considered entirely in isolation from the challenges it might bring in terms of side effects and overall wellness.
In candid conversations with patients, clinicians must weigh the following points:
- Impact on Daily Living: Treatments that allow patients to maintain a relatively normal routine are often seen as superior, especially when considering the long-term management of a chronic condition.
- Psychological Well-Being: A less frequent dosing schedule can significantly reduce anxiety around treatment, making it easier for patients to commit to ongoing care.
- Financial Considerations: Reduced appointment frequency may also lower the indirect costs associated with treatment, such as travel, time off work, and caregiver responsibilities.
From a broader perspective, balancing treatment efficacy and quality of life remains a cornerstone of cancer care. Patients who fully understand both the potential gains and the possible side effects of new therapies are better equipped to make informed choices about their health. This balanced approach not only optimizes clinical outcomes but also supports overall well-being over the long run.
A Glimpse into Future Research Directions
The constantly shifting landscape of bladder cancer treatment suggests that we are only beginning to grasp the potential benefits—and challenges—of newer therapies like nadofaragene firadenovec. In the near future, several important areas of research need to be addressed:
Future studies should focus on:
- Direct Comparative Studies: Robust, randomized controlled trials comparing nadofaragene firadenovec with other salvage therapies will provide clearer guidance on sequencing and optimal patient selection.
- Biomarker Validation: Research into biomarkers that predict treatment response will be super important. Such markers could help clinicians better match patients with the most effective therapy, thereby enhancing outcomes.
- Long-Term Outcome Analysis: Extended follow-up studies are needed to assess the durability of treatment responses, incidence of adverse events over time, and overall survival benefits.
- Patient-Reported Outcomes: Incorporating patients’ perspective on quality of life, symptom management, and treatment satisfaction into clinical trials will provide a fuller picture of the therapy’s real-world impact.
Table 1 below offers a summary of some key research prospects and their associated benefits:
| Research Focus | Potential Benefit |
|---|---|
| Head-to-Head Comparative Studies | Clearer insights into efficacy and proper treatment sequencing |
| Biomarker Validation | Customized therapy plans and improved patient outcomes |
| Long-Term Follow-Up | Understanding durability and managing late-occurring side effects |
| Patient-Reported Outcomes | Enhanced focus on quality of life and treatment acceptability |
These research directions are more than academic exercises—they have the potential to transform patient care. By addressing these tense, unsolved questions head-on, the field of bladder oncology can ensure that the next generation of treatments provides both effective cancer control and a better quality of life.
Concluding Reflections: A Balanced Appreciation of New Therapeutic Options
In summary, the introduction of nadofaragene firadenovec into the treatment of BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer marks an exciting turning point. Its quarterly dosing schedule, potential to decrease treatment-related disruptions, and promising early real-world outcomes are all encouraging signs for patients and clinicians alike.
As we figure a path through this rapidly evolving area, it is important to remember:
- Radical cystectomy remains the gold standard for many patients, and any alternative treatment must be weighed against the long-term benefits of surgery.
- New therapies bring their own set of complicated pieces and challenging parts, but they also offer hope for those who need treatment options beyond traditional methods.
- Continued research and well-designed comparative trials will be essential to uncover the fine points of treatment sequencing and patient selection, ensuring that each patient gets the best possible care.
- Multidisciplinary teamwork and patient-centered communication are critical in managing expectations and ensuring that patients are comfortable with the chosen treatment path.
These reflections highlight that while the introduction of new therapeutic agents like nadofaragene firadenovec presents its own set of challenges, it ultimately enriches the options available for managing a complex disease. Collaboration among researchers, clinicians, and patients is key to evolving treatment paradigms and making the best use of these innovative therapies.
As a community committed to medical advancement and holistic patient care, we must continue to take a closer look at not only the efficacy of new treatments, but also their impact on everyday life. With thoughtful integration, ongoing research, and honest patient engagement, the future of bladder cancer treatment looks promising—a future where the burden of frequent treatments may be alleviated, and the quality of life significantly improved.
In closing, it is evident that while challenges remain and many details are still to be clarified, the potential benefits of therapies such as nadofaragene firadenovec make it a valuable addition to the armamentarium against BCG-unresponsive bladder cancer. For those who are not candidates for radical cystectomy, this innovation offers hope—a reminder that even in the midst of tricky therapeutic choices, progress is being made. We look forward to more robust data and comprehensive results that will help guide future treatment decisions in this dynamic field.
Ultimately, whether you are a clinician working through the practical bits of introducing new treatments or a patient exploring options for managing your condition, remember that every step forward—no matter how small—contributes to a larger journey toward better health outcomes. The ongoing dialogue between research and real-world practice is paving a promising path forward, where collaboration, continued inquiry, and adaptive strategies will lead to improved care for all.
Read more about this topic at
Transformative advances in bladder cancer treatment
Bladder Cancer Treatment – NCI