Advanced Endometrial Cancer Treatment Outcomes: Evaluating New Maintenance Strategies
The landscape of advanced endometrial cancer treatment is constantly evolving, and recent research on selinexor maintenance therapy offers a promising glimpse into how patients with TP53 wild-type disease might experience improved outcomes. In this opinion editorial, we take a closer look at the phase 3 SIENDO trial and its long-term findings, discussing the potential benefits of this approach and highlighting what it might mean for future treatment plans.
With modern oncology steadily advancing, it is crucial to figure a path through the tricky parts of cancer treatment. The SIENDO trial’s results have sparked conversations among clinicians about not only the improved progression-free survival (PFS) but also the extended time intervals to subsequent therapies, providing patients with more time to enjoy life between treatment cycles.
Understanding Endometrial Cancer and Treatment Challenges
Endometrial cancer remains one of the most common gynecologic malignancies worldwide, particularly affecting post-menopausal women. The management of advanced or recurrent disease, however, is riddled with confusing bits and twists and turns. For patients who respond to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy, the introduction of maintenance therapies like selinexor could provide a bridge to longer, more manageable remissions.
The challenge is not only in treating the aggressive nature of the cancer but also in managing the side effects and quality-of-life concerns for patients. As clinicians continue to figure a path through these complicated pieces, every incremental improvement in treatment durability is welcomed.
Selinexor Maintenance: A Promising Option for TP53 Wild-Type Patients
One of the key findings from the SIENDO trial revolves around the efficacy of selinexor maintenance therapy in patients with TP53 wild-type endometrial cancer. This subset of patients, representing about 43% of the study population, showed an impressive improvement in several clinical outcomes, even after factoring in the additional burden of managing delicate side effects.
In the realm of advanced cancer care, identifying treatment strategies for patient subgroups is critical. For TP53 wild-type patients, regardless of whether they are mismatch repair–proficient (pMMR) or mismatch repair–deficient (dMMR), selinexor has been observed to extend the duration of progression-free survival and delay the time to both first and second subsequent therapies. This benefit points to how the sustained clinical effect of maintenance therapy could become a key component of treatment protocols in the near future.
TP53 Wild-Type Endometrial Cancer Maintenance Therapy Insights
Patients with TP53 wild-type advanced or recurrent endometrial cancer can potentially benefit significantly from selinexor maintenance. The SIENDO trial, a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase 3 study, was designed to test the hypothesis that selinexor could work as a long-term strategy after an initial positive response to platinum-based chemotherapy.
For many, the idea of introducing a maintenance therapy after initial treatment can feel a bit intimidating, given how overwhelming additional medication regimens may be. However, the trial data indicate that when used appropriately, selinexor’s administration—even at adjusted doses based on BMI—could balance clinical benefit with manageable toxicity.
Key outcomes from the trial include:
- Improved median progression-free survival (PFS) rates in both the pMMR and dMMR subgroups.
- Significant extensions in the time to first subsequent therapy (TFST) and the time to second progression (PFS2).
- Enhanced durability of the therapeutic effects without compromising the subsequent use of immunotherapy.
Digging into the SIENDO Trial Data: What the Numbers Tell Us
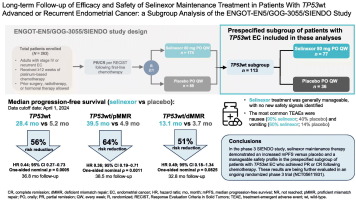
The SIENDO trial results are rich with insights. In particular, they underscore the potential of selinexor maintenance to extend key endpoints. One of the most striking contrasts was seen in the TP53 wild-type/mismatch repair–proficient group, where the median PFS reached 39.5 months with selinexor compared to just 4.9 months with placebo.
This dramatic difference is not only encouraging but also suggests that selinexor may allow patients a more extended period free from the stressful burden of disease progression. Even in the TP53 wild-type/mismatch repair–deficient subgroup, the extension of median PFS from 3.7 months (placebo) to 13.1 months (selinexor) provides hope even though the statistical significance was a bit more challenging to pin down.
Interpreting Key Endpoints: PFS, TFST, TSST, and PFS2
To better understand the significance of these findings, it is important to break down the key endpoints:
- Progression-Free Survival (PFS): This is the duration over which the disease does not worsen. A longer PFS indicates that selinexor is effectively prolonging a phase where the cancer is under control.
- Time to First Subsequent Therapy (TFST): This measures the interval between the end of the initial treatment and the start of another therapy. Longer TFST suggests that patients enjoy a longer window of improved quality of life before requiring additional treatments.
- Time to Second Subsequent Therapy (TSST): Similar to TFST, TSST provides deeper insights into the long-term benefits of maintaining disease control.
- PFS2: This allows us to see if the benefits of selinexor extend beyond the immediate maintenance phase, indicating cumulative treatment effectiveness over multiple therapy lines.
These endpoints, interpreted together, help clinicians and patients figure a path through treatment decisions by offering clear signals about treatment durability and overall benefit, even as they cope with the practical challenges of extended therapy regimens.
Safety Profile and Managing Side Effects in a Real-World Setting
No conversation about maintenance therapy would be complete without discussing the safety and tolerability of the treatment. In the SIENDO trial, while selinexor demonstrated significant clinical benefits, it also brought with it a range of treatment-emergent adverse effects (TEAEs) that must be managed effectively.
Common side effects reported among patients receiving selinexor included nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, asthenia (physical weakness), fatigue, thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite, and neutropenia. Although most of these effects were observed at lower grades, the grade 3 or higher events—particularly neutropenia, significant thrombocytopenia, and severe nausea—remind us that managing these treatments requires careful consideration and a tailored approach.
Selinexor Side Effects: Balancing Efficacy and Tolerability
For many clinicians, the decision to initiate a treatment like selinexor maintenance comes down to balancing the super important clinical benefits with the potential for uncomfortable side effects. A summary table often used to capture the essence of this balance in the SIENDO trial is shown below:
| Side Effect | Any-Grade Occurrence (Selinexor) | Grade 3 or Higher (Selinexor) |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 90% | 13% |
| Vomiting | 60% | 3% |
| Diarrhea | 45% | Data not separately highlighted |
| Constipation | 33% | Not associated with grade 3 or higher effects |
| Asthenia | 32% | Not reported as grade 3 or higher |
| Fatigue | 30% | Data not separately highlighted |
| Thrombocytopenia | 42% | 10% |
| Neutropenia | 34% | 20% |
| Anemia | 33% | 7% |
| Abdominal Pain | 26% | Data not highlighted as severe |
This table makes it clear that while side effects are common, most are manageable with proactive monitoring and supportive care. The comparatively lower frequency of severe adverse events may help clinicians reassure patients who are understandably nervous about potential toxicity.
Comparing Clinical Benefits: Selinexor Versus Placebo
Perhaps one of the most compelling aspects of the SIENDO trial is the demonstrable difference in outcomes between patients receiving selinexor maintenance and those on placebo. When viewed across multiple endpoints – including progression-free survival, TFST, TSST, and PFS2 – the data reveal a consistent benefit favoring selinexor.
In the context of advanced endometrial cancer, these differences can translate into more quality time for patients who are already facing a maze of treatment decisions. The improvements in median survival times, especially in the pMMR subgroup, indicate that extended disease control can provide a meaningful pause from the nerve-racking demands of switching to new therapies repeatedly.
Clinical Outcomes in Focus: Detailed Comparison
Let’s break down the comparison further:
- Progression-Free Survival: In the pMMR subgroup, patients on selinexor enjoyed a median PFS that was nearly eight times longer than that of the placebo group, showcasing the drug’s potential to delay disease progression substantially.
- TFST: The extended interval before patients needed a subsequent therapy is a critical measure of treatment sustainability. With selinexor, the TFST was markedly improved, suggesting better maintenance of disease stability.
- PFS2: This secondary endpoint even hints at the possibility that selinexor does not adversely affect the overall long-term treatment plan, including the efficacy of subsequent therapies like immunotherapy.
For both clinicians and patients, these outcomes are not just numbers in a study—they represent tangible, quality-of-life improvements that are super important in the fight against such a relentless disease.
Working Through the Difficult Bits: The Role of MMR Status
The SIENDO trial further teased apart outcomes within the TP53 wild-type population by looking at mismatch repair status—a key factor in how cancers respond to treatment. In the world of oncology, details like these can add layers of subtle differences that influence treatment decisions. The study differentiated between pMMR and dMMR tumors, revealing that selinexor was beneficial across both subgroups, though the magnitude of benefit varied.
In practical terms, this means that even when confronted with the messy, tangled issues of individual tumor biology, selinexor shows promise as a broadly applicable maintenance therapy option. Whether patients have tumors that are proficient or deficient in mismatch repair, the therapy appears to manage the tricky parts of the disease’s progression without undermining future treatment choices.
Understanding Mismatch Repair (MMR) and Its Impact on Treatment
Mismatch repair status is a critical determinant in endometrial cancers, affecting both prognosis and the suitability of various therapeutic approaches. In the SIENDO study, patients were meticulously classified into pMMR and dMMR groups, allowing researchers to explore how selinexor’s benefits might differ across these categories.
Here are some key points regarding MMR status and treatment outcomes:
- pMMR Patients: In these patients, the maintenance therapy yielded a remarkable extension in PFS and TFST, indicating a robust response to selinexor.
- dMMR Patients: Although the improvement in PFS was modest in numerical terms compared to the pMMR subgroup, selinexor provided meaningful prolongation that could pave the way for more sequential therapies, including the later use of immunotherapy.
This analysis underscores the need for personalized therapy plans. Clinicians must carefully weigh these subtle details as they tailor treatment strategies, ensuring that patients receive a balance between clinical benefits and manageable side effects.
Future Directions: The Ongoing Quest for Improved Therapies
The promising results from the SIENDO trial have already paved the way for further investigations, including the currently enrolling phase 3 XPORT-EC trial. This upcoming study aims to corroborate the benefits of selinexor maintenance and potentially expand its use in the broader treatment landscape for advanced endometrial cancer.
As we work through these nerve-racking treatment decisions, the continuous evolution of clinical trials provides hope. The research not only refines our understanding of how maintenance therapy can extend periods of remission but also guides us in finding your way through the later treatment options that many patients might eventually require.
Integrating New Findings Into Clinical Practice
What does the future hold for clinicians managing advanced endometrial cancer? With the phase 3 XPORT-EC trial underway, the promise of maintenance therapy with selinexor is being weighed against the need for evidence-based, long-term solutions. The ongoing research is expected to address several of the small distinctions in patient response and help refine dosing protocols, especially in patient populations that are more vulnerable due to lower BMI or other risk factors.
In the clinical setting, integrating these findings involves:
- Educating patients and families about the potential benefits and side effects.
- Carefully monitoring patients to catch and manage any adverse events early.
- Tailoring treatment protocols to consider individual differences in tumor biology, such as TP53 wild-type status and MMR classification.
- Collaborating across specialties to ensure that supportive care measures are optimized alongside primary therapy.
Such a multi-pronged approach is necessary to not only extend survival but also maintain a better quality of life for patients as they manage the challenging bits of their treatment journey.
Long-Term Outlook: Quality of Life and Disease Management
One of the most enduring questions in cancer care is how to improve patients’ lives beyond the immediate battle against tumor progression. The findings on selinexor maintenance therapy emphasize that, by delaying the need for subsequent lines of therapy, patients might enjoy longer intervals of relative well-being—a key factor in overall quality of life.
Extended progression-free intervals also allow patients time to manage the practical issues associated with advanced cancer. From reducing the frequency of hospital visits to easing the psychological burden of constantly shifting treatment regimens, these improvements could both literally and figuratively provide patients with breathing room during an already nerve-racking journey.
Benefits Beyond Clinical Metrics
When considering treatment options, it is important for both clinicians and patients to appreciate the broader impacts of a therapy. The longer intervals measured by endpoints like TFST and TSST translate into more time for patients to focus on their everyday lives—whether that means engaging in physical fitness activities, spending quality time with loved ones, or pursuing personal goals without the constant interruption of medical procedures.
This focus on quality of life is key. Effective maintenance therapy, such as that offered by selinexor, might represent not only an opportunity to delay disease progression but also a strategy to better balance treatment efficacy with the patient’s overall well-being.
Expert Perspectives: Weighing the Benefits Against Practical Concerns
From an editorial standpoint, it is clear that the promise of selinexor maintenance in advanced endometrial cancer stokes both optimism and cautious realism. On one hand, the extended progression-free survival and delayed need for further treatments are compelling reasons to consider incorporating this approach into clinical practice. On the other hand, the management of side effects and ensuring patient adherence to the maintenance regimen require constant attention.
Clinicians now have the task of steering through both the clinical benefits and the complicated pieces related to adverse effects. This means a proactive approach: educating patients, closely monitoring lab results, and implementing supportive care protocols to manage symptoms like nausea or thrombocytopenia before they escalate. Each patient’s journey is unique, and minor adjustments might be needed along the way.
Addressing Clinical Concerns in a Collaborative Environment
Patient care in this context is truly a team effort. Key strategies for addressing these challenges include:
- Frequent Monitoring: Regular lab tests and clinical evaluations help catch any detrimental side effects early.
- Personalized Dosing: Adjustments based on factors such as BMI can ensure that patients receive a dose that is both effective and tolerable.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about what to expect and when to report symptoms is critical in the proactive management of treatment-related issues.
- Multidisciplinary Collaboration: Oncologists, oncology nurses, nutritionists, and supportive care teams must work together to provide comprehensive care.
This collaborative model is particularly important in the management of diseases that come with so many little twists, ensuring that both patient safety and treatment effectiveness remain at the forefront of therapeutic decision-making.
Reflections on the Evolving Role of Maintenance Therapy in Oncology
As we take a closer look at the current and future directions of endometrial cancer treatment, it becomes evident that maintenance therapy—despite its nerve-racking aspects—holds significant promise. The extended survival benefits, as evidenced by improved PFS, TFST, TSST, and PFS2, are more than statistical milestones; they are emerging as practical tools in the continuum of cancer care.
The use of selinexor as a maintenance agent in TP53 wild-type advanced endometrial cancer challenges us to reconsider how long-term treatment strategies can be integrated into standard care. While further research remains necessary, especially through trials like XPORT-EC, the cumulative evidence suggests that maintenance therapy may soon be an indispensable part of managing advanced disease.
Maintaining Hope Amidst Treatment Complexities
In the journey of cancer treatment, every new approach must be weighed against the potential pitfalls and the practical challenges of everyday clinical practice. The SIENDO trial’s results remind us that innovations in treatment are rarely free of complications. Instead, they require a balanced approach that honors both the potential for improved survival and the need for effective side effect management.
For patients and caregivers, these trial outcomes are a beacon of hope. They represent not only a scientific breakthrough but also a meaningful step toward extending the quality and duration of life for those grappling with advanced endometrial cancer.
Final Thoughts: Charting a Course Through Complicated Pieces of Treatment Decisions
As an observer and advocate for better patient care, it is clear that the developments in selinexor maintenance therapy highlight both the promise of modern medicine and the ongoing need to figure a path that minimizes treatment burdens. Every patient’s case is unique, made up of many small distinctions and tangled issues that influence both prognosis and treatment tolerance.
It is our responsibility to work collaboratively with clinical teams, ensuring that cutting-edge research translates into real-world benefits. Whether it is carefully monitoring adverse events, customizing treatment plans, or engaging in open dialogues with patients about their expectations and concerns, every aspect of care is super important.
The journey through an advanced cancer diagnosis is on edge and often feels overwhelming. However, as new therapies continue to emerge and clinical trials shed light on sustainable management strategies, there is a renewed sense of optimism. The future of maintenance therapy in endometrial cancer—bolstered by trials like SIENDO and upcoming studies like XPORT-EC—offers tangible hope that we can not only delay disease progression but also significantly improve a patient’s quality of life.
A Call to Action for the Medical Community
The evolving landscape of cancer therapy demands that all of us—clinicians, researchers, and healthcare advocates—stay abreast of emerging data and be ready to incorporate these insights into our practices. While the journey is filled with confusing bits and nerve-racking treatment decisions, it is also ripe with opportunities to make a lasting impact on patient outcomes.
It is critical that we continue to support robust clinical trials, invest in education for healthcare professionals, and adopt a patient-centered approach to care. By doing so, we can more effectively work through the practical challenges of modern oncology and ensure that promising treatments, such as selinexor maintenance, reach those who could benefit most.
Conclusion: Embracing Tomorrow’s Possibilities Today
In summary, the long-term follow-up from the SIENDO trial offers compelling evidence that selinexor maintenance therapy brings significant benefits to patients with TP53 wild-type advanced endometrial cancer. Through improved progression-free survival, longer intervals before subsequent treatments, and manageable side effects, this approach may soon become a cornerstone in the management of advanced endometrial cancer.
While there are still plenty of tricky parts and tangled issues that need further investigation, the advances we see today empower both clinicians and patients to engage in meaningful discussions about treatment options. The collaboration between different specialties, along with the continuous evolution of clinical research, promises a future where quality of life is cherished as much as improved survival metrics.
As we take our next steps on this journey, it is encouraging to know that by tackling the hidden complexities of modern cancer care, we can continue to improve how we manage, respond to, and ultimately overcome advanced endometrial cancer. Embracing these new possibilities with a balanced and informed approach will be key to ensuring that tomorrow’s treatment decisions are even more effective and patient-centered than today’s.
Ultimately, the promise of selinexor maintenance therapy and other innovative treatments lies not only in extending life but also in enhancing its quality. For those facing the overwhelming challenges of advanced cancer, every additional month of stability, every delay in disease progression, and every carefully managed treatment-related issue represents a significant victory in the enduring fight against this formidable disease.
As we chart our course forward, it remains essential to keep our focus on both the clinical benefits and the human aspects of cancer care. By finding your way through the tricky parts and working through the nerve-racking details together, we can create a future where every patient has access to treatment protocols that are both effective and compassionate.
Originally Post From http://www.oncnursingnews.com/view/selinexor-maintenance-offers-durable-benefit-in-advanced-endometrial-cancer
Read more about this topic at
Optimal Supportive Care With Selinexor Improves …
Optimal Supportive Care With Selinexor Improves …