Retifanlimab: A New Frontier in the Treatment of Advanced Anal Cancer
The global healthcare community is increasingly focused on the tough parts of treating advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal (SCAC). Recent developments have sparked hope for a cancer that was once seen as having few new options after decades of stagnant treatment. In my view, the introduction of retifanlimab, when combined with standard carboplatin-paclitaxel chemotherapy, truly marks a turning point in managing this challenging disease.
Based on a robust, multicenter phase 3 trial, a growing body of evidence now strongly supports the use of retifanlimab. The results, which have been published in respected journals and have led to early regulatory approval, underscore the progress that modern oncology can achieve when innovative immunotherapy meets well-established chemotherapy protocols. In this editorial, I’d like to take a closer look at the study results, discuss the promising benefits, and examine the fine points that healthcare professionals must consider when deciding on new treatment approaches.
retifanlimab Combination with Carboplatin Paclitaxel: Improving Patient Outcomes
The global, randomized, controlled POD1UM-303/InterAACT-2 trial enrolled over 300 patients with locally recurrent or metastatic SCAC who had not received prior systemic treatment. Designed to compare the combination of retifanlimab with the standard carboplatin-paclitaxel regimen versus the standard treatment plus placebo, the trial set out to measure progression-free survival (PFS) as its primary goal.
The study’s findings are both exciting and compelling. Patients treated with retifanlimab experienced a median PFS of 9.3 months compared to 7.4 months for those receiving placebo. Statistically, this 37% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death is nothing short of a breakthrough, particularly in a condition where treatment options have changed little over time.
This improvement in PFS, bolstered by higher overall response rates and longer duration of response, has fueled adrenal discussions about upgrading retifanlimab in combination with chemotherapy to a new standard of care. Considering this promising data, it is clear that the potential of immunotherapy combined with traditional chemotherapeutic regimens is now becoming an imperative part of our treatment dialogue.
Advanced Anal Cancer Treatment Approaches: Evolving Strategies and Immunotherapy Insights
Many of us in the oncology field have wrestled with the tangled issues of limited treatment options for advanced SCAC. The current standard, which usually includes carboplatin and paclitaxel, offers only modest improvements in survival outcomes. This has been a source of frustration and, at times, an intimidating barrier to providing patients with the care they deserve.
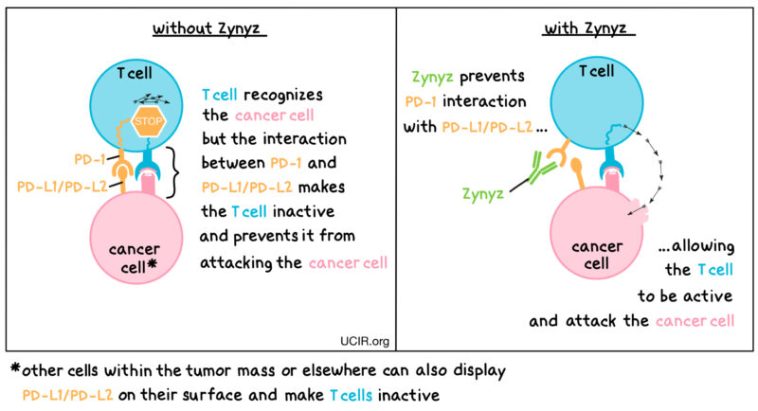
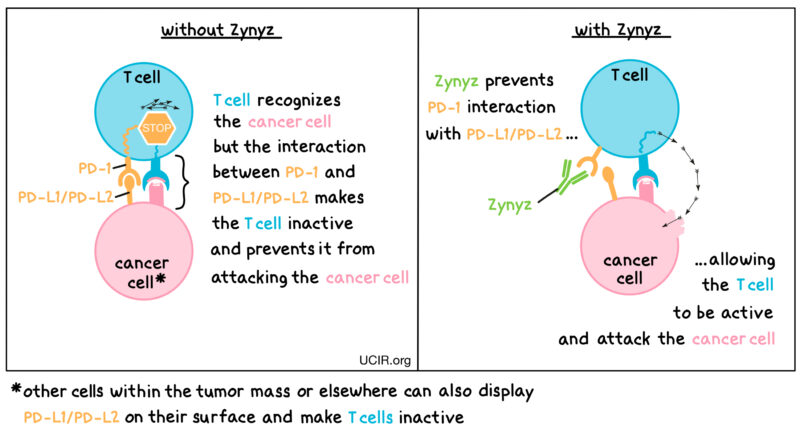
Retifanlimab introduces a new angle by embracing an immunotherapy approach. Immunotherapies are designed to stimulate the body’s own immune system to fight cancer cells. In the context of SCAC – especially another cancer tied intricately to HPV infection – this method provides both a novel and welcome perspective. With a heightened response rate and a longer duration of response reported in the trial data, we witness an encouraging trend where a combination therapy is proving to be more effective than chemotherapy alone.
Given that SCAC prevalently affects individuals with compromised immune systems, particularly patients with HIV, it is essential that we take a careful look at treatment adaptations designed for diverse populations. For example, in this trial, select HIV-positive patients were included in the cohort with well-managed HIV. Although the numbers were small, this subgroup demonstrated that immunotherapy could be integrated safely without compromising HIV control, a welcome relief for those who previously felt caught in a nerve-racking cycle of limited treatment choices.
Immunotherapy and Its Role in Difficult-to-Treat Patient Populations
The disproportionate impact of SCAC on HIV-positive patients is one of the more tangled issues in modern oncology. HIV-infected individuals face a 25 to 35 times higher risk of developing SCAC compared to their HIV-negative counterparts. This disparity highlights the urgency of tailoring new treatments to fit these patients’ needs.
From my perspective, immunotherapy – as represented by retifanlimab – appears to strike the right balance between efficacy and safety for these vulnerable groups. The trial’s inclusion of HIV-positive patients (with carefully monitored immune parameters like CD4+ counts and viral loads) demonstrates that these new treatment modalities can be safely extended to populations that are frequently excluded from clinical research. This is essential, as it opens up the path to more inclusive therapy protocols that address the unique challenges of immunocompromised individuals.
In addition to HIV-positive patients, the trial also touched on many other subgroups that present with their own set of tricky parts when it comes to treatment. These include patients with different levels of PD-L1 expression, age ranges, and varying performance statuses. Such complexities require that oncologists stay well informed about the subtle parts that may affect the overall treatment strategy. By integrating retifanlimab into standard care, clinicians now have an additional tool in the toolbox that may benefit these diverse demographic groups.
Understanding the Fine Points of Progression-Free Survival and Overall Response Rates
Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall response rate (ORR) are two essential metrics that often guide our treatment decisions. The POD1UM-303/InterAACT-2 trial has provided new data that clearly illustrate the benefits of combining retifanlimab with carboplatin and paclitaxel.
A few key highlights from the study include:
- A median PFS increase from 7.4 months to 9.3 months.
- A significant 37% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death.
- An improvement in overall response rates, with the retifanlimab group reaching 55.8% compared to 44.2% in the control group.
- A prolonged median duration of response, nearly doubling from 7.2 months in the control arm to 14.0 months in the retifanlimab arm.
These findings go beyond mere numbers; they suggest an improved quality of life and potential for extended survival in a population that has long faced limited options. As clinicians, we must embrace these results and consider how they can be applied across our practices, especially for those patients who have historically been left wrestling with the off-putting constancy of older treatment regimens.
Table: Key Efficacy Endpoints in Retifanlimab Trials
| Endpoint | Retifanlimab + Chemotherapy | Placebo + Chemotherapy |
|---|---|---|
| Median Progression-Free Survival (months) | 9.3 | 7.4 |
| Overall Response Rate (%) | 55.8 | 44.2 |
| Median Duration of Response (months) | 14.0 | 7.2 |
The table above offers a quick reference to those small distinctions in efficacy between the treatment groups. It is these subtle details that enable healthcare professionals to figure out which pathway might be best suited for each individual patient.
Immune-Related Adverse Events and Navigating the Safety Landscape
While the efficacy data are dazzling, one cannot ignore the safety profile and the potential side effects inherent in any new therapy. The trial reported higher rates of serious and grade 3 or worse adverse events (AEs) in the retifanlimab group compared to the placebo arm. Although these numbers may seem overwhelming at first glance, it’s important to put them in perspective.
Common AEs such as neutropenia and anemia were observed at slightly higher percentages in the retifanlimab group. Similarly, immune-related AEs were more frequently reported—49% compared to 26% with placebo. However, most immune-related AEs were only grade 1 or 2 in severity and did not usually result in dose interruptions or treatment cessation.
For professionals managing their way through these challenging issues, the safety data offer reassurance. The detailed breakdown of adverse events, including fatal incidences (which were very few and only one of which was deemed treatment-related in the retifanlimab arm), provides a nuanced picture that supports the overall benefit-risk profile of this new combination therapy.
A helpful way to view these findings is by listing the common safety concerns alongside their management strategies:
- Neutropenia: Monitor blood counts regularly and adjust chemotherapy dosing if necessary.
- Anemia: Provide supportive care, including possible transfusions and iron supplementation.
- Immune-related AEs: Be vigilant for early signs; most cases are manageable with prompt intervention, such as steroids for inflammation.
These management strategies are part of our daily routine in oncology clinics. Addressing these potential hazards head on—by using established supportive care measures—allows us to steer through the complexities of cancer therapy while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
FDA Approval and the Real-World Translation of Trial Outcomes
The journey from clinical trial to clinical practice is often a long and winding road. However, the recent FDA approval of retifanlimab in May 2025, both as a single agent and in combination with chemotherapy, marks a milestone that can significantly alter the treatment landscape for advanced SCAC.
Regulatory approval not only validates the scientific rigor behind the trial findings but also paves the way for wider access in routine clinical settings. From a practical standpoint, this approval is a must-have for clinicians who are continuously seeking better solutions for patients who have been stuck with an off-putting lack of progress in their treatment options.
As we take a closer look at how these changes impact clinical practice, it becomes evident that the following points are critical for successful translation into real-world settings:
- Access to the new drug: Ensuring that retifanlimab is available in cancer centers globally.
- Healthcare provider education: Training practitioners on the management of both the efficacy and safety profiles.
- Patient selection: Refining criteria for which patients will benefit the most from this new treatment strategy.
It should be noted that while the overall survival (OS) data remain relatively immature, the interim analysis has hinted at a possible improvement in OS for the retifanlimab group. This early signal has the potential to further bolster the case for adopting retifanlimab as a first-line treatment option, although additional follow-up will be needed to confirm this advantage over the long term.
Integrating Patient-Centered Care into Advanced SCAC Treatment
At the heart of every treatment decision in oncology lies the patient. Beyond clinical trial endpoints such as progression-free survival and response rates, the actual experience of the patient navigating cancer therapy is filled with many twists and turns. Modern treatment guidelines underscore the importance of a patient-centered approach that takes into account quality of life, treatment tolerability, and individual health backgrounds.
For patients with advanced SCAC, many of whom may have already experienced the overwhelming side effects of chemotherapy, the introduction of retifanlimab brings a note of hope. With a manageable safety profile—even when immune-related AEs exist—the combination therapy offers a balance between effectiveness and tolerability that was previously hard to attain.
As healthcare providers, we must also consider careful selection and close monitoring of our patients, especially those with co-morbidities such as HIV infection. As part of an integrated care model, support from nutritionists, mental health professionals, and rehabilitation services is super important to ensure that patients remain as resilient as possible throughout their treatment journey.
Here are a few suggestions for integrating patient-centered care in the context of advanced SCAC treatment:
- Comprehensive patient education: Provide clear explanations about treatment options, benefits, and possible side effects.
- Multidisciplinary care teams: Involve a range of specialists to manage the complicated pieces of care.
- Regular follow-up: Ensure patients have frequent check-ins to monitor both treatment efficacy and side effects.
- Support networks: Connect patients with support groups and counseling services to help them manage the nerve-racking aspects of cancer treatment.
Weighing the Benefits Against the Risks: A Balanced Perspective
No new treatment comes without its set of confusing bits and potential risks. The addition of retifanlimab to a rigorous chemotherapy regimen is accompanied by an increased risk of serious adverse events, and indeed, this warrants a cautious yet forward-looking evaluation by clinicians. The fact that immune-related AEs were more common in the retifanlimab group is a reminder that even promising therapies have their hidden complexities.
However, when one weighs the improved progression-free survival and response rates against the manageable safety profile, the benefit-risk ratio appears to lean favorably towards the new treatment. In today’s challenging oncology field, where treatment strategies are constantly evolving, every incremental improvement counts.
Indeed, the decision to adopt a new therapeutic regimen should always be made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the patient’s overall condition, other existing health issues, and personal preferences. Effective communication among the oncology care team and the patient is key to making informed decisions that truly benefit patient outcomes.
Future Research Directions and Ongoing Challenges in SCAC
There is no doubt that the introduction of retifanlimab in combination with carboplatin-paclitaxel is a watershed moment for advanced anal cancer treatment. However, as with any new treatment strategy, the journey is far from over. The trial’s results raise several interesting questions that future research must address:
Some of the areas that deserve further investigation include:
- Expanded patient populations: Future studies should include more HIV-positive patients and other subgroups to better understand subgroup-specific benefits.
- Combination strategies: Beyond chemotherapy, combining retifanlimab with novel targeted agents may unveil even greater therapeutic potential.
- Long-term survival data: With overall survival data still maturing, longer follow-up is crucial to determine the enduring benefits of this treatment approach.
- Biomarker studies: Identifying the fine points that predict which patients are most likely to benefit from retifanlimab could help tailor treatments even further.
Clinicians and researchers alike must dig into these areas with well-designed clinical trials and real-world studies. Only by collecting detailed evidence can we fully figure a path through the tricky parts of treating advanced SCAC.
The evolving landscape of cancer therapy is a reminder that every new discovery, every improved metric, and every managed adverse event collectively contributes to gradually improving patient outcomes. The POD1UM-303/InterAACT-2 trial is a testament to the power of international collaboration and multidisciplinary research, highlighting the benefits that emerge when diverse expertise converges on a common problem.
The Importance of Multidisciplinary Collaboration in Implementing New Treatments
The transition from clinical trial success to everyday clinical practice is more than just a regulatory hurdle—it’s an ongoing process that demands collaboration, education, and proactive management of care. As we integrate retifanlimab into treatment plans, several stakeholders must work together:
- Oncologists: Educate themselves continuously on the new evidence and understand the subtle details of both the clinical benefits and management of side effects.
- Nursing staff: Play a key role in monitoring patient responses and ensuring that any emerging side effects are managed promptly.
- Pharmacists: Help adjust dosages and provide important information about drug interactions, ensuring patient safety throughout treatment.
- Patient support services: Offer counseling and assistance, making sure that patients do not feel overwhelmed by the nerve-racking aspects of their treatment journey.
- Regulatory bodies: Continue to review new evidence to update guidelines and ensure the highest standards of patient care.
When all these elements are in place, the translation of advanced therapies like retifanlimab into standard practice becomes smoother and more effective. The coming years will undoubtedly see an increased focus on combining immunotherapy with other modalities to tackle cancer more effectively, and a multidisciplinary approach remains super important for this success.
Final Thoughts: Embracing a New Standard of Care
Reflecting on the data from the POD1UM-303/InterAACT-2 trial, I firmly believe that retifanlimab combined with carboplatin-paclitaxel represents a new era in the treatment of advanced SCAC. The trial’s success in extending progression-free survival and improving overall response rates is a beacon of hope for patients who have long been constrained by limited treatment options.
Indeed, while challenges remain—especially concerning the management of adverse events and the need for further long-term data—the overall gains are too significant to ignore. As the FDA’s approval of retifanlimab illustrates, regulatory agencies now recognize the clinical promise of this approach, setting the stage for more widespread use in everyday clinical practice.
It is my hope that this breakthrough will inspire further research into overcoming the tricky parts and tangled issues of SCAC and other cancers with similar profiles. By continuing to explore these new treatment avenues in a thoughtful, patient-focused manner, we can finally begin to offer long-overdue improvements in survival and quality of life to patients living with advanced anal cancer.
To sum up, the introduction of retifanlimab as part of a combined treatment regimen is not just another incremental step forward—it’s a bold stride into a future where even the most intimidating diseases can be confronted with innovative and effective therapies. Let us use these promising results to push the boundaries of our current practices, ensuring that our patients receive the best care possible in a landscape that is continuously evolving.
Looking Ahead: The Future Path for Oncology Care in SCAC
While the results we have discussed mark a significant milestone, the road ahead is filled with both promise and challenges. Many are now asking: What will it take to fully integrate these advances into regular practice and extend their benefits to a broader range of patients?
Future studies might explore:
- Different dosing strategies to further balance efficacy and safety.
- Combination protocols that add targeted therapies or other immunomodulatory drugs, potentially overcoming some of the lingering problems associated with chemotherapy alone.
- Real-world effectiveness studies that evaluate not only survival outcomes but also quality of life improvements among diverse patient populations.
- In-depth biomarker studies to predict the small distinctions in treatment responses and fully customize therapy for each patient.
The journey forward will require coordinated efforts from researchers, clinicians, and policy makers alike to ensure that these scientific advancements are not lost in translation. By continuing to figure a path through the complicated pieces of modern oncology care, we can build upon this breakthrough and work toward a future where advanced SCAC is not a terminal diagnosis but a manageable condition with multiple effective treatment options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evidence supporting retifanlimab in combination with carboplatin-paclitaxel for advanced SCAC is a landmark in cancer treatment. It opens up new possibilities for patients who have long faced overwhelming odds and presents oncologists with an additional strategy to enhance treatment outcomes. While we must remain vigilant about managing adverse effects and continue to gather long-term data, the current findings provide a strong foundation for rethinking first-line therapies in this disease.
As we take a closer look at these developments, it is clear that embracing new treatment paradigms—especially those that integrate immunotherapy with chemotherapy—will be key to advancing patient care in oncology. Let this breakthrough in advanced anal cancer serve as both inspiration and a call to action for the entire medical community, encouraging us to continue exploring and innovating to meet the ever-evolving demands of modern cancer care.
Ultimately, retifanlimab represents much more than a new drug; it embodies the promise of modern medicine to transform even the most intimidating challenges into opportunities for healing and hope. In the coming years, let us continue to work together, learning from each success and each setback, as we move toward a future where every patient has access to the most effective and compassionate care available.
Originally Post From https://www.targetedonc.com/view/new-hope-for-anal-cancer-retifanlimab-extends-progression-free-survival
Read more about this topic at
Breakthrough in anal cancer treatment
Breakthrough in anal cancer treatment