Precision Oncology in Pancreatic Cancer: A New Era of Treatment
Pancreatic cancer is notorious for its tricky parts and confusing bits, making it one of the most challenging cancers to treat. Recent advancements in precision oncology have paved the way for innovative therapies that could significantly alter the course of this aggressive disease. Emerging biomarkers, device-based treatments, and novel targeted agents are beginning to work together to form a more personalized and effective treatment approach for patients with metastatic and locally advanced pancreatic cancer.
Enhancing Treatment Monitoring With Circulating Tumor DNA
One of the promising breakthroughs involves the use of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as a biomarker. In metastatic pancreatic cancer, ctDNA analysis can provide oncologists with critical information about tumor behavior and treatment response. By using blood tests alongside tissue analysis, physicians can better capture the untidy and complicated pieces of tumor genetics.
Recent studies, such as the observational ARTEMIS-PC trial, have shown that measuring variant allele frequency (VAF) via ctDNA can help predict improved treatment response and longer progression-free survival. For instance, patients who achieved clearance of ctDNA had a notably higher objective response rate compared to those who did not. This approach allows clinicians to take a closer look at the fine points of tumor evolution and make informed treatment decisions quickly.
Key benefits of using ctDNA include:
- Real-time monitoring of disease progression
- Enhanced detection of minimal residual disease
- A less invasive alternative compared to repeated tissue biopsies
- Potential to guide adjustments in therapy based on the patient’s molecular profile
These findings affirm that integrating ctDNA testing into clinical practice can help steer through the challenging landscape of pancreatic cancer treatment.
Revolutionary Role of Tumor-Treating Fields in Enhancing Survival Rates
In addition to molecular testing, device-based therapies like tumor-treating fields (TTFields) have gained traction as adjunctive treatments in pancreatic cancer. TTFields utilize low-intensity, alternating electric fields delivered continuously via a portable device. Their role is to disrupt the division of cancer cells while also triggering an enhanced immune response.
Recent data from global phase 3 studies have underscored the potential benefits of adding TTFields to conventional chemotherapy. For instance, combining TTFields with a regimen of gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel resulted in a statistically significant boost in overall survival and improvements in quality of life. Although skin toxicities such as dermatitis and rash were observed, these were mostly low grade and manageable with proper skin care.
A summary of the trial outcomes is presented below:
| Population | Median Overall Survival (OS) | 1-Year OS Rate | Median Progression-Free Survival (PFS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intention-to-Treat (TTFields) | 16.2 months | 68.1% | 10.6 months |
| Intention-to-Treat (Chemotherapy Alone) | 14.2 months | 60.2% | 9.3 months |
| Modified ITT (TTFields) | 18.3 months | 75.1% | 12.5 months |
| Modified ITT (Chemotherapy Alone) | 15.1 months | 65.9% | 10.4 months |
This table outlines the improved performance outcomes in the TTFields arms compared to chemotherapy alone, reminding us that while challenges remain, these new modalities are forging a path toward better patient care.
Molecular Testing: Digging Into the Fine Points of Pancreatic Cancer
One of the essential steps in managing pancreatic cancer is early and comprehensive molecular testing. Since next-generation sequencing (NGS) is often limited by tissue availability, complementing tissue-based tests with blood-based NGS enhances the chances of capturing driver mutations. These tests are critical for identifying key genetic aberrations such as KRAS mutations, which are known to drive the aggressive nature of pancreatic tumors.
Experts in the field now advocate routinely ordering both tissue and blood NGS to gather a complete picture of the tumor’s molecular makeup. This dual approach means that even if a tissue biopsy falls short, doctors can still rely on a ctDNA assay from a blood sample to get the data they need.
Points to consider when ordering molecular tests:
- Request both tissue and ctDNA analysis to overcome sample shortages
- Schedule testing early in the disease course to guide timely treatment decisions
- Include driver mutation panels, with a particular focus on KRAS, which plays a key role in tumor aggression
- Review test results in the context of the patient’s age, sex, and clinical stage
As our understanding of the subtle details of tumor biology grows, molecular testing stands out as a must-have element in the tailored treatment blueprint for pancreatic cancer patients.
Next-Generation RAS Inhibitors: Targeting the Holy Grail of Pancreatic Cancer
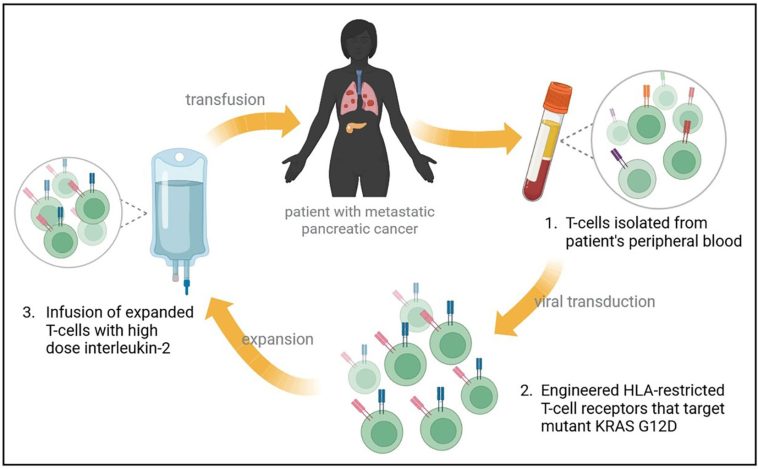
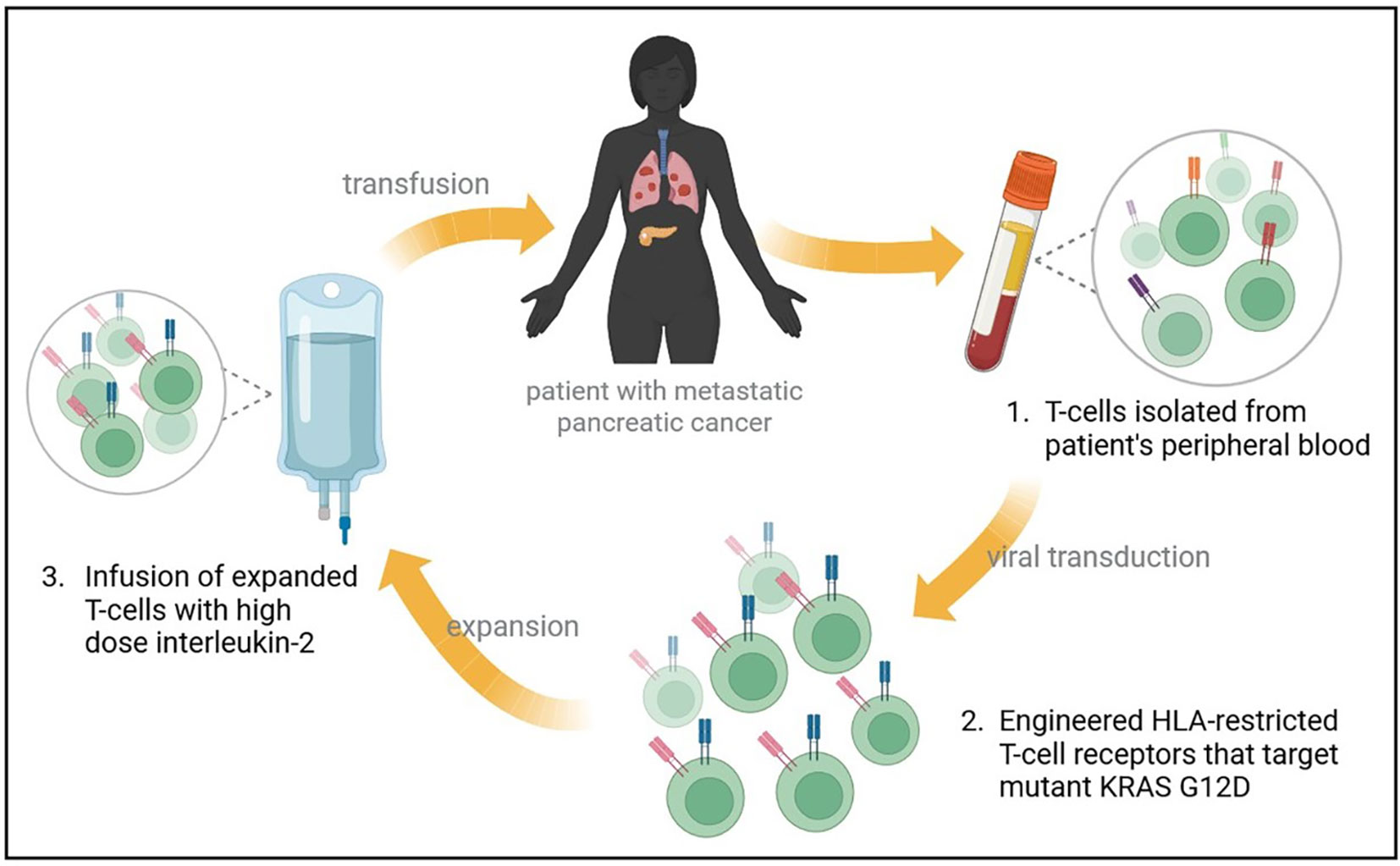
Perhaps one of the most exciting developments in the treatment of pancreatic cancer is the emergence of next-generation RAS inhibitors. For years, the protein KRAS was considered an almost untouchable target due to its tricky structure and the complex microenvironment created by stromal deposition. However, newer agents such as daraxonrasib (RMC-6236) are beginning to chip away at this obstacle.
In phase 1 trials, daraxonrasib demonstrated encouraging efficacy in patients with KRAS-mutant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Early data indicate that this oral RAS inhibitor not only improves progression-free survival but also achieves higher response rates in a subset of patients with KRAS G12X mutations. This progress has been so compelling that the FDA has granted breakthrough therapy designation for daraxonrasib in previously treated metastatic pancreatic cancer.
A bulleted list of promising aspects of next-generation RAS inhibitors includes:
- Improved progression-free survival compared to standard therapies
- Enhanced response rates in specific genetic subgroups
- Potential for integration with existing chemotherapy regimens
- Breakthrough therapy status highlighting its clinical promise
For many patients, therapies directed at KRAS mark a breakthrough in targeting the underlying causes of tumor aggression. As more development and larger trials like RASolute-302 continue, the future looks increasingly hopeful for those struggling with this formidable cancer.
Improving Diagnostics With Innovative Assays
Alongside targeted therapy, major leaps are being made in the realm of diagnostics. New assays, such as the PAC-MANN-1 test, offer a promising alternative to the traditional biomarker CA 19-9. This blood-based assay employs a fluorescently labeled, protease-sensitive peptide attached to a magnetic nanosensor to detect protease activity, a key indicator of tumor presence.
The PAC-MANN-1 assay has shown superiority in distinguishing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from both healthy samples and other pancreatic conditions. Initial validation studies reported high specificity and notable sensitivity, which are crucial when it comes to the early detection of cancer. This kind of progress opens doors for earlier intervention, which can be critical in a fast-moving disease like pancreatic cancer.
Advantages of next-generation diagnostic assays include:
- Higher specificity and sensitivity compared to conventional biomarkers
- Capability to detect all stages of pancreatic cancer
- Minimally invasive procedures that offer rapid results
- Potential integration into routine screening protocols for high-risk patients
The adoption of these innovative assays could lead to a paradigm shift in how early pancreatic cancer is detected and monitored, ultimately enabling more targeted therapy decisions and boosting survival outcomes.
Personalized mRNA Vaccines: A Glimpse Into the Future
In addition to the molecular and device-based innovations, another promising frontier in pancreatic cancer treatment is the development of personalized mRNA vaccines. These vaccines are designed based on the unique mutational profile of each patient’s tumor, triggering an immune response that could help control cancer growth.
Preliminary data from trials involving autogene cevumeran have shown that these vaccines are safe and well tolerated, with half of the patients demonstrating a measurable immune response. While the research is still in its early stages, these personalized treatments represent a super important step toward harnessing the body’s own defenses to fight off cancer.
Core points regarding mRNA vaccine development include:
- Customization to each patient’s unique tumor mutations
- Encouraging safety profiles with minimal severe adverse events
- Potential to restore immune function in a tumor microenvironment known to be immunosuppressive
- Integration with other treatment modalities, including chemotherapy and targeted therapies
Although still in the trial phase, personalized mRNA vaccines offer a refreshing approach in what has long been seen as a highly intimidating area of cancer therapy.
Addressing the Challenges of Tissue Availability and Sequencing Gaps
One of the recurrent challenges in advanced pancreatic cancer treatment is obtaining an adequate tissue sample for next-generation sequencing. This issue, compounded by the complex and tangled issues involved in pancreatic tumor architecture, often leaves a gap in the information needed to choose the best treatment path.
Oncology professionals now encourage a dual approach that incorporates blood-based NGS along with standard tissue analysis. This method ensures that clinicians have sufficient data to determine driver mutations, even when tissue samples are limited. In addition, this strategy supports early intervention, as obtaining accurate molecular information as soon as possible can make a difference in treatment planning.
The table below outlines the common challenges and proposed solutions when it comes to molecular testing in pancreatic cancer:
| Challenge | Proposed Solution |
|---|---|
| Tissue scarcity for NGS | Utilize blood-based ctDNA assays alongside traditional biopsies |
| Delayed mutational analysis | Initiate molecular testing early in the treatment process |
| Incomplete molecular profiles | Complement tissue testing with comprehensive blood panels |
This table not only simplifies the hidden complexities of sample collection but also stresses the importance of a combined diagnostic approach.
Integrating Innovative Therapies With Standard of Care
Modern oncology increasingly recognizes that innovative treatments should not replace current therapies but rather complement them. The integration of TTFields, next-generation RAS inhibitors, and personalized diagnostic assays with conventional chemotherapy is yielding promising results. In combination, these modalities help address the little details that can significantly affect patient outcomes.
Important considerations for integrating new treatments include:
- Patient selection: Identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from combination therapies through molecular screening
- Timing: Coordinating the delivery of novel therapies alongside standard chemotherapy protocols
- Safety: Monitoring and managing side effects that may arise from the use of combined treatment modalities
- Quality of Life: Evaluating not only progression-free and overall survival but also symptom management and patient-reported outcomes
This multifaceted approach is essential when dealing with an overwhelming disease such as pancreatic cancer, which is loaded with issues that extend beyond simple tumor growth.
Managing Side Effects and Improving Quality of Life
When introducing innovative therapies into treatment regimens, it is equally critical to manage the potential side effects. For example, the addition of TTFields to chemotherapy has shown to increase skin toxicities like dermatitis, rash, and pruritus. While these effects are usually of low grade, they require careful management to ensure that patients can tolerate the therapy over the long term.
Key strategies to address and manage these adverse events include:
- Educating patients on proper skin care routines to minimize irritation from TTFields arrays
- Regular monitoring and prompt intervention when adverse events develop
- Adjusting treatment regimens based on patient tolerance while maintaining therapeutic efficacy
- Implementing supportive care measures to help patients maintain quality of life during treatment
By putting emphasis on managing side effects, clinicians can help patients find their path through the nerve-racking treatment journey while maintaining important quality-of-life benchmarks.
Understanding the Immunologic Implications of Pancreatic Cancer Therapies
The immune environment of pancreatic cancer is notably complicated, with the tumor microenvironment being both immunosuppressive and protective of the cancer cells. New therapies are trying to overcome these obstacles, and the addition of immunotherapies such as mRNA vaccines and CD73 inhibitors is showing promise in restoring immune function.
When considering the integration of these immune-based therapies, several important factors come into play:
- Restoration of immune cell function through agents like quemliclustat, a CD73 inhibitor that targets adenosine formation
- Potential synergy with traditional chemotherapy, thereby improving overall outcomes
- The capability to trigger an immune response against tumor-specific neo-antigens, as seen with personalized mRNA vaccines
- Ongoing research to identify biomarkers that may predict which patients are most likely to respond to immunotherapy
These immunologic strategies are not only innovative but also critical in breaking down the barriers that have traditionally made pancreatic cancer treatment so intimidating.
The Future Landscape of Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
The future of pancreatic cancer care looks increasingly bright with the advent of precision oncology, innovative diagnostic assays, and integrated treatment strategies. Although significant challenges remain, especially concerning the tricky parts of tumor accessibility and the complexities of the tumor microenvironment, the new approaches embraced by modern oncologists provide a hopeful outlook.
Moving forward, the following areas are poised to shape the future landscape of pancreatic cancer treatment:
- Expanded use of ctDNA monitoring, enabling real-time adjustments in treatment plans
- Wider adoption of TTFields in combination with chemotherapy, fostering improved survival outcomes
- Development and integration of next-generation RAS inhibitors that target KRAS mutations directly
- Implementation of next-generation diagnostic assays that allow for earlier and more accurate detection
- Personalization of treatment plans through mRNA vaccines and immunomodulatory agents
As these therapies move from clinical trials into standard use, healthcare providers will have a broader toolbox at their disposal to deal with the tangled issues of pancreatic cancer. This evolution not only exemplifies scientific progress but also reinforces the indispensable role of personalized medicine in providing hope where traditional treatments have often fallen short.
Collaboration and Continuous Learning in Oncology
The rapid pace of discovery in pancreatic cancer treatment makes collaboration and continuous learning essential. Oncologists, researchers, and healthcare professionals must work together to share insights, manage unexpected twists and turns, and fine-tune treatment protocols based on emerging data. Conferences, webinars, and interdisciplinary publications play an important role in keeping practitioners updated on the latest advances and subtle differences between varying treatment outcomes.
Collaboration also involves close communication with patients to ensure that they are fully informed of the potential benefits and risks associated with new therapies. In a clinical landscape full of both promise and overwhelming details, having patients as active participants in their care decisions helps foster better overall outcomes and improves adherence to complex treatment regimens.
Some key elements for effective collaboration include:
- Cross-disciplinary meetings that incorporate oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, and even nutrition experts
- Regular updates from clinical trials and emerging studies posted in professional journals and online portals
- The use of digital platforms to share practical treatment tips and success stories
- A focus on patient education to demystify complicated treatment options and build trust
Working through these channels is essential for managing not just the biology of pancreatic cancer but also its social and emotional dimensions as patients and their families navigate an often intimidating treatment landscape.
Integrating Nutrition and Lifestyle in Support of Cancer Therapy
While the scientific advances in treatment options are promising, it is important to remember that a comprehensive approach to managing pancreatic cancer also includes attention to nutrition, physical fitness, and overall well-being. Patients undergoing treatments like chemotherapy combined with TTFields or novel targeted therapies benefit from guidance on diet and exercise, which can help them better tolerate and recover from treatment.
Some practical measures that patients can consider include:
- Consulting with nutritionists to create an eating plan that minimizes inflammation and supports immune function
- Engaging in moderate physical activity, tailored to individual ability, to maintain strength and mobility
- Participating in support groups and community programs to cope with the emotional stress of treatment
- Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals to adjust dietary and lifestyle recommendations as treatment progresses
Integrating lifestyle modifications with advanced medical treatment is not only a strategy for managing the side effects of therapy but also a proactive approach to reinforcing the body’s resilience against cancer’s many twists and turns.
Conclusion: A Hopeful Outlook Amid Challenging Times
In conclusion, the multifaceted advancements in the management of pancreatic cancer represent a turning point in the fight against this aggressive disease. By integrating modern molecular diagnostics with innovative therapies such as ctDNA monitoring, TTFields, next-generation RAS inhibitors, and personalized mRNA vaccines, oncologists are crafting treatment plans that are more tailored, effective, and adaptive than ever before.
Although the path is still loaded with issues and nerve-racking challenges, the progress made in recent years provides a strong foundation for future breakthroughs. It is critical that the medical community continues to work together—sharing data, refining treatment protocols, and finding creative ways to support patients throughout their journey.
The evolution in precision oncology for pancreatic cancer is a vivid reminder that even the most complicated cancer can be tackled with a combination of scientific innovation, tailored therapy, and compassionate care. As we look ahead, it is clear that every step forward in understanding the nitty-gritty of tumor biology and refining our treatment strategies will make a super important difference in the lives of patients battling this formidable foe.
For patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals alike, these developments signal that the future of pancreatic cancer treatment is not only centered on overcoming current challenges but also on building a robust framework for improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life. The advances discussed herein are not just medical milestones; they are beacons of hope for those navigating the winding path of pancreatic cancer treatment.
As new trials continue to evolve and further refine our approaches, we remain optimistic that the combination of cutting-edge diagnostics, targeted therapies, and supportive care measures will ultimately transform pancreatic cancer from a disease with limited options to one with a well-charted path to recovery.
Originally Post From https://www.targetedonc.com/view/precision-oncology-spans-biomarkers-and-device-therapy-targeting-kras-in-pancreatic-cancer
Read more about this topic at
Breakthrough in pancreatic cancer therapy advances to …
Gene Therapy: Transforming the Battle Against Pancreatic …