Prostate Cancer Treatment Updates at ESMO 2025: A Transformative Outlook
The 2025 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress in Berlin brought forward a wave of exciting updates in prostate cancer treatment. As a long-time observer and advocate for improving patient outcomes, I find that the new data from trials such as EMBARK, PSMAddition, and CAPItello-281 not only clarify the tricky parts of prostate cancer management but also point the way to a future where treatment is increasingly guided by biomarkers and personalized strategies.
In my opinion, the recent announcements are more than just academic milestones—they represent concrete steps toward refining our approach to a disease traditionally viewed as overwhelming. The studies have provided us with fresh insights into treatment efficacy and survival benefits, offering a roadmap for clinicians facing the tangled issues inherent in managing advanced prostate cancer.
Critical Insights from the EMBARK Trial: Refining Treatment for Biochemically Recurrent Disease
The updated results emerging from the phase 3 EMBARK trial have shifted the conversation on treatment for biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. In earlier publications, the combination of enzalutamide (Xtandi) with leuprolide showed significant improvements in metastasis-free survival compared with leuprolide alone. Now, new data reveals that this combination can also extend overall survival, a finding that holds key implications for how we treat patients with early indications of disease recurrence.
It is important to consider that, for many clinicians, the decision to combine therapies amid the confusing bits of cancer treatment has often been riddled with tension. The EMBARK trial has now provided evidence that helps to clear these murky waters. Here are some notable details:
- Combination Therapy Benefits: The use of enzalutamide with standard androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) not only prevents disease progression but now shows a statistically significant improvement in overall survival.
- Survival Metrics: The hazard ratio (HR) reported at 0.597, with a 95% confidence interval (CI) of 0.444 to 0.804 (P = .0006), suggests that patients are experiencing a nearly 40% reduction in the risk of death compared to those receiving ADT alone.
- Clinical Impact: This data affirms the importance of early intervention and the potential benefits of aggressive treatment combinations—an approach that can help us steer through the confusing bits of prostate cancer therapy planning.
For practitioners, these findings serve as a super important reminder that treatment strategies may benefit from reconsidering traditional monotherapy approaches. The study underscores how a thoughtful blend of therapies can yield a measurable survival benefit, giving hope to patients who previously faced an intimidating prognosis.
Advancements in Radioligand Therapy: A Closer Look at the PSMAddition Study
Another major highlight at ESMO 2025 was the PSMAddition study, which brought forward new evidence on using targeted radioligand therapy in combination with conventional treatments. The study evaluated the addition of 177Lu-PSMA-617 to ADT and androgen receptor pathway inhibitors (ARPIs) for patients with PSMA-positive metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (mHSPC).
This trial is particularly notable because it addresses the often nerve-racking challenge of choosing the right candidate for radioligand therapy. By focusing on a biomarker-driven approach—using PSMA as a key identifier—the study has effectively paved the way for more tailored treatment plans.
Key takeaways from the PSMAddition trial include:
- Extended Radiographic Progression-Free Survival: The trial showed that the addition of 177Lu-PSMA-617 significantly prolonged the period during which patients did not experience radiographic disease progression, marking an essential milestone in treatment strategy.
- Complementary to Existing Therapies: Rather than replacing established treatments, radioligand therapy is used in combination with ADT and ARPIs. This integrated method is crucial for confronting the small distinctions in how tumors respond to therapy.
- Patient Selection and Precision: With patient eligibility based on PSMA positivity, the approach exemplifies how modern medicine can use fine details to guide treatment decisions, ensuring that each therapy is matched with the right patient profile.
In my view, this study also highlights the need for clinicians to be comfortable with diving into novel treatment modalities—even when the science behind them may seem full of problems at first glance. The potential benefits far outweigh the concerns, making a compelling case for incorporating radioligand therapy into everyday clinical practice for select patients.
Combination Treatment Strategies: Insights From the CAPItello-281 Trial
The CAPItello-281 trial brought another refreshing angle to the ongoing debate on the best way to approach metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer—especially in the challenging subgroup of patients with PTEN-deficient tumors. PTEN is a tumor-suppressor gene, and its deficiency often complicates treatment outcomes. The trial evaluated the impact of adding capivasertib (Truqap) to a regimen that included abiraterone acetate (Zytiga), prednisone, and ADT, reporting encouraging results in the form of prolonged radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS).
This study is particularly noteworthy for a number of reasons:
- Addressing Specific Patient Profiles: By focusing on patients with PTEN deficiency, the trial is a prime example of how our growing understanding of the nitty-gritty of prostate cancer biology can lead to more personalized care.
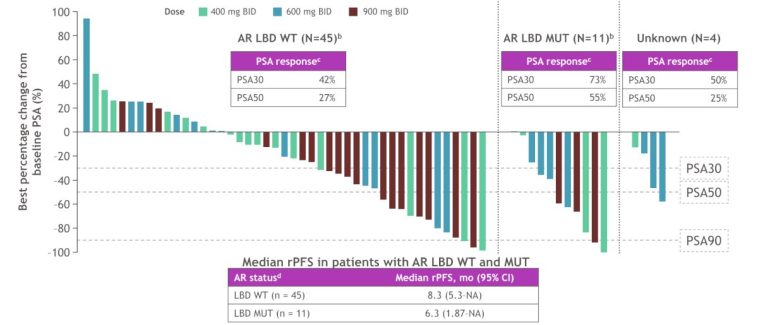
- Improved rPFS Outcomes: The median rPFS in the capivasertib arm was 33.2 months versus 25.7 months in the placebo group, with an HR of 0.81 (P = .034). This improvement, though seemingly modest, could translate into significant quality-of-life benefits and extended time before the need for subsequent therapies.
- Consistency Across Secondary Endpoints: The robustness of the data across multiple metrics underscores that the benefits of adding capivasertib are not isolated but rather weave through several critical aspects of disease management.
These findings offer a clear message: while the road to optimal prostate cancer treatment is lined with twists and turns, tailoring treatment to genetic and molecular profiles holds the promise of overcoming some of the most intimidating challenges in this field. As we learn more about the role of biomarkers like PTEN, it becomes easier to make informed decisions that ultimately improve patient care.
Biomarker-Driven Approaches: The Future of Prostate Cancer Management
One of the most compelling trends emerging from these studies is the shift toward a biomarker-driven strategy in prostate cancer management. Historically, treatment paradigms relied primarily on standardized regimens that did not account for the little twists in tumor biology observed between patients. However, the latest trials clearly underscore that such an approach is no longer sufficient.
In today’s landscape, clinicians are increasingly encouraged to:
- Identify Specific Biomarkers: Use markers such as PSMA or PTEN status to decide on tailored therapeutic approaches.
- Employ Combination Therapies: Adopt multipronged strategies that may include ADT, ARPIs, radioligand therapy, and novel agents like capivasertib, providing a multifaceted assault on the disease.
- Monitor Molecular Changes: Make routine use of molecular monitoring and imaging to track how tumors are responding to treatment, allowing adjustments when required.
This approach not only improves the precision of treatment but also eases the nerve-racking process of decision-making for both clinicians and patients. When treatment is closely aligned with the molecular characteristics of an individual’s cancer, it offers a blueprint for managing the complicated pieces of the disease more effectively.
Integrating Radioligand Therapy with Traditional Hormonal Approaches
Over the past decade, the medical community has struggled with the challenge of integrating innovative radioligand therapies with traditional hormonal treatments for prostate cancer. The recent insights from the PSMAddition trial provide strong evidence that these two modalities can work together in a harmonious fashion, yielding benefits that neither could achieve alone.
From my own perspective, this integrated approach has several key benefits:
- Enhanced Efficacy: The combined use of radioligand therapy with ADT and ARPIs not only delays disease progression but may also enhance the overall treatment response by targeting tumors through multiple mechanisms.
- Minimized Resistance: By employing a combination of agents, the therapy may help in preventing or delaying the development of resistance—one of the common challenges in long-term prostate cancer management.
- Streamlined Patient Management: When the different treatment components are aligned, it becomes less nerve-racking for clinicians to figure a path through the treatment landscape and to counsel patients on what to expect.
This melding of newer and established therapies creates an opportunity to overcome the subtle parts and more intimidating aspects of treatment resistance. Clinicians need not work in isolation but rather embrace a collaborative approach that leverages the strengths of both modalities.
Summary of Key Trial Findings
For clarity, the following table provides a concise summary of the major prostate cancer trials discussed at ESMO 2025:
| Study | Treatment | Main Outcome | Key Statistics |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMBARK (NCT02319837) | Enzalutamide + Leuprolide | Extended metastasis-free and overall survival | HR: 0.597; 95% CI: 0.444-0.804; P = .0006 |
| PSMAddition (NCT04720157) | 177Lu-PSMA-617 + ADT + ARPI | Extended radiographic progression-free survival | Significant improvement in rPFS in PSMA-positive mHSPC |
| CAPItello-281 (NCT04493853) | Capivasertib + Abiraterone + Prednisone + ADT | Prolonged rPFS in PTEN-deficient mHSPC | Median rPFS: 33.2 vs 25.7 months; HR: 0.81; P = .034 |
This table succinctly groups the findings, allowing clinicians and researchers alike to easily grasp the impact of each study. The clarity provided by direct comparison can be especially helpful when trying to work through the many small distinctions between similar treatment regimens.
Practical Implications for Clinicians: Working Through the Twists and Turns
The evolving treatment landscape outlined by these studies is a clarion call for clinicians who are actively managing prostate cancer. With options rapidly expanding, the profession now faces the task of making informed choices while addressing the tricky parts of seemingly overwhelming data. In everyday practice, these impulses translate into several actionable insights:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment based on genetic markers (e.g., PTEN, PSMA) can provide a needs-based approach that decreases the risk of overtreatment and minimizes unnecessary side effects.
- Balanced Combination Therapies: Integrating newer agents with time-tested treatments may prove to be the best strategy to get around resistance and prolong patient survival.
- Continuous Education: The rapidly advancing field necessitates that healthcare professionals remain updated on emerging research, ensuring that they always have the most current evidence at hand when counseling patients.
From my perspective, the most significant takeaway is the encouragement to adopt a proactive stance. Rather than feeling overwhelmed by the many complicated pieces of treatment data, clinicians are urged to figure a path that combines established knowledge with cutting-edge research. By doing so, they can offer patients not only extended survival but also an improved quality of life—an outcome that is truly essential when dealing with a disease as challenging as prostate cancer.
Patient Considerations: Understanding Treatment Options and Outcomes
While these study results have situated themselves proudly at the forefront of oncology discussions, it is equally important to understand the patient perspective. Prostate cancer patients and their families often face a nerve-racking journey filled with uncertainty and confusing bits related to treatment decisions. Here are a few points that can help patients better understand the evolving treatment landscape:
- Clarity Through Biomarkers: Biomarker testing can demystify many of the complex details related to the prognosis and potential treatment responses, offering patients a clearer picture of what to expect.
- Combination Regimens Explained: The use of combination therapies is designed not to complicate treatment but rather to attack the disease from multiple angles—which may lead to better outcomes and a delay in disease progression.
- Continuous Monitoring: Frequent assessments ensure that treatment modifications can be made in a timely fashion, thereby alleviating some of the worry associated with an initially off-putting prognosis.
- Improved Communication: Open dialogue with healthcare providers is super important. Patients who understand the role of each therapy component are better prepared to manage their expectations and participate actively in treatment planning.
This patient-centered approach is a key part of modern medicine. When treatments are designed to match the unique characteristics of an individual’s cancer, it helps everyone involved—patients, caregivers, and providers—feel more confident about the road ahead, even when that road is dotted with the occasional twist and turn.
Bridging the Gap: Integrative Medicine and Prostate Cancer Care
As we continue to witness these modern breakthroughs in prostate cancer therapies, another discussion that increasingly comes to the forefront is the role of integrative medicine. Traditionally, alternative methods, nutrition, and lifestyle interventions have played supporting roles in oncology. However, in the era of precision medicine, these modalities are being revisited and integrated with conventional therapies to manage not only the disease itself but also its accompanying side effects and overall patient wellness.
This integrative approach has several important benefits:
- Nourishment and Wellness: Patients can potentially improve their overall health through tailored nutritional plans that support immune function and counteract treatment-related fatigue.
- Stress Reduction: Complementary therapies such as mindfulness, gentle exercise, and yoga can help ease the nerve-racking tension of a new diagnosis and rigorous treatment regimens.
- Synergy with Medical Treatments: By incorporating nutrition and lifestyle adjustments into the treatment plan, patients are better equipped to manage side effects. These adjustments can help counterbalance the small distinctions in how patients may react to aggressive treatments.
The blending of traditional and alternative treatment approaches serves as a reminder that the management of prostate cancer is as much about addressing the patient’s overall well-being as it is about targeting the tumor. It is a holistic view—one that can turn what is often perceived as a daunting battle into a series of manageable, step-by-step strategies aimed at maintaining quality of life throughout the journey.
Challenges and Opportunities: Making Your Way Through Evolving Clinical Evidence
Every advancement in prostate cancer treatment brings with it both promise and a set of confusing bits that require careful thought. The current era is characterized by rapid scientific progress and an ever-growing pool of data. For many in the medical community, the challenge lies in making sense of these abundant, sometimes conflicting, reports. However, these same challenges open up valuable opportunities for better care.
Some practical strategies for handling this evolving evidence include:
- Staying Informed: Regular engagement with scientific conferences, journals, and CME opportunities can help clinicians keep abreast of the latest findings. Networking with colleagues during these events often dispels the overwhelming nature of new data.
- Collaboration and Peer Exchange: Discussing case-based perspectives and real-life experiences with peers can ease the process of interpreting the subtle details of new treatment protocols.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leveraging well-structured data, like the comparative outcomes outlined in the EMBARK, PSMAddition, and CAPItello-281 trials, fosters a rational approach to designing therapy regimens that are both aggressive and patient-friendly.
In my view, the field is steadily moving towards a future where practical decision-making is anchored in clear evidence and individualized patient profiles. The integration of multiple data points not only helps clinicians figure a path through the myriad treatment options but also enhances the confidence patients have in the proposed strategies.
Future Directions: Embracing Triplet Regimens and Beyond
Looking ahead, the current trials suggest that the next wave in prostate cancer therapy may very well be led by triplet regimens. This involves using ADT in combination with an ARPI and an additional agent—exemplifying the modern approach to work through the much-debated twists and turns of treatment resistance.
There are several promising aspects to this approach:
- Broader Molecular Targeting: By targeting different pathways simultaneously, triplet regimens can help to overcome the subtle parts of resistance that often emerge in a single-agent therapy.
- Enhanced Survival Benefits: Early data suggests that these multi-agent approaches could extend not only progression-free survival but overall survival, offering hope for improved long-term outcomes.
- Personalization Through Biomarkers: With biomarkers guiding the selection of additional agents, these regimens have the potential to be finely tuned to the individual’s disease profile, reducing the risk of unnecessary side effects while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
The evolution towards such combination therapies reflects the broader trend in oncology. As we continue to learn more about the hidden complexities of prostate cancer at the molecular level, these strategies will undoubtedly serve as a key platform for future research and patient care.
Concluding Thoughts: Charting a Clearer Path Forward for Prostate Cancer
In sum, the research updates shared at the 2025 ESMO Congress provide a breath of fresh air for those involved in prostate cancer treatment. The data from the EMBARK, PSMAddition, and CAPItello-281 trials is not merely an academic exercise—it is a call to action for clinicians who are keen to adopt a more personalized, multi-faceted approach to managing this challenging disease.
These advances remind us that while the road ahead may be filled with confusing bits and nerve-racking uncertainties, the potential to transform patient outcomes is within our grasp. For healthcare professionals, embracing new data and working through the tangled issues of treatment options means that every patient can benefit from therapies that are as dynamic and adaptable as the disease itself.
In my opinion, the promise of modern medicine lies not just in the development of new drugs but also in the integration of diverse treatment modalities—ranging from radioligand therapy to hormonal treatments and beyond. And while there remain plenty of twists and turns along the way, the opportunity to combine scientific advances with compassionate, patient-centered care is an inspiring prospect.
Crucially, these developments underscore the fact that treating prostate cancer is not just about tackling the disease itself, but also about understanding the full scope of patient needs. Whether it is through the lens of a groundbreaking clinical trial or the everyday observation of individual patient responses, every piece of evidence contributes to a clearer, more effective treatment strategy.
As we move forward, it is clear that collaboration among oncologists, urologists, radiologists, and other care specialists will be key in making your way through the modern treatment landscape. Sharing experiences, discussing case-based perspectives, and update-driven continuing education will allow us all to better serve those battling prostate cancer.
Final Reflections: Embracing Innovation with Caution and Optimism
Turning a critical eye to the rapid progress in prostate cancer treatment reminds us of the balance between innovation and caution. While the promise of extended overall survival and the effectiveness of combination therapies are super important, we must remain aware of the learning curve that comes with any new treatment paradigm.
For patients, families, and clinicians alike, it is reassuring to see objective data supporting a more personalized approach to care. Novel therapies are emerging not in isolation, but as part of a broader, integrative strategy that advocates for personalized, biomarker-guided treatment planning. This approach is poised to reduce the intimidation inherent in handling advanced prostate cancer while offering a handhold through the nerve-racking moments of uncertainty.
Ultimately, the integration of traditional and modern methods—ranging from hormone therapies to radioligand treatments—heralds a new chapter in the fight against prostate cancer. With continued research, cooperative clinical practice, and an unwavering commitment to patient well-being, the vision of turning prostate cancer into a manageable, if not entirely curable, condition becomes ever more tangible.
In this rapidly evolving era of oncology, it serves us well to remember that every piece of new evidence is a stepping stone toward more rational, effective, and compassionate care. As we adapt to the subtle details of an ever-changing landscape, our guiding principle should remain simple: to provide each patient with the best possible chance for a healthier, happier life.
References and Further Reading
For those interested in a more technical analysis, the following references detail the studies discussed:
- EMBARK Trial: Shore ND, de Almeida Luz M, De Giorgi U, et al. Overall survival with enzalutamide in biochemically recurrent prostate cancer. Presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress, Berlin, October 17‑21, 2025. (Link to Abstract).
- PSMAddition Study: Tagawa ST, Sartor O, Piulats JM, et al. Phase III trial of [177Lu]Lu‑PSMA‑617 combined with ADT + ARPI in PSMA‑positive metastatic hormone‑sensitive prostate cancer. Presented at the 2025 ESMO Congress, Berlin, October 17‑21, 2025. (Link to Abstract).
- CAPItello‑281 Trial: Fizazi K, Clarke NW, De Santis M, et al. A phase III study of capivasertib plus abiraterone versus placebo plus abiraterone in patients with PTEN‑deficient de novo metastatic hormone‑sensitive prostate cancer. Presented at the 2025 ESMO Congress, Berlin, October 17‑21, 2025. (Link to Abstract).
These sources provide more in‑depth information for those looking to get into the fine points of this evolving field and are excellent resources for continued professional development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the progress announced at ESMO 2025 marks a significant milestone in the journey toward more personalized and effective prostate cancer treatment. Although the path forward may be loaded with issues and the occasional confusing bit of emerging evidence, the collective advancements instill hope for better patient outcomes. With a balanced approach that embraces both innovation and careful clinical judgment, we can optimally integrate these therapies into practice, ultimately benefiting patients and advancing the field of oncology.
This is an exciting time for prostate cancer research, and as we get into the nuanced details of these studies, it is clear that collaboration and ongoing education will be the driving forces behind future breakthroughs. By aligning treatment with the individual characteristics of each patient’s disease, we can overcome the nerve-racking challenges of advanced prostate cancer and chart a clearer, more promising course for the future.
Originally Post From https://www.urologytimes.com/view/jason-hafron-md-recaps-prostate-cancer-data-from-esmo-2025
Read more about this topic at
Advances in Prostate Cancer Research – NCI
Latest in Prostate Cancer Treatment