Integrative Healthcare: Aligning Ancient Wisdom with Modern Practices
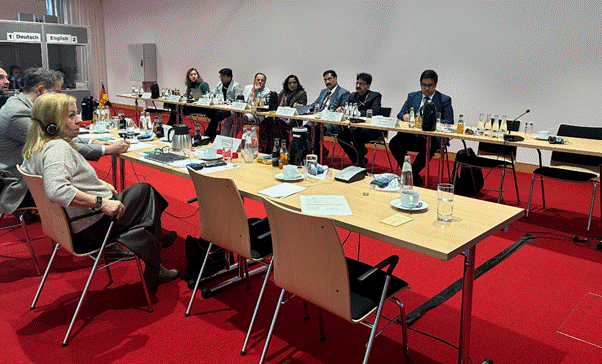
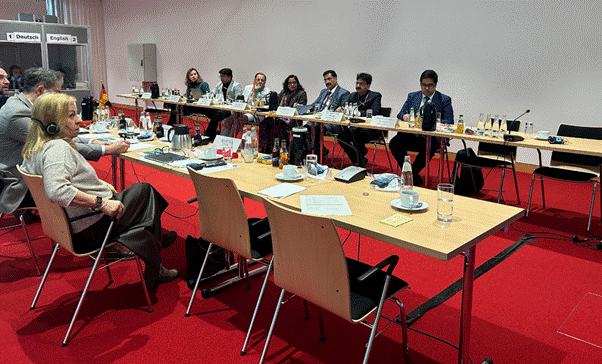
In an era when the worlds of modern medicine and age-old healing traditions are increasingly overlapping, the recent collaboration between India and Germany in Berlin represents a promising step forward. The meeting, which was held from November 18 to November 20, 2025, brought together experts and policymakers dedicated to building bridges between traditional systems of medicine and contemporary health practices. This union of progressive ideas and time-honored therapies is critical to ensuring that the best of both worlds is accessible to patients everywhere.
The strategic discussions at the meeting addressed a range of subjects—from integrating traditional practices into larger public health systems to ensuring that patients have smoother access to reimbursement systems. With the global landscape of healthcare continuously evolving, there is real significance in revising outdated approaches and finding innovative paths that respect cultural nuances while keeping clinical safety and efficacy in mind.
Many have pondered how to steer through the tricky parts of merging systems as fundamentally different as traditional and Western medicine. The answer seems to lie in collaboration, transparent dialogue, and rigorous research. This joint working group meeting demonstrated that both nations are more than ready to manage their way through the complicated pieces and confusing bits that arise when harmonizing ancient wisdom with modern scientific practices.
Strengthening Evidence-Based Research in Traditional Medicine
One of the key outcomes of the Berlin meeting was a mutual commitment to enhance evidence-based research in traditional medicine. The discussion went beyond surface-level talks on integration and sank deeper into the fine points of scientifically validating traditional practices.
The Indian delegation, led by prominent officials from the Ministry of Ayush and research bodies, stressed the importance of building robust scientific frameworks. They believe that, by gathering documented evidence and performing meticulous research, traditional medicine can be proven effective in treating a variety of conditions. Germany’s experts, well-grounded in rigorous regulatory practices, contributed by sharing their approaches to regulation and quality assurance.
This collaboration is not just about combining two healthcare models; rather, it is about sticking together in the quest for quality, safety, and improved patient outcomes. Innovative research models, enhanced clinical trials, and cross-cultural studies were some of the methods discussed, exposing all parties to the little twists and fine shades that make each system unique.
Key Discussion Points and Their Implications
- Integration into Public Health Systems: Both nations are targeting ways to weave traditional medicine into the fabric of conventional healthcare, recognizing that such integration can address the neglected areas in current public health systems.
- Reimbursement Mechanisms: To make traditional medical practices more accessible, participants explored strategies to establish reimbursement pathways. This approach aims to reduce the intimidating and off-putting nerve-racking financial barriers that many patients face.
- Regulatory Framework Improvements: Enhancing the regulatory frameworks for approvals and safety standards was a high-priority topic. It calls for setting up clear, consistent pathways that ensure integrative treatments are safe, effective, and of high quality.
- Collaborative Research Initiatives: Another focus was on setting up research partnerships with academic and healthcare institutions. These initiatives are expected to bridge the current gaps and untangle the small distinctions that influence treatment outcomes.
From Theory to Practice: Collaborative Models between India and Germany
The Berlin meeting was more than just theoretical discussions. The Indian team’s visit to Germany included several high-level engagements with healthcare and research institutions where practical models of integrative care were demonstrated. The Indian representatives were particularly keen to review care models in anthroposophic medicine at Community Hospital Havelhohe, an initiative that illustrates how traditional therapies can be aligned with modern clinical services.
During these sessions, discussions focused on how to actively lower the barriers to patient access by streamlining both insurance reimbursements and approval processes. The Indian and German teams agreed that practical collaboration is an essential step—and that these joint models have the potential to be replicated on a larger global scale.
In practical terms, the collaboration entailed detailed discussions about:
- The design of integrated treatment protocols that blend conventional and traditional methods.
- The standardization of dosage, quality control, and patient monitoring processes across different treatment modalities.
- Establishing transparent communication channels between clinicians, researchers, and regulatory bodies.
These practical strategies illustrate how the team is determined to actively monitor and steer through the tangled issues that often arise when trying to synchronize systems with vastly different operational modes. With these mechanisms in place, the goal is to build safer and more effective treatment plans that benefit patients worldwide.
Overcoming the Tricky Parts of Integrating Traditional Practices
One of the most challenging aspects of integrating two very different healthcare systems is managing the twists and turns that emerge from conflicting methodologies and philosophies. The Berlin meeting provided a platform to dig into these tricky parts, and both sides demonstrated an openness to understand the confusing bits involved in the integration process.
Many healthcare professionals have noted that when traditional healing practices are combined with modern medical approaches, there can be a tendency to get lost in the fine points of each system’s respective methodologies. In this context, the challenges include not only scientific validation but also cultural beliefs, historical contexts, and patient expectations. Both delegations acknowledged that these issues are not merely abstract problems; they are issues that influence everyday medical practice and patient trust.
To manage these challenges, the experts suggested several proactive measures:
- Collaborative Workshops: Organizing ongoing training sessions, workshops, and conferences can make it easier for professionals to figure a path through the complex overlap of diverse healthcare practices.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Combining scientists, traditional healers, and modern clinicians can foster a common language and shared understanding. This collaboration is key to appreciating the subtle parts that constitute traditional medicine.
- Patient-Centered Models: Designing treatment approaches that consider patient preferences and expectations ensures that healthcare remains a human-centered endeavor even as regulatory and research aspects evolve.
These measures highlight the need for an organized approach in sorting out the nerve-racking and overwhelming issues that come with integrating different medical philosophies. Over time, such methods can help smooth out the little twists and subtle details that might otherwise create friction.
Exploring Financial and Regulatory Support Systems
One of the critical, yet often overlooked, topics discussed during the collaboration was the need to establish robust financial and regulatory support systems. The discussion highlighted that, for traditional medicine to be truly adopted within public health frameworks, there must be secure economic structures that support both patients and research institutions.
Both delegations agreed on the following key financial and regulatory support areas:
| Support Area | Key Focus | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
| Reimbursement Pathways | Making integrative treatments financially accessible |
|
| Regulatory Frameworks | Ensuring safety and quality in practice |
|
| Research and Development Funding | Supporting robust scientific investigations |
|
The above table clearly lays out the necessary areas that require continued attention. By establishing these crucial backbones, both India and Germany aim to make integrative medicine a mainstream part of healthcare delivery. The challenge remains to get around the intimidating bureaucracy that often complicates such efforts. However, through sustained dialogue and shared objectives, both countries are forging a promising path forward.
Advancing Patient Access through Insurance Innovations
One of the scariest and most overwhelming aspects of integrating traditional medicine into conventional care is ensuring that patients have the necessary financial support to afford these services. The Berlin meeting went into depth about potential insurance and reimbursement models that could lower the financial barriers for patients.
Insurance companies in Germany, represented by leaders like Andrea Galle of the statutory health insurer BKK mkk, explained how their reimbursement mechanisms could be adapted to include traditional medicine. The discussions centered on creating a reliable, evidence-backed process that would allow patients to use integrative treatments without worrying about unmanageable costs.
By adopting strategies such as clearly defined benefit packages, transparent approval procedures, and a standard set of dosage recommendations, both sides believe that the integration process can be made significantly more patient-friendly. These innovations are expected to smooth out the nerve-racking financial challenges that many patients face when they are introduced to alternative therapies.
Some of the insurance innovations discussed include:
- Tiered Benefit Structures: Creating different tiers accommodating both standard and integrative treatment options.
- Outcome-Based Reimbursements: Linking payments to proven patient outcomes rather than just approved treatment types.
- Cross-Border Health Policies: Evaluating models for international collaborations can help set up reimbursement networks that span nations.
These initiatives are designed to ensure that patients have the freedom to choose treatments that best suit their individual needs, without worrying about how to pay for them.
Integrating Traditional Medicine into Mainstream Healthcare Systems
An essential objective of this international collaboration is the effective integration of traditional health systems into mainstream medical care. By examining current practices and bringing in insights from both research and practice, the participating delegates underscored the significance of ensuring that traditional medicine works seamlessly alongside modern treatments.
This goal, however, is not without its challenges. Integrating disparate approaches is like trying to make sense of tangled issues, where each system carries its own set of protocols, treatment methods, and underlying philosophies. Yet, with patience, open dialogue, and mutual respect, both sides showcased models of care that illustrate how these contrasting elements can work together to improve patient outcomes.
Key strategies discussed in this regard include:
- Interdisciplinary Training Programs: Offering combined education for practitioners of both modern and traditional medicine.
- Joint Clinical Guidelines: Developing standardized protocols that take into account the subtle parts and little details of both treatment methods.
- Institutional Partnerships: Establishing research institutions and collaborative centers that focus on integrative care across national borders.
This multifaceted approach enables healthcare professionals to figure a path through complex treatment scenarios. It also builds trust among patients, as they see that both modern and traditional approaches are being carefully considered and merged in a way that safeguards their well-being.
Adopting a Patient-Centered Approach in Integrative Care
At the heart of the collaboration between India and Germany is a commitment to patient-centric care. The emphasis on research, regulatory harmonization, and financial accessibility is ultimately aimed at improving the end-user experience. In an era where healthcare choices abound, patients deserve a system that is both flexible and responsive to their needs.
A patient-centered approach means that the models developed during this collaboration are designed with the following guiding principles:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Recognizing that not every patient fits into a standardized treatment protocol, the integrative approach caters to unique health needs.
- Clear Communication: Building transparent channels that help patients understand both the modern and traditional options available.
- Improved Accessibility: Streamlining reimbursement systems and regulatory approvals to reduce the financial and bureaucratic burdens that patients might otherwise face.
- Holistic Health Outcomes: Emphasizing not just clinical results, but also overall well-being, quality of life, and patient satisfaction.
This patient-first model resonates with the broader global trend toward personalized healthcare. By taking a closer look at these methods and refining them through continuous feedback, both nations are laying the groundwork for a healthcare system that is as adaptable as it is effective.
Charting the Future of Global Health Collaboration
The joint working group meeting in Berlin offers a glimpse into what the future of global health collaboration might look like. By building bridges between culturally and scientifically distinct approaches, India and Germany are setting an example for how integrative healthcare can be scaled up worldwide.
Looking ahead, several future-oriented initiatives were discussed that have the potential to further enhance this model of cooperation:
- Expanding Collaborative Networks: Building larger networks that include additional countries and institutions committed to integrative medicine.
- Long-Term Research Committees: Establishing permanent committees that continuously analyze, refine, and update integrative practices based on new evidence.
- Patient and Practitioner Exchanges: Facilitating exchange programs where practitioners can experience different healthcare models in real time, thus accelerating learning and adaptation.
- Digital Platforms for Integrative Care: Leveraging technology to create digital resources, telemedicine platforms, and mobile health applications that help disseminate integrative practices across borders.
These forward-thinking ideas demonstrate that the collaboration is not a one-off diplomatic gesture but an ongoing commitment to work together on global health challenges. Both India and Germany realize that the future of healthcare depends on making informed choices, sharing the burden of research costs, and building partnerships that capitalize on the strengths of each system.
Lessons Learned and the Road Ahead
The Berlin meeting has provided several valuable lessons about managing your way through the tangled issues found at the convergence of tradition and modern science. Here are some of the main takeaways:
- Open Communication is Essential: Honest, transparent discussions help clear up the confusing bits that often deter innovative ideas. Both sides are learning to speak a common language of research and patient care.
- Flexibility in Policy-Making: As both countries work on harmonizing their approaches, it is evident that policies need to be flexible enough to take into account the fine points of traditional practices while adhering to rigorous safety standards.
- Building Trust Among Stakeholders: Trust is a must-have in integrative healthcare. By continuously engaging with healthcare practitioners, patients, and regulatory authorities, both nations are nurturing an environment of mutual respect.
- Commitment to Continuous Improvement: The process is ongoing, and each new session and workshop offers fresh insights and new ways to tackle nerve-racking challenges.
These lessons remind us that even when confronted with intimidating bureaucracy and overwhelming adjustments, taking the wheel and actively participating in change is critical. Both countries are now better prepared to figure a path through the tricky parts and tangled issues that come with reforming healthcare systems.
The Role of International Partnerships in Healthcare Reform
International partnerships such as the one between India and Germany hold the key to broader healthcare reform. In a globalized world, where diseases and treatments cross borders quickly, working on an international level has become super important. Such alliances provide a multi-faceted view of health challenges, combining local expertise with global research data.
Some of the benefits of these international collaborations include:
- Diverse Expertise: Working with experts from different backgrounds allows for a richer exchange of ideas and a broader perspective on complex healthcare challenges.
- Resource Sharing: By pooling resources, both financial and intellectual, partners can more effectively address the overwhelming health challenges that individual nations might find too intimidating to tackle alone.
- Regulatory Learning: Collaboration provides opportunities to get around the bureaucratic twists and turns more smoothly by drawing on best practices from different regulatory environments.
- Enhanced Innovation: Exposure to alternative models of care and research methodologies can spark innovation that benefits patients everywhere.
In addition to these benefits, international partnerships foster a sense of solidarity. They create networks where health professionals can bounce ideas off one another, thus ensuring that even the smallest nuances and confusing bits are addressed in a thoughtful manner.
Emphasizing Quality, Safety, and Evidence in Traditional Medicine
One of the recurring themes throughout the Berlin meeting was the emphasis on quality and safety. Traditional medicine, while rich in heritage and potential efficacy, is sometimes viewed with skepticism due to the lack of standardized, evidence-based protocols. Presenting a well-documented, scientific case behind each practice is critical to overcoming these perceptions.
By focusing on these key areas—quality control, outcome measurement, and rigorous scientific standards—both India and Germany are striving to replace any hesitancy with confidence in traditional health practices. The collaborative effort is geared towards generating reliable research results that can be used to support wider public health initiatives.
Measures that are being put in place include:
- Standardization of Treatment Methods: Developing uniform protocols that maintain the subtle parts and little details that make traditional treatments unique while also meeting modern safety standards.
- Enhanced Clinical Trials: Conducting comprehensive studies to validate the efficacy of traditional practices, ensuring that claims are backed by solid scientific evidence.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Creating joint committees between the nations that analyze and update safety protocols regularly, ensuring that both traditional and modern treatments are held to the highest standards.
These steps aim to demystify traditional methods, making them more acceptable not only to the medical community but also to patients who seek safe and effective treatments backed by credible science.
Taking a Closer Look at the Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
The road ahead, although filled with potential, is not free from challenges. There remain several nerve-racking bureaucratic and financial hurdles that need to be addressed before integrative healthcare can become commonplace. However, by taking a closer look at these challenges, stakeholders are better positioned to design strategies to overcome them.
Some of the small distinctions and subtle parts that must be addressed include:
- Inter-System Communication: Creating effective channels of communication between practitioners of traditional and modern medicine to reduce the risk of misunderstandings.
- Intellectual Property Concerns: Protecting traditional knowledge while promoting research and clinical innovation can be a delicate balancing act.
- Financial Viability: Structuring reimbursement policies that are fair and sustainable for patients, practitioners, and insurance systems alike.
- Regulatory Adaptation: Ensuring that regulatory frameworks can adapt quickly to incorporate advances from both traditional research and technological innovations in modern medicine.
By addressing these issues head on, the collaboration between India and Germany represents a model for how countries can work together to tackle even the most tangled issues of healthcare reform. Their proactive, united approach serves as a beacon for future international partnerships in the medical field.
Conclusion: A New Era for Global Healthcare Collaboration
The recent meeting in Berlin between India and Germany has highlighted that the blending of traditional and modern medicine is both possible and promising. The event showcased numerous forward-thinking ideas and underscored the significance of breaking down the intimidating barriers between established medical practices and innovative therapies. By addressing both the fine points of traditional practices and the innovative research methodologies of modern medicine, the collaboration is setting the stage for a global movement towards more integrated, patient-focused healthcare systems.
The ongoing dialogue and active problem-solving demonstrated at the meeting underscore that while the road ahead may present confusing bits and tangled issues, the commitment to quality, safety, and accessibility remains unwavering. Both nations are dedicated to ensuring that the best of ancient wisdom and contemporary science converge to offer more effective, inclusive, and affordable healthcare options.
As stakeholders continue to work through the nerve-racking challenges and untangle the small distinctions between different approaches, one thing is clear: the future of global healthcare is evolving into a more collaborative, integrative model. Through persistent efforts to dig into detailed research, develop cross-border regulatory frameworks, and improve financial support systems, India and Germany are not only shaping their respective healthcare landscapes—they are lighting the way for a more cohesive, efficient, and holistic approach to health worldwide.
In this brave new era, the integration of traditional and modern medicine is emerging as more than just a theoretical concept. It is becoming a practical, patient-centered solution, built on shared values, mutual respect, and a relentless drive to find effective paths through even the most intimidating bureaucratic and scientific hurdles. With ongoing collaboration, continued research, and the commitment to address every confusing bit and tricky part along the way, the global community can look forward to a future where the best of all worlds is at our fingertips.
Originally Post From https://www.tribuneindia.com/news/world/india-germany-boost-collaboration-on-traditional-medicine-at-berlin-joint-working-group-meeting/
Read more about this topic at
WHA78: Traditional medicine takes centre stage
Strengthening the scientific base of traditional medicine …