A Closer Look at Daptomycin-Induced Eosinophilic Pneumonia: An Opinion Editorial
Antibiotic therapy has undoubtedly revolutionized modern medicine, helping to treat life-threatening infections and improve patient outcomes. However, as healthcare providers take a closer look at drug-related complications, cases like daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia (DIEP) remind us that even well-regarded treatments can have tricky parts. In this opinion editorial, we explore the tangled issues surrounding DIEP, reflecting on a notable case and considering how early diagnosis and proper management can help curb these adverse effects. Our discussion aims to shed light on the subtle details of drug-induced lung complications while offering insight for both clinicians and patients.
Our journey today will take a closer look into the challenges faced when a patient develops respiratory symptoms while receiving daptomycin. We will dive in to examine the clinical presentation, the role of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) in diagnosis, the importance of distinguishing between similar lung conditions, and the key management strategies required. In doing so, we highlight lessons learned from this case and underscore recommendations for safe antibiotic usage that every healthcare provider should consider.
A Broader Perspective on Antibiotic-Associated Lung Complications
Respiratory complications related to medications are not new, but they are often full of problems that require diligent observation. When antibiotics such as daptomycin are used, the resulting side effects—though rare—can present as pleuritic chest pain, cough, and dyspnea. What can seem like just another case of pneumonia at first can quickly spiral into a situation with extra layers of confusing bits and challenging diagnostic puzzles.
It is important to remember that lung infiltrates have many causes. They can appear as the result of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections, or even as a consequence of cardiac conditions like pulmonary edema. In our case, the patient’s initial diagnosis was complicated by the overlapping features of healthcare-associated pneumonia versus a drug-induced pneumonitis. It reminds us that making your way through such cases involves not only knowledge of common infections but also an awareness of drug-induced complications.
Recognizing the Tricky Parts of Daptomycin’s Side Effects
Daptomycin is highly regarded for its robust anti-gram-positive activity, especially in treating skin and soft tissue infections as well as bone and joint infections. However, it comes with its own set of tricky parts, one of which is the rare but noteworthy occurrence of eosinophilic pneumonia. In this opinion editorial, it is essential to emphasize that while the risk may be low, the severity of this adverse reaction puts a spotlight on the importance of early recognition.
When a patient develops respiratory symptoms two weeks after switching from vancomycin to daptomycin for osteomyelitis, clinicians should consider the possibility of drug-induced pneumonitis. This vigilance becomes super important in cases where the patient’s physical condition includes additional chronic illnesses, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, or renal insufficiency.
Case Snapshot: A Patient’s Journey Through DIEP
In the case under discussion, a 56-year-old male presented to the emergency department with pleuritic chest pain, a productive cough, and signs of lung infiltrates on imaging. His history of diabetes and kidney issues, alongside a shift in antibiotic therapy, set the stage for this complication. The challenge was to make your way through a differential that included common pneumonia and less common drug-induced pneumonia.
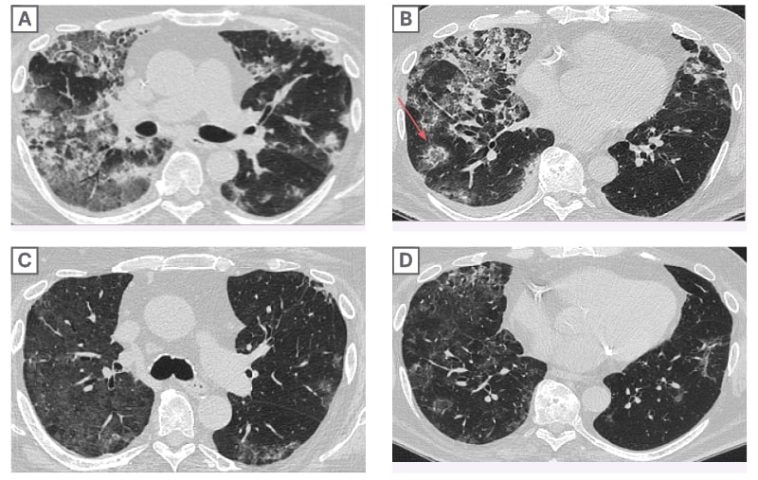
A series of diagnostic tests were carried out, including chest X-rays and a high-resolution CT scan. These imaging studies revealed bilateral scattered opacities and ground-glass appearances—findings that can easily be mistaken for pneumonia or pulmonary edema. Overlapping symptoms and imaging results make it a nerve-racking task for clinicians, highlighting the need to probe deeper into a patient’s medication history.
Understanding the Diagnostic Process: Balancing the Fine Points
Amidst all the ambiguous signs on imaging and the tangled issues of overlapping conditions, a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) provided a clear path forward. BAL remains one of the most effective diagnostic tools in confirming eosinophilic pneumonia. In cases like this, discovering an eosinophil percentage of more than 25% in the BAL fluid gives clinicians a stronger footing in the diagnosis.
Below is a simplified table summarizing the laboratory parameters that can provide clues in such cases:
| Parameter | Result | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin | 8.9 g/dL | 12.0-16.0 g/dL |
| Eosinophils (Blood) | 13.6% | <5% |
| Pro-BNP | 303 pg/mL | 0-450 pg/mL |
This table demonstrates the abnormal findings that raised suspicion. Likewise, a BAL test further revealed more than 25% eosinophils in the lung fluid, strongly suggesting an allergic reaction to daptomycin. Such detailed lab work helps sort out the confusing bits when faced with overlapping symptoms.
The Role of Imaging in Pinpointing the Diagnosis
Imaging studies are indispensable when it comes to identifying pulmonary infiltrates. In our case, chest X-rays and CT scans played a part in outlining the spread and character of the lung involvement. Ground-glass opacities, described as a hazy area with fine shades of density on the CT scan, are particularly important in showing the patient’s underlying lung condition.
It is critical, however, to note that these radiological findings can be seen in many lung conditions. Therefore, clinicians need to figure a path through subtle details provided by imaging, combined with other clinical information like recent medication changes and laboratory findings, to reach a definitive diagnosis.
Weighing the Risks and Paying Attention to Hidden Complexities
For many practitioners, daptomycin represents a safer alternative to vancomycin based on its pharmacological profile and a generally favorable side effect trend, such as a lower incidence of adverse reactions. Yet, the emergence of eosinophilic pneumonia, although rare, is a striking reminder that every treatment option brings its own set of complications.
Risk factors that tip the balance include:
- Age over 70 years
- Extended duration of daptomycin therapy (beyond two weeks)
- A higher cumulative dosage of the drug
- Existing conditions like renal insufficiency or diabetes
- An elevated Charlson Comorbidity Index
These factors serve as key indicators that healthcare providers should look out for when prescribing or monitoring daptomycin therapy. Ensuring that every patient’s profile is evaluated for these risks can help figure a path to minimizing adverse outcomes.
Identifying the Early Signs: Pushing Aside Overwhelming Uncertainty
Early recognition remains a cornerstone in managing daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia. In practice, being able to get into the subtle details of symptom onset, particularly when it coincides with the start or change of an antibiotic, is essential. Clinicians are encouraged to keep a keen eye on the following early warning signs:
- Pleuritic chest pain
- Persistent cough with unusual sputum color
- Shortness of breath or dyspnea that seems disproportionate
- Radiological findings such as ground-glass opacities or centrilobular nodules
- Elevated blood eosinophil levels
By actively looking for these indicators, healthcare providers can steer through the nerve-racking early moments of diagnosis, making sure that treatment adjustments are both timely and well-informed.
Steering Through the Management of DIEP: Treatment Options and Strategies
Once the diagnosis of DIEP is established, the management strategy is both straightforward and critical. The first step involves discontinuing the offending antibiotic immediately. This action alone often leads to a significant improvement, sometimes observable within 24 hours after stopping the drug.
However, the situation can sometimes get a bit more complicated. In patients showing severe symptoms or hypoxia, adjunct therapy with corticosteroids may become necessary to quell the inflammatory response in the lungs. Below is a bulleted list outlining the main management steps:
- Immediate cessation: Stop daptomycin as soon as DIEP is suspected.
- Corticosteroid therapy: Initiate steroids, such as prednisone, particularly in patients with severe respiratory distress.
- Monitoring: Closely observe the patient’s respiratory status, oxygen saturation, and overall improvement.
- Alternative antibiotics: Evaluate safe substitutes that cover the same infectious organisms without risking a recurrence of pulmonary complications.
- Follow-up imaging: Conduct subsequent pulmonary imaging to confirm the resolution of lung infiltrates.
These management strategies are not only standard practice but also emphasize the need for a balanced approach in the face of tricky parts. While the resolution of symptoms can be rapid, consistent monitoring ensures that any recurrent or lingering issues are adequately addressed.
Understanding the Mechanism: The Little Details Behind DIEP
The precise mechanism by which daptomycin leads to eosinophilic pneumonia is still a subject of investigation. It is proposed that the drug may bind to calcium, affecting the cytoplasmic membrane of lung cells, and possibly interact with surfactant, leading to an accumulation in the alveolar space and subsequent epithelial injury. Although these hidden complexities may not be fully unraveled yet, recognizing them is essential for further research and improved clinical protocols.
This dialogue about the underlying mechanism is super important, as it not only underlines the biochemical processes at play but also encourages a broader view on how similar antibiotics might cause comparable side effects. By getting into the nitty-gritty of these processes, researchers can design better safety profiles and perhaps develop predictive markers for susceptibility to DIEP.
Alternative Perspectives: Weighing the Benefits Against the Risks
While the report of DIEP certainly raises concerns, it is also worth emphasizing that daptomycin remains an essential tool in combating severe gram-positive infections. The benefits of effective antibiotic therapy, particularly in cases with resistant organisms, often outweigh the relatively low risk of developing eosinophilic pneumonia. With that said, physicians must be ever watchful of any adverse signs that could indicate a transition from a manageable infection to a potentially drug-induced pulmonary condition.
In our opinion, clinicians should maintain a balanced view—appreciating the power of daptomycin while also preparing to act rapidly should complications arise. This balanced approach involves:
- Thorough patient risk assessment before initiating therapy
- Clear communication with the patient about possible side effects
- Regular monitoring, especially during the critical two-to-four week period after starting daptomycin
- Collaboration between specialists such as pulmonologists, infectious disease experts, and primary care providers to ensure a coordinated response
Such a collaborative strategy can go a long way in addressing what might otherwise be overwhelming uncertainties, ensuring that even subtle signs are not overlooked.
Lessons from the Case: Getting Into Future Prevention Strategies
No single case report can capture the full spectrum of challenges associated with antibiotic-related lung complications. However, the case of daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia offers several critical lessons that should guide future practice:
- Patient History Matters: Always review the patient’s medication history thoroughly, especially when new respiratory symptoms emerge after a change in treatment.
- Timely Diagnostic Testing: Use diagnostic tools such as BAL and advanced imaging early in the evaluation process to cut through the tangled issues.
- Risk Factor Identification: Recognize that older age, prolonged therapy, and additional comorbidities are important risk markers that can signal an increased likelihood of adverse responses.
- Cross-Disciplinary Communication: Involve specialists across disciplines to manage patient care effectively, ensuring that all opinions and expertise are leveraged.
- Review and Adaptation: As new research surfaces, remain open to adapting treatment guidelines to improve patient safety and outcomes.
By taking these simple yet critical steps, clinicians can better figure a path through the complicated pieces associated with DIEP, potentially reducing the risk of severe complications and improving overall patient care.
Exploring the Diagnostic Dilemma: Getting Into the Fine Shades of Differentiation
A central challenge in cases like these is differentiating between drug-induced eosinophilic pneumonia and other forms of lung injury or infection. Since many respiratory diseases share overlapping imaging features, the following points can help clinicians in the decision-making process:
- Temporal Relationship: Note the timing between drug initiation and symptom onset. DIEP typically occurs within two to four weeks after starting daptomycin.
- Imaging Characteristics: Bilateral ground-glass opacities and centrilobular nodules are clues, yet they can also be present in diffuse alveolar damage. A comprehensive analysis of imaging studies is therefore super important.
- Laboratory Data: Elevated blood eosinophils and confirmatory findings from BAL provide strong evidence. Laboratory tests should be repeated as needed to track trends over time.
- Patient Symptoms: Even minor differences in symptom presentation—such as the nature of the cough or the presence of pleuritic chest pain—can provide essential clues when interpreted alongside objective data.
Piecing together these subtle details allows healthcare providers to steer through diagnostic uncertainties, ensuring that the appropriate therapeutic strategy is implemented before the patient’s condition becomes full of problems.
The Future of Antibiotic Safety: Research Directions and Clinical Implications
The case of DIEP also raises important questions about the future of drug safety and the need for more comprehensive research into adverse reactions. While daptomycin is associated with a relatively low rate of eosinophilic pneumonia overall, understanding the small distinctions between patient responses could lead to early detection and prevention strategies. Researchers are invited to poke around further into the following areas:
- Genetic or biochemical markers that might predict susceptibility to DIEP
- Refinement of dosing schedules to reduce the risk while maintaining efficacy
- The role of combination therapies, particularly when drugs like statins are co-administered
- Long-term follow-up studies to document patient outcomes after discontinuing the drug
Engaging in these research pursuits will not only help clarify the underlying mechanisms behind adverse reactions but also pave the way for improved patient safety protocols that can be integrated into everyday clinical practice. These studies represent a key opportunity to manage your way through the unpredictable twists and turns of antibiotic therapy.
Patient Communication and Shared Decision-Making
One of the understated aspects of managing DIEP and similar conditions is the importance of transparent communication with patients. Patients should be made aware of the potential side effects of any medication, and clinicians should take the time to explain how early symptoms are identified and managed. This not only helps in reducing anxiety but also fosters a shared decision-making process that benefits both parties.
Effective patient communication can be broken down into a few key steps:
- Informing on Risks: Clearly discuss both common and less common side effects of daptomycin.
- Explaining Diagnostic Procedures: Explain the purpose and process of tests like BAL and imaging studies so that patients understand the reasoning behind each step.
- Clarifying Management Steps: Outline the treatment plan, including drug discontinuation and potential steroid therapy, so that patients are aware of what to expect once DIEP is suspected.
- Encouraging Feedback: Invite patients to share their symptoms and concerns promptly, which can help in catching any early signs of adverse reactions.
These open lines of communication help reduce the overwhelming feeling a patient might experience when faced with complicated pieces of unexpected side effects, ultimately leading to a more collaborative and reassuring healthcare environment.
Practical Tips for Healthcare Providers: Sorting Out the Nitty-Gritty
Given the challenges posed by DIEP, here are some practical tips for clinicians to consider when treating patients on daptomycin:
- Conduct a thorough medication review: Ensure that any switch from one antibiotic to another, like from vancomycin to daptomycin, is accompanied by close monitoring for new pulmonary or systemic symptoms.
- Schedule regular follow-ups: Especially within the first month of therapy, having regular assessments can help catch early signs of lung involvement.
- Utilize multidisciplinary case reviews: When patients exhibit ambiguous symptoms, a team including pulmonologists, infectious disease experts, and primary care providers can provide a more comprehensive evaluation.
- Document and report: Given the rarity of DIEP, detailed documentation of each case contributes to the broader medical community’s understanding and can guide future research and management protocols.
- Educate staff and peers: Increasing awareness about the possible side effects of daptomycin ensures that every member of the healthcare team remains vigilant.
By following these guidelines, clinicians can better manage the unpredictable twists and turns that occasionally arise during antibiotic therapy, ensuring that patient safety remains the top priority.
Concluding Thoughts: Embracing a Balanced and Informed Approach
As we reflect on the case of daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia, it becomes clear that while the benefits of antibiotic therapies are immense, every treatment modality carries its own set of challenging parts. Healthcare providers must remain aware of the potential for rare complications like DIEP, particularly when subtle early signs could easily be dismissed as a common respiratory infection.
Through comprehensive risk assessment, timely diagnostic evaluation, and clear communication with patients, clinicians can figure a path through the confusing bits and tangles of antibiotic side effects. The detailed insights gained from the case discussed here serve as a reminder that a balanced and informed approach is the cornerstone of patient safety in today’s complex healthcare landscape.
By prioritizing early detection through tools such as BAL, leveraging high-resolution imaging, and adopting a collaborative approach among medical professionals, the evolving challenge of managing drug-induced lung conditions can be addressed head-on. The opportunity to refine our treatments based on lessons learned from such cases is both a responsibility and a chance to enhance overall patient care.
Moving forward, continued research and open dialogue will be crucial. Greater understanding of the little details behind DIEP could lead to improved guidelines and prevention strategies, further mitigating the risks associated with antibiotic therapy. With a focus on patient safety and a commitment to investigating every minute twist and turn, the future of antibiotic therapy is poised to become even more effective and safer for all.
In summary, while the occurrence of daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia is relatively rare, its impact is super important in reminding us of the need for vigilance. Healthcare providers are encouraged to remain up-to-date with the latest research, actively engage in multidisciplinary communication, and educate patients about what to expect during their treatment journey. By doing so, we can ensure that the benefits of powerful antibiotics like daptomycin are maximized, while the risks are minimized through early intervention and informed clinical decision-making.
This case not only highlights the complex yet critical need to figure a path through diagnostic challenges but also emphasizes the broader responsibility of the medical community to continue refining care practices. In an ever-evolving field where treatments are as potent as they are life-saving, staying alert to the potential for unexpected side effects is a responsibility we all share. The lessons gleaned here will undoubtedly contribute to better safety protocols and a more resilient approach to patient management amid the tricky parts of modern antibiotic therapy.
Ultimately, maintaining this balance between therapeutic promise and patient safety is a continuous process—one that involves every clinician, researcher, and patient alike. As we move forward, let us take these insights as a call to action to remain proactive, informed, and collaborative in our pursuit of excellence in healthcare.
Originally Post From https://www.cureus.com/articles/348907-a-case-of-daptomycin-induced-eosinophilic-pneumonia-and-its-management-insights?score_article=true
Read more about this topic at
Daptomycin-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity: A Case Series
Daptomycin-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia – PMC