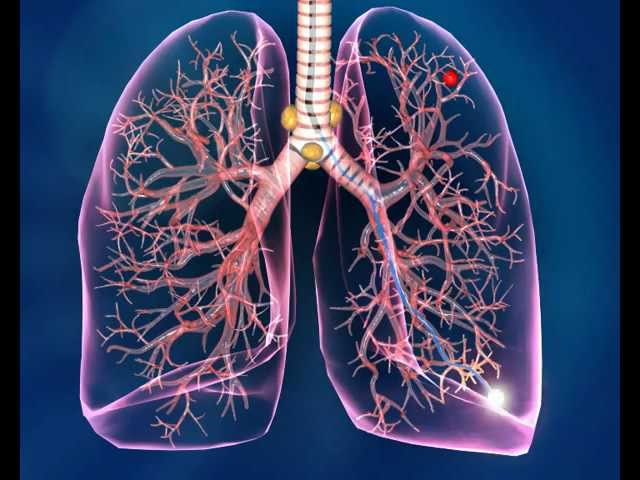
Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy: A Safer, Faster Frontier in Lung Nodule Localization
The fight against lung cancer has always been one of the most pressing battles in modern medicine. With lung cancer remaining the top killer among cancers worldwide, medical experts are continuously on the lookout for better methods for early detection and effective treatment. In recent years, one breakthrough technique—electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy-guided preoperative localization (ENBDM)—has shown promising results as an alternative to traditional computed tomography (CT)-guided lung puncture (CTPLP). This editorial examines the effectiveness of ENBDM, its advantages over older methods, and its potential role in revolutionizing lung nodule management, all while considering the tricky parts of the existing technology, the tangled issues behind patient safety, and the subtle details that differentiate one method from the other.
In many ways, the journey towards improving preoperative localization of lung nodules is like trying to find your way through a labyrinth of complicated pieces and confusing bits. Traditional techniques, such as CTPLP, have served us well, but their limitations, especially in patients with multiple ipsilateral nodules, demand a rethinking of our strategies. The emergence of ENBDM in recent years displays a significant leap forward—a leap that steers through many nerve-racking challenges while promising fewer complications and a more streamlined process.
Understanding the Tricky Parts of Lung Nodule Localization
The detection of pulmonary nodules has grown exponentially with the use of low-dose spiral computed tomography (LDCT) in health screening programs. Along with this increase in detection comes the challenge of accurately localizing and diagnosing multiple, often very small nodules distributed in the lungs. Traditional localization methods, like CTPLP, involve techniques such as dye marking, radiotracer labeling, hook wire placement, and micro-coil placement. While these methods have proven robust over time, they are not without their share of tangled issues and intimidating risks.
When dealing with multiple ipsilateral nodules, CTPLP tends to amplify radiation exposure and elevate the risk of procedure-related complications. These complications can include pleural reactions, pneumothorax (air leaking into the space between the lung and chest wall), and hemothorax (blood in the chest cavity). Not only do these risks pose immediate health concerns for patients, but they also complicate the surgical workflow and overall treatment strategy.
Why Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy Deserves a Closer Look
Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) introduces a refreshing approach that promises to cut through the twists and turns of traditional methods. ENBDM allows doctors to localize lung nodules inside an integrated operating room, effectively eliminating the nerve-racking patient transport from the CT scan area to the surgery room. This single-room approach not only simplifies the process but also significantly reduces the risk of complications.
Several key points highlight why ENBDM is steadily capturing the attention of the medical community:
- Shorter Localization Time: ENBDM drastically lowers the time needed for marking pulmonary nodules. Studies have shown that the procedure averages around 8 minutes compared to the 22 minutes or so typically required with CTPLP.
- Reduced Radiation Exposure: Unlike CT-guided methods, ENBDM minimizes radiation exposure by eliminating the need for repeated CT scans during localization.
- Minimal Invasiveness: The procedure is less invasive, which is particularly important for patients with multiple nodules, reducing the overall stress on the body.
- Fewer Complications: Clinical data indicates a marked reduction in complications such as pneumothorax, hemothorax, and pleural reactions when using ENBDM.
These benefits paint an optimistic picture for the future of pulmonary nodule management, one where patients can look forward to a process that is both safer and quicker, without sacrificing accuracy.
Side-by-Side: Comparing ENBDM and CTPLP
When contrasting these two localization strategies, it is essential to understand both the fine points and the little details that set them apart. The following table summarizes some of the most critical differences between ENBDM and CTPLP:
| Parameter | ENBDM | CTPLP |
|---|---|---|
| Localization Time | Approximately 8 minutes | Approximately 22 minutes |
| Radiation Exposure | Minimal | High |
| Overall Accuracy | 94.9% | 97.4% |
| Procedure-Related Complications | None reported | Includes pleural reactions, pneumothorax, hemothorax |
| Integration in OR | Performed in an integrated operating room | Requires transportation between scanning and surgery areas |
This table underscores the super important aspects of ENBDM when it comes to reducing not only the operation time but also the associated risks, making it an attractive alternative for patients who face the nerve-racking prospect of invasive procedures.
The Intricate Dance: The Importance of Accurate Localization
When it comes to lung nodule localization, accuracy is key. Doctors need to mark and target nodules precisely before video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) proceeds. While the overall localization accuracy of both ENBDM (94.9%) and CTPLP (97.4%) is comparable, the slight differences become less significant when weighed against the potential complications presented by CTPLP.
In any medical procedure, especially one involving cancer, it is the little twists and subtle details that can make all the difference in patient outcomes. When a procedure is minimally invasive and considerably reduces the risk of complications, it often signifies a turning point in clinical practice. ENBDM, by offering a reliable alternative with fewer negative side effects, brings us closer to achieving that ideal scenario.
Streamlining the Process: The Role of Integrated Operating Rooms
One of the most significant advantages of the ENBDM approach is the integration of the localization procedure within the operating room itself. This integration is more than just a logistical improvement; it has far-reaching implications for patient care and overall workflow efficiency.
Consider the following bullet list summarizing the benefits offered by performing ENBDM within an integrated OR setup:
- Elimination of Patient Transport: Keeping the procedure within the same room minimizes the risk of complications associated with moving patients between different departments.
- Simplified Process: A streamlined process results in fewer delays and a less nerve-wracking experience for both patients and the medical team.
- Enhanced Coordination: Surgeons, radiologists, and the entire operative team can work more cohesively in a single environment, ensuring rapid response in case of any issues.
- Improved Safety: The removal of inter-departmental transfers is linked with a lower chance of errors and mishaps.
This streamlined approach allows healthcare providers to focus on what they do best: providing key, life-saving interventions with a high degree of precision and care.
Patient Safety: Cutting Through the Confusing Bits of Complication Risks
One of the more intimidating aspects of lung nodule localization is the worrying risk of complications such as pneumothorax and hemothorax, which are not only stressful for the patient but also challenge the medical team with additional, often nerve-racking emergency procedures. In the case of CTPLP, the increased radiation and the consequent higher complication rate have long been topics of concern.
Research comparing ENBDM with traditional CTPLP indicates that the newer technique virtually eliminates these risks. Zero complications related to pleural reactions, pneumothorax, or hemothorax have been reported in studies involving ENBDM. This fact alone has the potential to transform patient perceptions of lung biopsy procedures and engender greater trust in minimally invasive methods.
When patients and physicians alike are faced with the prospect of a diagnostic procedure, the assurance that their chosen method minimizes risk can be incredibly reassuring. In a field where the stakes are as off-putting and overwhelming as lung cancer treatment, any advancement that contributes to patient safety is a welcome development.
Overcoming the Tangles: Addressing the Challenges with Multiple Nodules
One of the trickier challenges in lung nodule localization is managing patients with multiple ipsilateral pulmonary nodules. Using CTPLP in such cases not only increases the radiation load on the patient but also lengthens the procedure time, potentially leading to a cascade of nerve-racking issues and heightened procedural risks.
ENBDM, however, has shown consistent performance even when faced with multiple nodules. Studies have highlighted that as the total number of nodules increases, ENBDM continues to maintain a significantly shorter localization time compared to CTPLP. This suggests that the electromagnetic navigation approach is not only effective but also particularly well-suited for the complicated pieces of multi-nodule cases.
By reducing the time required for each procedure and lowering the risk factor, ENBDM is well-poised to become the method of choice, especially for patients with a high number of nodules. It enables physicians to tackle the fine points of localization even in the most loaded scenarios with accuracy and speed.
Real-World Impact: How Revised Procedures Benefit Patients and Clinicians
Beyond the technical metrics and clinical trial data lies the real-world impact of these medical innovations on both patients and healthcare professionals. For patients, the move towards ENBDM means facing fewer nerve-racking procedures, experiencing less discomfort, and benefiting from reduced recovery times. For clinicians, it translates to more efficient surgeries performed under conditions that favor quick responses and reliable outcomes.
The integrated nature of ENBDM procedures in the operating room also means that every member of the medical team can better coordinate and respond to any challenges that arise. This enhanced coordination ensures that the entire process, from localization to surgical resection, proceeds in a smooth, timely manner. Such improvements may ultimately lead to better post-operative results and elevated overall patient care.
The Future of Lung Nodule Localization: Embracing Technological Advancements
Innovation in medicine is a journey marked by constant improvement and a drive to overcome the overwhelming and sometimes intimidating aspects of traditional approaches. With ENBDM proving its worth, it stands not only as a safer alternative but also as a beacon of what the future holds for pulmonary diagnostics.
Several key areas point to the direction in which the technology is headed:
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence: Emerging AI technologies promise to refine the accuracy and decision-making capabilities during localization procedures.
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: With advances in imaging, ENBDM can potentially integrate higher resolution visuals, aiding in the identification of even the smallest nodules.
- Customizable Patient Approaches: Future developments may see the personalization of procedures based on patient-specific lung anatomy and nodule characteristics, further optimizing outcomes.
Collectively, these innovations could pave the way for a multi-modality approach that blends electromagnetic navigation with advanced imaging and AI-based analytics—ushering in a new era of targeted, patient-centered care for lung cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Expert Opinions on ENBDM: Balancing Innovation with Caution
While the clinical data supporting ENBDM is promising, many practitioners urge a balanced perspective. The shift from well-established CTPLP methods to ENBDM is a major change and requires adequate training, standardized protocols, and long-term studies to ensure that early successes translate into enduring improvements in patient outcomes.
Some experts argue that the adoption cycle for any new technology is inevitably accompanied by a period of adjustment. Critical assessments are necessary to dig into the fine shades of care provided by ENBDM and understand how these improvements translate in varied clinical settings. Typically, transitioning to a novel approach may involve:
- Comprehensive training for medical staff to efficiently make their way through the new technology.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation of procedures in real-time clinical environments.
- Regular updates to procedural guidelines based on evolving evidence and feedback from early adopters.
Given that ENBDM is still relatively novel compared to CTPLP, it is super important not to rush into widespread adoption without carefully managing risks. Such due diligence ensures that once the technology is broadly accepted, it will have overcome the little twists and small distinctions that could otherwise lead to unexpected challenges.
Patient Perspectives: Trusting in the Improved Process
From the viewpoint of patients who have been subjected to nerve-racking diagnostic procedures, the arrival of innovative techniques like ENBDM brings new hope. For many, the idea of reducing exposure to radiation and avoiding complications that arise from repeated CT scans is a game changer.
Patients often express relief at knowing that modern methods prioritize not just the accuracy of diagnosis but also their overall safety and comfort. This comfort level is essential in building trust between patients and healthcare providers. When the process is perceived as less intimidating and off-putting, patients are more inclined to undergo necessary diagnostic and therapeutic interventions without hesitation.
In a healthcare environment where timely diagnosis can mean the difference between life and death, having a procedure that manages your way through the tricky regulatory protocols while remaining patient-friendly is invaluable. In many ways, ENBDM not only redefines a technical process but also reshapes the narrative of patient care in lung cancer management.
Economic and Operational Benefits: A Win-Win for Hospitals and Patients
While the clinical advantages of ENBDM are clear, the technique also presents several economic and operational benefits for hospitals. The integration of localization within the operating room simplifies scheduling, minimizes equipment usage across different departments, and speeds up the overall surgery schedule—factors that can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Hospitals often operate under tight budgets and face numerous challenging parts when trying to adopt new medical equipment or methods. By choosing a more efficient and less complication-prone method like ENBDM, healthcare facilities can reduce both the direct and indirect costs associated with lung nodule localization procedures. Consider the following breakdown:
| Aspect | CTPLP | ENBDM |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure Time | Longer (approx. 22 minutes) | Shorter (approx. 8 minutes) |
| Resource Utilization | Multiple equipment and room transfers | Single integrated operating room |
| Risk Management | Higher complication management costs | Lower risk reduces follow-up interventions |
This cost-benefit analysis is not just about immediate savings—it’s also about long-term improvements to patient throughput, better allocation of staff time, and ultimately, a more robust healthcare delivery system. Hospitals that step up to incorporate ENBDM into their workflows might well see both enhanced patient satisfaction and improved financial outcomes.
Integrating ENBDM: Implementation Challenges and Future Directions
No new technology is implemented without encountering some nerve-racking challenges. While ENBDM brings many benefits to the table, integrating it into existing clinical workflows involves managing your way through some complicated pieces and subtle details that require thorough planning and training.
The following points highlight some key factors that hospitals and clinics must address when transitioning to ENBDM:
- Staff Training and Adaptation: Transitioning from CT-guided methods to electromagnetic navigation requires comprehensive education and hands-on training for physicians and support staff.
- Equipment and Infrastructure Updates: Hospitals may need to invest in new equipment and upgrade their operating rooms to enable a seamless, single-room localization and surgery process.
- Protocol Standardization: Establishing clear guidelines to ensure that ENBDM is performed consistently and safely across various clinical environments is critical.
- Ongoing Evaluation and Research: Continued clinical studies and long-term follow-up are needed to confirm the benefits of ENBDM in broader patient populations and diverse clinical scenarios.
Looking ahead, future research is likely to address the current limitations, fine-tune the procedure to tackle any nerve-racking complications early on, and potentially extend the application of ENBDM to other areas of thoracic surgery. As the technology evolves, one can expect a more integrated, patient-centered approach that leverages the advantages of minimal invasiveness, speed, and enhanced safety.
Final Thoughts: Embracing a New Era in Lung Cancer Management
The evolution of lung nodule localization reflects the broader evolution of medical technology—a journey replete with modest steps and giant leaps. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy-guided preoperative localization represents one such giant leap. By reducing procedure times, minimizing radiation exposure, and eliminating many of the nerve-racking complications associated with CTPLP, ENBDM not only tackles the confusing bits of traditional procedures but also elevates patient safety to a super important level.
In today’s healthcare landscape, where every minute matters and every twist and turn has a direct impact on patient outcomes, embracing innovative techniques like ENBDM can mark the difference between a predictable outcome and a potentially life-saving intervention. As we continue to dig into the finer points of lung cancer diagnosis and treatment, it is essential for stakeholders—ranging from clinicians to hospital administrators—to weigh the advantages of these new technologies against the challenges of their implementation.
For patients facing the intimidating reality of lung nodule diagnosis, the transition to minimally invasive, integrated procedures offers renewed hope and reassurance. For the medical community, it is a call to continuously sort out and refine our methods, ensuring that each step we take is guided by evidence, efficiency, and empathy.
In summary, while no medical procedure is free of challenges, the data and expert reviews increasingly point to ENBDM as a key advancement in the battle against lung cancer. As healthcare providers and patients alike start to figure a path through the tangled issues and nerve-racking risks associated with older methods, ENBDM stands out as a safer, faster, and more patient-friendly alternative—one that promises to improve both the quality of care and the overall journey through lung cancer management.
Conclusion: A Call for Balanced Optimism and Continued Innovation
The path forward in lung nodule localization is not without its twists and turns. The adoption of ENBDM is a prime example of how modern advancements can offer practical solutions to tricky parts of traditional practices. However, it is critical to maintain an approach of balanced optimism. Ongoing research, standardized training programs, and clear operational protocols will be necessary to ensure that all the benefits of this breakthrough are fully realized in everyday clinical settings.
Looking to the future, the integration of technologies such as artificial intelligence, higher resolution imaging, and custom-tailored procedural approaches promises to further enhance the capabilities of ENBDM. As our understanding of the small distinctions in lung cancer pathology deepens, the combination of innovative technologies and refined clinical methods may well unlock new frontiers in cancer diagnostics and treatment.
Ultimately, the journey of transforming lung nodule localization is one of continuous learning and adaptation. While the switch from CTPLP to ENBDM may require adjustments and patience, it is a journey that promises improved outcomes, streamlined processes, and, most importantly, enhanced patient safety. It is the responsibility of medical professionals, healthcare institutions, and policymakers to work together in making these advancements accessible, ensuring that the future of lung cancer management is as bright and as promising as the technology that drives it.
As we stand at this crossroads of innovation and tradition, the call is not to entirely replace the old with the new but rather to integrate the best of both worlds. By doing so, we can conquer the nerve-racking challenges of lung nodule localization and steer through the complicated pieces of modern lung cancer care with confidence, precision, and compassion.
In closing, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy-guided localization presents a vital opportunity for the evolution of lung cancer management – one that saves time, reduces risk, and most importantly, fosters a safer environment for both patients and clinicians. The debate is far from over, but for now, the evidence suggests that embracing ENBDM could be the key to unlocking a new era where technology and patient care find common ground in the battle against one of the world’s deadliest forms of cancer.
Originally Post From https://www.news-medical.net/news/20250621/Electromagnetic-navigation-bronchoscopy-emerges-as-an-effective-alternative-for-lung-nodule-localization.aspx
Read more about this topic at
Lokalise: The most user-friendly localization platform
Falcom Is Looking To Speed Up Localization For Its Games …