Innovative Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy: A Closer Look at the ELI-002 7P Phase 2 Trial
The field of cancer immunotherapy has witnessed a remarkable evolution over the past few years, and one recent clinical trial has added another exciting chapter. In the ongoing Phase 2 AMPLIFY-7P trial, researchers have observed robust, mKRAS-specific T cell responses in patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) treated with ELI-002 7P. This investigational treatment appears to stimulate an immune response across a wide range of Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) types, potentially offering hope to a diverse group of patients in need of new treatment options.
Today, we will take a closer look at this promising immunotherapy approach by Elicio Therapeutics, a biotechnology company focused on developing novel immunotherapies for high-prevalence cancers. By breaking down the findings and discussing their potential implications, we can better appreciate the challenges, opportunities, and future directions in this rapidly evolving area of medicine.
Diverse HLA Backgrounds and T Cell Activation: Understanding the Key Evidence
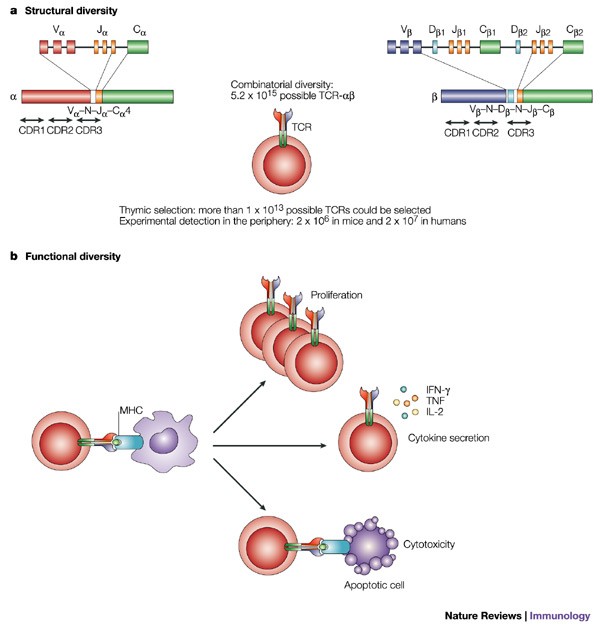
A central piece of the puzzle in the current trial relates to the diversity of HLA types among the study participants. Out of 89 patients treated with ELI-002 7P, a total of 1,132 unique HLA types were represented among 1,398 overall HLA backgrounds. This wide-ranging profile illustrates that the immune response triggered by ELI-002 7P is not limited to a narrow patient subset but may be effective for many individuals regardless of their genetic makeup.
HLA Diversity: The Game-Changer in Immunotherapy
The ability to induce mKRAS-specific T cell responses across a broad array of HLA alleles addresses some of the tricky parts that have long challenged immunotherapy for PDAC. Specifically:
- Wide-Ranging Genetic Variability: The presence of 1,132 unique HLA types emphasizes that the treatment can potentially engage the immune systems of patients with very different genetic backgrounds.
- Broad Patient Applicability: With 99% of the patients assessed showing a measurable immune response, the trial results indicate a groundbreaking level of effectiveness across a broad spectrum of individuals.
- Setting a New Benchmark: This evidence builds on previous studies where T cells specific to mKRAS mutations, such as G12D and G12V, were found in all healthy donors, underscoring that most patients naturally possess HLAs capable of presenting these antigens.
These findings are refreshing, particularly when we take into account the confusing bits often encountered in cancer treatment where a patient’s unique genetic profile can significantly influence responsiveness to therapy. The fact that ELI-002 7P appears to bypass these tangled issues by working across various HLA types is both promising and innovative.
Understanding the Mechanism: The Role of the AMP Platform and Lymph Node Engagement
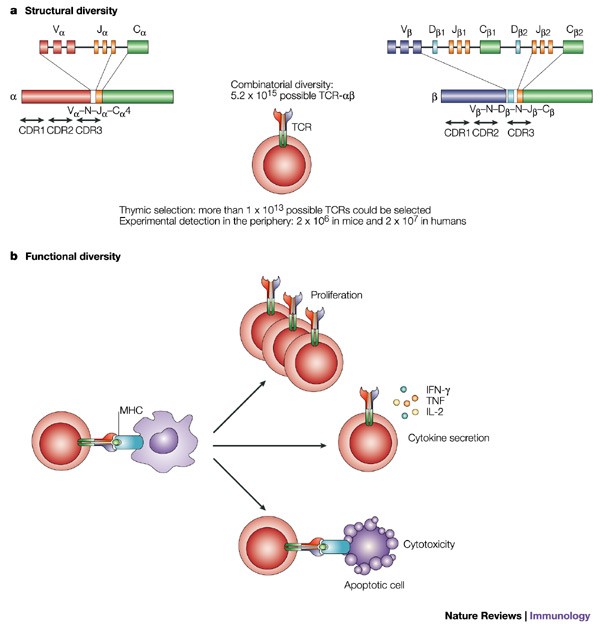
Elicio Therapeutics harnesses a proprietary technology called the Amphiphile (“AMP”) platform. This innovative method aims to deliver immunotherapeutics directly to the lymph nodes – the command centers of the immune system – in order to educate, activate, and amplify cancer-specific T cells. The AMP platform represents one of the most exciting advancements in the effort to get into the fine points of how the immune system can be trained to fight cancer more effectively.
Lymph Node Targeting: How It Enhances Immune Response
One of the challenges in modern immunotherapy has been finding an efficient way to intensify the body’s natural defenses against cancer. By steering therapeutic agents directly to the lymph nodes, the AMP platform transforms the effectiveness of these treatments. Here are some key points about this approach:
- Direct Delivery to Immune Hubs: Lymph nodes are the primary sites where immune cells are primed. By targeting these areas, the AMP platform ensures that the treatment reaches the very heart of immune activation.
- Enhanced T Cell Education: The delivery of mKRAS peptide antigens alongside an AMP-modified CpG oligodeoxynucleotide adjuvant (ELI-004) helps in the detailed education and activation of T cells.
- Persistent Immunity: Preclinical studies suggest that this method can drive immune responses that are more durable, a super important factor in ensuring long-term cancer suppression.
Using this strategy, the treatment appears to overcome many of the scary twists and turns that have previously hindered conventional immunotherapies. The advantage here is the possibility for off-the-shelf availability, meaning that these therapies could be produced faster and at a lower cost compared to personalized approaches, which are typically more expensive and time-consuming.
The AMP Platform Compared to Conventional Treatments
Conventional immunotherapy approaches often face limitations such as high production costs, delayed manufacturing times, and difficulties in targeting the immune system efficiently. In contrast, Elicio Therapeutics’ off-the-shelf approach, bolstered by the AMP platform, offers several benefits:
- Rapid Manufacturing: The off-the-shelf nature allows for scalable, efficient production, ensuring that patients get timely access to the treatment.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower production costs can potentially make these treatments more widely available, addressing a significant need in high-risk populations.
- Wider Applicability: By working across diverse HLA types, the chance to extend this treatment to patients with varying genetic backgrounds is much higher, compared to personalized therapies that require tailor-made solutions.
This approach may mark a turning point in how we manage your path through cancer treatment by reducing both the financial and logistical burdens that have historically slowed down immunotherapy development.
Implications for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) Treatment
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma is one of the most challenging cancers to treat, with many patients facing a high risk of relapse even after standard therapies. In this context, the robust T cell responses induced by ELI-002 7P carry significant promise. Let’s break down why these findings could lead to substantial improvements in our approach to PDAC:
Meeting a Critical Unmet Need
PDAC is notorious for its nerve-racking prognosis and the limited treatment options available for patients following standard therapies. The current trial’s early indications that ELI-002 7P can induce specific T cell responses across a diverse patient population may signal a breakthrough. Consider these factors:
- Extensive Immune Activation: The induction of mKRAS-specific T cell responses suggests that patients could benefit from a durable immune surveillance mechanism. This may help in reducing relapse rates, a critical factor in PDAC management.
- Diverse Applicability: With nearly every patient in the trial exhibiting an immune response irrespective of their HLA background, this treatment could address the needs of a broad population, not just a select few.
- Potential for Combination Therapies: Robust T cell responses can pave the way for combining ELI-002 7P with other treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies, thereby potentially boosting overall treatment outcomes.
By addressing the tricky parts associated with immune variability among patients, this innovative immunotherapy could rival conventional treatments that have often fallen short in managing PDAC’s many challenges. Furthermore, expanding the potential market opportunity for these treatments aligns with the critical healthcare need to find better ways to manage high-relapse risk cancers.
Table: HLA and T Cell Response Data from the AMPLIFY-7P Trial
| HLA Category | Unique HLA Types | Total HLA Types |
|---|---|---|
| HLA Class I – HLA-A | 116 | – |
| HLA Class I – HLA-B | 158 | |
| HLA Class I – HLA-C | 118 | |
| HLA Class II – HLA-DR | 292 | – |
| HLA Class II – HLA-DP | 180 | |
| HLA Class II – HLA-DQ | 268 | |
| Total | 1,132 | 1,398 |
This table elegantly summarizes the variety found within the study population and underlines why the trial outcomes are not only promising but also broadly applicable. The vast range of HLA types analyzed in this trial helps to remove some of the intimidating barriers that arise from genetic heterogeneity among patients.
Future Directions: Expanding the Reach Beyond Pancreatic Cancer
While the current focus is on mKRAS-positive PDAC, Elicio Therapeutics is not stopping there. Their pipeline includes additional candidates that target other critical mutations such as BRAF-driven cancers and p53 hotspot mutations. This ambition reflects the broader potential of off-the-shelf immunotherapy as a transformative approach in modern oncology.
Opportunities in Other mKRAS-Driven Cancers
The principle underlying the ELI-002 7P trial could extend to a variety of other solid tumors that share similar genetic drivers. For instance:
- Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Early Phase 1 studies in mKRAS-positive CRC patients have shown promising outcomes, suggesting that further research could unlock effective treatment regimens based on similar immunotherapeutic principles.
- Lung Cancer: Given that a significant percentage of lung cancers are also driven by mKRAS mutations, there is reason to be optimistic that patients with lung cancer could benefit from comparable mechanisms of T cell activation.
- Other mKRAS-Positive Tumors: The concept of targeting mKRAS mutations—and, by extension, harnessing the inherent strength of the patient’s immune system—may well pave the way for treating a wider array of solid tumors in the future.
As more research is underway, many are eager to see if the encouraging early results from the PDAC trial will hold true when applied to other cancer types. The ability to work through a variety of cancers using a unified immunotherapeutic approach is a prospect that is both promising and full of potential.
Off-the-Shelf Versus Personalized Immunotherapy: A Comparative Look
One of the main differences between traditional personalized immunotherapy and off-the-shelf approaches like ELI-002 is the speed at which treatment can be administered. Personalized therapies often require painstaking preparation, which can be overwhelming for practitioners and patients alike. In contrast, off-the-shelf treatments offer:
- Rapid Availability: Patients can receive treatment without the nerve-racking delays associated with customizing a therapy for each individual.
- Scalability: Once these treatments pass clinical trials, they can be manufactured en masse, ensuring wider availability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: With lower production costs, healthcare systems may find it easier to integrate such treatments into standard care practices.
This approach not only makes it easier for doctors to figure a path through treatment planning but also provides patients with the reassurance that effective therapies are accessible more quickly. The off-the-shelf model, powered by the AMP technology, could very well make the difference between an overwhelming wait and prompt, effective care for high-risk individuals.
Evaluating the Broader Impact on the Healthcare Ecosystem
The implications of these findings stretch well beyond the immediate sphere of PDAC treatment. Elicio Therapeutics’ research shines a light on a new era where the unique genetic backgrounds of patients do not necessarily limit the efficacy of treatment. Instead, by leveraging the hidden complexities of lymph node-targeted delivery systems, innovative therapies like ELI-002 7P can overcome the tangled issues historically associated with immunotherapy.
The Ripple Effect on Oncological Research
There are several ways in which these trial outcomes might influence the broader landscape of cancer treatment research:
- Encouraging Further Research: The robust T cell responses observed lend significant momentum to additional studies investigating similar mechanisms of action in other cancer types.
- Setting New Standards: By demonstrating that a vast majority of patients, regardless of their HLA background, can benefit from a single immunotherapy approach, these results may prompt a rethinking of current treatment paradigms.
- Enhancing Collaborative Efforts: The success of this trial may stimulate more partnerships between biotechnology companies, research institutions, and clinical centers dedicated to unraveling the subtle parts of immune system interactions with cancer cells.
Moreover, by transforming what was once seen as the off-putting challenge of genetic diversity into an asset, researchers and clinicians can now approach immunotherapy with a renewed sense of optimism and clarity. The findings encourage us to embrace the potential of modern medicine to tackle even the most complicated pieces of cancer treatment.
Patient-Centric Advantages: What This Means for Individuals and Families
The potential benefits of treatments like ELI-002 7P extend well beyond the clinical trial data. For patients and their families, such advances signify hope in the face of daunting odds. Here are some ways in which this research could make a tangible difference in patients’ lives:
- Improved Survival Rates: With early results showing promising immune response and longer recurrence-free survival times, patients might enjoy a longer, more productive life after treatment.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By reducing the chance of relapse, the therapy not only prolongs survival but could also improve the overall quality of life for patients burdened by the emotional and physical impacts of PDAC.
- More Treatment Options: A broader immunotherapy strategy means that even those with less common HLA types can have access to potentially lifesaving treatments—effectively leveling the playing field for many patients.
These outcomes are not just data points in a clinical report; they are real-world improvements that could reshape how we make our way through the challenges of cancer care. The hope is that with continued research and investment, such therapies might one day become a standard part of treatment protocols, offering nearly universal benefits across diverse populations.
Addressing the Confusing Bits: Challenges and Considerations in Immunotherapy Development
Despite the promising nature of these findings, it’s important to recognize that cancer immunotherapy is still a field riddled with tension and loaded with potential pitfalls. Every new treatment, no matter how promising, comes with its own set of tricky challenges and nerve-wracking uncertainties. As we take a closer look, here are some of the aspects that warrant care and attention:
Understanding Response Variability Among Patients
While the trial results are encouraging, the real-world application of such treatments always presents accompanied challenges:
- Individual Immune System Differences: Not all patients will respond identically, as subtle differences in immune system function can impact outcomes.
- Long-Term Efficacy: Robust T cell responses in the short term are promising, but researchers need to monitor whether these effects translate into long-lasting clinical benefits.
- Potential Side Effects: As with any therapy that manipulates the immune system, there is always a concern, however slight, that overstimulation could lead to unintended autoimmune responses or other complications.
These are the nerve-racking aspects that scientists and clinicians must continuously monitor as further data emerges from ongoing and future studies. It is through addressing these subtle details with rigorous research that innovative therapies eventually earn their place in routine clinical care.
The Need for Continued Research and Improvement
While expert opinions and early trial data are promising, key long-term questions remain. Some of these include:
- Durability of Response: Can these robust T cell responses provide persistent immunosurveillance over many years?
- Combination Strategies: How might the addition of other therapies, such as chemotherapy or radiation, complement the off-the-shelf immunotherapy approach?
- Optimization of Dosing: What is the ideal dosing regimen for maximizing benefits while minimizing risks?
It is essential for the broader medical community, including researchers, oncologists, and pharmaceutical companies, to work together in order to figure a path through these complex questions. By doing so, we can confidently extend the reach of immunotherapy to more patients and more cancer types, even as we face the intimidating task of addressing every little twist these challenges present.
Looking Ahead: The Promise of a Revolution in Immunotherapy
The potential of ELI-002 7P and the technologies underlying its development signal a new chapter in the battle against cancer. The trial’s robust demonstration of T cell activation across varied HLA types hints at an era where treatments are not limited by the genetic differences that once seemed insurmountable. Instead, the off-the-shelf nature of this immunotherapy could democratize treatment, making it accessible and effective for a wide array of patients.
Bridging the Gap Between Research and Routine Clinical Practice
One of the biggest challenges in modern medicine is bridging the gap between innovative research and everyday clinical practice. There are several key areas where progress is being made:
- Streamlined Manufacturing: The off-the-shelf approach, driven by the AMP platform, cuts down on the nerve-racking wait times associated with personalized therapies. This means patients can receive treatment faster, without the delays that can be detrimental in aggressive cancers.
- Enhanced Collaboration: As biotech companies like Elicio Therapeutics push the envelope, collaborations between research institutions, clinical centers, and industry experts are becoming more commonplace. These partnerships are essential for translating promising trial results into reliable, real-world treatment options.
- Regulatory Innovations: The FDA and other regulatory bodies are increasingly open to approving novel treatment approaches that demonstrate significant promise, even as they come with their own tactical challenges. Streamlined regulatory pathways can help ensure that breakthroughs reach patients more rapidly.
The effective integration of these elements not only highlights the strengths of novel immunotherapies but also paves the way for a broader, more inclusive approach to cancer treatment—one that encourages practitioners to get into the subtle parts of patient care with renewed vigor and understanding.
Embracing the Future Amidst Uncertainty
Even with all its promise, the road ahead for cancer immunotherapy is full of problems and unpredictable turns. However, it is precisely through addressing these challenging bits that future breakthroughs may emerge. The ongoing collaboration, continuous monitoring, and gradual fine-tuning of therapies like ELI-002 7P are critical for success. In the face of overwhelming data and rapidly changing research landscapes, a balanced approach that acknowledges real-world challenges while celebrating promising outcomes is key.
It is an exciting time for those involved in cancer research and treatment, as incremental advances build on each other to create a more complete picture of how our immune systems can be best harnessed to fight cancer. As we see new studies and trials progressing, every step forward gives us hope for treatments that are more efficient, more accessible, and more effective.
Conclusion: A Step Forward in the Battle Against High-Risk Cancers
The robust outcomes observed in the Phase 2 AMPLIFY-7P trial of ELI-002 7P represent a significant advance in cancer immunotherapy. By generating strong mKRAS-specific T cell responses across a wide spectrum of HLA backgrounds, this investigational therapy offers a ray of hope to patients fighting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma—a cancer known for its overwhelming challenges.
Elicio Therapeutics’ innovative use of the AMP platform to directly target lymph nodes not only provides a more immediate way to activate the immune system but also sets the stage for broader applications in other mKRAS-driven cancers and beyond. The off-the-shelf approach opens the door to faster, more cost-efficient therapies that can eventually become standard care, helping patients get around the traditionally complex barriers associated with personalized treatments.
While there remain several nerve-wracking challenges and unresolved questions, the clinical results so far are a promising sign that we are on the verge of a revolution in immunotherapy. With continued research, collaboration, and investment, treatments like ELI-002 7P may soon help steer through even the toughest cases of high-risk cancers—providing not only a longer life but also a higher quality of life for those in desperate need.
In summary, the ongoing progress in immunotherapy, exemplified by the impressive outcomes of the ELI-002 7P trial, marks a major turning point. As researchers, healthcare professionals, and patients alike continue to work through the small distinctions and complicated pieces of immune response, the future looks brighter for the development of effective, accessible cancer treatments. It is a journey full of subtle details and challenging turns, but the destination—a world where cancer is no longer an insurmountable foe—seems closer than ever.
As we move ahead, it is essential for all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem to stay informed, remain engaged, and support initiatives that pave the way for these revolutionary treatments. The subtle parts and hidden complexities of our immune system offer a vast, untapped reservoir of potential waiting to be unlocked—and with innovative approaches like those from Elicio Therapeutics, that potential is fast becoming reality.
Originally Post From https://elicio.com/press_releases/elicio-therapeutics-reports-robust-t-cell-responses-across-diverse-hla-backgrounds-in-ongoing-phase-2-amplify-7p-trial/
Read more about this topic at
Researchers identify key source of T cell “exhaustion”
LAT encodes T cell activation pathway balance – PubMed – NIH