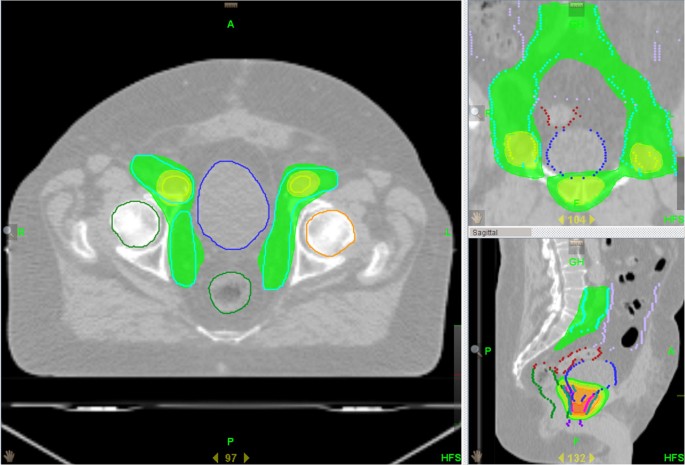
Reassessing Salvage Nodal Radiation Therapy: A Fresh Look at Prostate Cancer Recurrence
The field of oncology is no stranger to rapid innovations and breakthroughs. Recently, salvage nodal radiation therapy (SNRT) has caught the attention of experts as a promising treatment option for men facing prostate cancer recurrence. Over the past few years, modern imaging techniques like PSMA PET have truly revolutionized the way we find even the most hidden recurrences when PSA levels are still low. This transformation in diagnostics has ultimately opened a door for more tailored, targeted treatments that can potentially change patient outcomes for the better.
In this opinion editorial, we take a closer look at the study results presented at the 2025 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) Annual Meeting, discussing how SNRT blends technical precision with a patient-centered focus. In doing so, we examine the evidence, safety measures, and survival outcomes related to SNRT, while also exploring the challenges and rewards of integrating such new approaches into our established treatment protocols.
Modern Imaging and Its Role in Guiding Targeted Salvage Therapy
One of the major game changers in managing recurrent prostate cancer is the development of advanced imaging modalities. With systems such as PSMA PET and fluciclovine PET, clinicians are now able to dig into even the tiniest of nodal recurrences that might otherwise have gone undetected.
Prior to these advances, treatment decisions often hinged on less precise methods. Today, the enhanced sensitivity of modern imaging allows doctors to:
- Pinpoint the exact location of cancerous nodes
- Minimize damage to healthy surrounding tissues
- Develop more personalized salvage treatment strategies
Indeed, these imaging tools have made it easier to find your way through the tricky parts of treatment planning. As more professionals start using these methods, the ability to steer through challenging clinical scenarios becomes less overwhelming, opening the possibility for improved long-term outcomes.
Examining the Evidence: Safety and Survival Outcomes of SNRT
According to the recent data presented by experts at the ASTRO Annual Meeting, salvage nodal radiation therapy has shown promising tolerability along with low toxicity levels. The study, conducted at a single institution and involving 82 patients with recurrent prostate cancer, offers an encouraging glimpse into the future of salvage radiation treatments.
Key points from the study include:
- A median follow-up period of nearly 25 months
- A survival rate of 96% at the data cutoff
- Only minimal occurrences of adverse effects such as grade 2 genitourinary and gastrointestinal toxicities
These findings suggest that SNRT is not only effective in targeting recurrent tumors but also minimizes the risk of additional complications. While there were a few reported cases, such as a late grade 3 genitourinary toxicity and minor gastrointestinal side effects, the overall toxicity profile was reassuring for clinicians.
It is critical to acknowledge that the study emphasized the importance of careful patient selection and precise treatment planning. Given that the majority of patients received concurrent androgen deprivation therapy, the integrated approach appears to assist in the overall management, combining systemic and localized treatments to yield better responses.
Decoding the Treatment Process: What SNRT Involves
Salvage nodal radiation therapy is typically applied to patients who have already undergone radiotherapy in the past, for whom the recurrence of cancer within the lymph nodes signifies an evolving clinical scenario. The treatment involves several advanced techniques, each designed to maximize targeting accuracy while mitigating the risk to non-cancerous tissues.
The major methods used in SNRT include:
- Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
- Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
- Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
- Intensity-Modulated Proton Therapy (IMPT)
Each method comes with its own set of subtle details and a range of considerations that the treating physician must weigh carefully. When these technologies are used in conjunction with PET imaging findings, the resulting treatment plan is finely tuned to offer the best possible outcomes. In many ways, SNRT represents a marriage between cutting-edge technology and a nuanced understanding of prostate cancer behavior, providing hope for those whose treatment options were previously limited.
Understanding the Patient Profile: Who Benefits from SNRT?
The study involved a diverse group of patients with differing clinical backgrounds, but several common traits emerged among those who benefited most from SNRT. Most of the participants had undergone radical prostatectomy before, with a median age of 69 years. Additionally, the majority also had either high or unfavorable intermediate risk disease, a factor that underlines the significance of accurate imaging in detecting cancer recurrences earlier than before.
Other noteworthy points about the patient group include:
- An initial median PSA level of 8.9 ng/ml
- Most presented with T3a, T1c, T3b, and T2b stages at diagnosis
- A large percentage showed N0 disease at the time of their initial work-up
Assessing the patient profile is critical because it helps clinicians figure a path for targeted interventions. Knowing who stands to benefit most from SNRT allows for a more personalized approach to treatment, ensuring that patients are not exposed to unnecessary risks.
Balancing Toxicity and Efficacy: The Delicate Dance of SNRT
One of the trickier pieces in any cancer therapy is managing the balance between treatment efficacy and side effects. With salvage nodal radiation therapy, the low incidence of severe toxicities is a clear marker of its relative safety. However, clinicians remain cautious given the challenges presented by late side effects, even if they occur infrequently.
Looking at the specifics, the study reported the following adverse effects:
| Toxicity Type | Occurrence |
|---|---|
| Grade 2 Genitourinary Toxicity (noninfective cystitis) | 1 case |
| Grade 2 Gastrointestinal Toxicity (mainly diarrhea) | 5 cases |
| Late Grade 3 Genitourinary Toxicity | 1 case |
While these numbers might sound concerning at first glance, they represent a relatively low incidence, especially when compared to the potential risks of unchecked cancer progression or the side effects from more radical treatments. The low toxicity levels indicate that SNRT can be delivered with precision, minimizing collateral damage and thus maintaining a better quality of life for patients.
Long-Term Outcomes: A Closer Look at Progression-Free Survival
The study also revealed encouraging data regarding progression-free survival (PFS), with a median PFS of 35.6 months. This outcome is significant when you consider that certain groups—such as those with a lower Gleason score (6 to 7)—tended to remain free from disease progression for longer periods when compared to patients with higher scores (8 to 10).
This information is particularly important for patients and their families, as it provides a clearer picture of what to expect in the months and years following treatment. With an increasing emphasis on quality of life, these survival markers help guide decisions that weigh immediate treatment benefits against potential long-term risks.
Moreover, alongside the high overall survival rate reported in the study, these findings serve as proof that SNRT is not only a safe option but also an effective one in extending the period of disease control. The balance between efficacy and tolerability remains one of the key drivers when it comes to deploying new treatment options for recurrent prostate cancer.
Integrating SNRT into Multidisciplinary Treatment Approaches
No modern cancer treatment stands in isolation. SNRT, in particular, is best viewed as part of a broader multidisciplinary strategy that includes systemic therapies like androgen deprivation therapy. In the discussed study, 95% of patients received androgen deprivation therapy concurrently with SNRT, further reinforcing the idea that comprehensive care provides the best chance of success.
Working through the integration process means that oncologists, radiologists, urologists, and other specialists must not only agree on a treatment strategy but also communicate effectively about the fine points of each patient’s situation. This collaboration is crucial to face the tangled issues that arise in clinical settings. In practice, the steps involved in this multidisciplinary approach can be summarized as follows:
- Initial detection through advanced imaging techniques
- Careful assessment and staging of the cancer recurrence
- Development of a tailored treatment plan, combining SNRT with systemic therapy
- Monitoring outcomes and adjusting strategies based on patient response
By making coordinated decisions, the team can steer through the tricky parts of prostate cancer management and ensure that every patient receives not just a treatment, but a comprehensive plan designed to handle both the disease and its potential complications.
Addressing the Concerns: A Balanced Perspective on SNRT
While the initial data surrounding SNRT is promising, it is essential to recognize that every treatment modality comes with its own set of subtle details and potential pitfalls. There are a few areas where further research is necessary to fully understand the tangled issues associated with long-term outcomes and late toxicities.
Here are some of the key concerns that remain on the radar:
- The potential for late-onset adverse effects that might not be immediately evident during short-term follow-up
- The need for more extensive, multicenter trials to validate the preliminary findings
- Understanding the variability in patient responses based on different clinical profiles and prior treatment histories
It is also worth noting that such challenges are not unique to SNRT. They represent the typical twists and turns encountered in any evolving treatment approach. What is important, however, is that both researchers and clinicians remain committed to actively monitoring these issues and adjusting their strategies as new evidence comes to light.
Real-World Implications: What This Means for Patients and Clinicians
The promising data on salvage nodal radiation therapy has significant implications for both patients and the broader oncology community. For clinicians, the low toxicity and favorable progression-free survival outcomes provide confidence in adopting SNRT as a viable salvage option for men facing recurrent prostate cancer.
From the patient perspective, the combination of advanced imaging techniques, targeted radiation delivery, and an integrated therapeutic approach means that there is renewed hope even after initial treatments have been exhausted. When cancer returns, the options might seem limited and the path forward can appear full of problems. However, the emerging data on SNRT suggests that this is not necessarily the case.
Patients now have access to a treatment modality that not only aims to control the disease but also minimizes the risk of further complications. In many ways, it represents a shift towards more personalized, precision medicine—a trend that is rapidly reshaping oncology. With better diagnostic tools, targeted treatment options, and comprehensive supportive care, the modern approach to prostate cancer recurrence is evolving into one where each patient’s journey is managed with both scientific rigor and compassionate insight.
Comparing SNRT with Other Salvage Treatment Modalities
In the context of recurrent prostate cancer, emerging therapies must be weighed against one another. SNRT joins a growing list of salvage treatments, including surgical options and systemic therapies. Each comes with its own set of benefits and potential drawbacks, and it is crucial to understand where SNRT fits within this broader spectrum.
Here’s a quick comparison of salvage treatment options:
| Therapy Type | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Salvage Nodal Radiation Therapy |
|
|
| Surgical Approaches |
|
|
| Systemic Therapies (Androgen Deprivation) |
|
|
This table underscores that while no single treatment is perfect, SNRT shows its strength in providing targeted therapy with a relatively low incidence of side effects. The choice of therapy, ultimately, should reflect the individual patient’s overall health, prior treatments, and personal preferences.
Overcoming the Challenges: Fine-Tuning Treatment Delivery
Delivering SNRT effectively involves making your way through several layers of logistical and technical challenges. From choosing the right radiation technique to ensuring that concurrent therapies are adequately coordinated, the process can sometimes feel overwhelming. However, several measures can help ease these twists and turns:
- Advanced Planning: Detailed pre-treatment planning using high-resolution imaging ensures that the radiation targets are well defined.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Regular tumor board meetings and multidisciplinary discussions foster clearer communication and consensus on the best care pathways.
- Patient Monitoring: Close follow-up and the use of patient-reported outcomes can help catch any nerve-racking side effects early, allowing for prompt intervention.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing state-of-the-art radiotherapy equipment minimizes risks and maximizes treatment precision.
By paying careful attention to these subtle details, clinicians can effectively figure a path through the complicated pieces of treatment delivery. This integrated approach helps reduce potential complications and ensures that patients receive the safest, most effective care possible.
The Future of Salvage Nodal Radiation Therapy in a Changing Oncology Landscape
Looking ahead, the role of SNRT appears promising in an oncology landscape that is continuously evolving. As further studies corroborate the safety and efficacy of SNRT, we can expect its integration into standard care protocols to grow. Moreover, the combination of SNRT with emerging systemic therapies and immunotherapies offers an intriguing possibility for even greater improvements in patient outcomes.
Future research priorities include:
- Conducting larger, multicenter trials to validate current findings
- Refining patient selection criteria to maximize treatment benefits
- Exploring the synergistic potential of SNRT combined with new targeted agents
- Investigating the long-term quality of life among survivors who undergo SNRT
These steps represent critical milestones that must be met before SNRT can be widely recommended as a must-have option in the salvage treatment arsenal for recurrent prostate cancer. With ongoing commitment to research and clinical excellence, the management of prostate cancer is set to become more personalized and safer than ever before.
Balancing Risks and Rewards: A Pragmatic View
At its core, the decision to deploy salvage nodal radiation therapy is a balancing act. On one side are the clear rewards of improved progression-free survival and minimal toxicity. On the other are the occasional nerve-racking concerns about long-term side effects and the limited scope of existing data.
In weighing these factors, it is important for clinicians to engage in open dialogue with their patients. By explaining the key benefits and potential pitfalls in simple terms, doctors can help patients make fully informed decisions about their treatment pathways. Some of the aspects that should be discussed include:
- Expectations regarding treatment duration and follow-up assessments
- The likelihood of experiencing mild versus severe side effects
- How SNRT compares with alternative salvage therapies
- The potential impact on overall quality of life and daily functioning
This transparent exchange helps demystify the process and ensures that patients feel empowered at every step of their cancer journey. It also paves the way for shared decision-making, a crucial element in modern patient-centered healthcare.
Practical Considerations for Implementing SNRT in Daily Practice
For many oncology practices, the integration of SNRT into routine care is a process that requires careful planning, continuous education, and close attention to evolving clinical data. Here are some practical points that clinicians should consider:
- Training and Education: Stay updated on the latest research findings and technological advancements in radiotherapy techniques. Regular workshops and training sessions can help the clinical team prepare for integrating SNRT into practice.
- Infrastructure Investments: Equipping the radiation oncology department with state-of-the-art equipment, such as VMAT or SBRT, is integral to delivering high-quality SNRT.
- Multidisciplinary Meetings: Regular tumor board and patient case reviews ensure that all clinical decisions are made with the input of various specialists. This collaborative approach is key to addressing the tricky parts of treatment delivery.
- Patient Education: Provide comprehensive educational materials to help patients understand the details of SNRT, including potential side effects and the importance of regular follow-ups.
Implementing these steps can greatly ease the integration process and ensure that SNRT is delivered effectively. In doing so, oncology teams can not only improve patient outcomes but also reduce the burden of complications associated with salvage treatment.
Drawing Conclusions: The Promise of a Safer, More Effective Approach
Based on the current evidence, salvage nodal radiation therapy emerges as a compelling option for managing recurrent prostate cancer. With its low toxicity profile, promising progression-free survival statistics, and the benefits of modern imaging for treatment planning, SNRT is carving out a significant niche in the continuum of cancer care.
While challenges remain—particularly in relation to long-term outcomes and full-scale multicenter validation—the initial data has provided an optimistic outlook. There is a growing consensus among experts that when implemented as part of a broader multidisciplinary strategy, SNRT can play a key role in helping patients reclaim their lives after recurrence.
For clinicians, the evolving evidence on SNRT serves as both an inspiration and a call to continue making informed, patient-focused decisions. For patients, it offers renewed hope that even in the face of cancer’s tricky turns and tangled issues, there is a pathway designed to deliver effective, less invasive salvage therapy.
In summary, while no treatment is without its challenges, the current data supports the idea that SNRT is a super important addition to the array of tools available for managing recurrent prostate cancer. As research continues to dig into this promising approach, the future may well bring even more refined, personalized strategies capable of delivering better outcomes with fewer complications.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Innovation in Prostate Cancer Management
The progress made in the field of radiation oncology over recent years is a testament to how innovation can both confront and overcome obstacles that, at one time, seemed overwhelming. The development and refinement of SNRT reflect this broader trend—a movement toward precision medicine that truly accounts for the fine points of individual disease processes.
By embracing these new techniques and integrating them into comprehensive treatment strategies, the medical community is not only addressing the current challenges but also laying the groundwork for even greater achievements in the future. Patients can take comfort in knowing that every effort is being made to find their way through the confusing bits of cancer management with treatments that are both effective and manageable.
Ongoing discussions, continuous learning, and a commitment to evidence-based practice will ensure that therapies like SNRT continue to evolve. As our understanding deepens, and as we figure a path through the delicate dance of risks and rewards, the promise of a safer, more tailored approach to managing prostate cancer recurrences becomes more and more real.
In the end, the journey toward improved outcomes is a shared one—requiring collaboration, dedication, and most importantly, the willingness to embrace new technologies and strategies. As we look forward to the next chapter in prostate cancer management, salvage nodal radiation therapy stands out as a beacon of hope and a tangible reflection of how modern medicine continues to innovate in the face of challenging, yet conquerable, medical issues.
Originally Post From https://www.cancernetwork.com/view/salvage-nodal-radiation-shows-tolerability-low-toxicity-in-prostate-cancer
Read more about this topic at
Long-term tolerance and outcomes for dose escalation …
Salvage Therapy for Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO …