Fruquintinib in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A New Frontier in Later-Line Therapy
The landscape of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) treatment has seen many advances over the years. Recently, fruquintinib has emerged as a promising later-line option for patients who have exhausted traditional therapies. In this editorial, we take a closer look at fruquintinib’s role within the mCRC treatment paradigm, consider the evidence that supports its use, and discuss the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. We will explore the drug’s mechanism of action, review key trial data, and discuss patient selection and quality-of-life considerations—all while tackling some of the tricky parts and tangled issues inherent in cancer care.
With its FDA approval in November 2023 for patients who have been treated with fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, irinotecan-based chemotherapy, anti-VEGF therapy, and where appropriate, anti-EGFR treatment, fruquintinib is now cementing its role in the ever-evolving management of mCRC. This article offers a balanced opinion on how fruquintinib fits into current practices and what the future might hold in terms of treatment sequencing and combination therapies.
Understanding Fruquintinib’s Mechanism of Action and Its Clinical Implications
Fruquintinib is a highly selective oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that primarily targets receptors in the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway. This mechanism results in an anti-angiogenic effect that is critical in curbing tumor blood supply. It also exhibits activity against lymphogenesis via VEGFR3, which adds another layer of potential benefit for patients with advanced colorectal cancer.
By suppressing the VEGF signaling pathway, fruquintinib works to starve tumors of nutrients required for growth. This approach is distinct from traditional chemotherapy and provides patients with an alternative mechanism, particularly when other treatments have failed. Many clinicians appreciate that this targeted therapy, being an oral medication, offers ease of administration compared to intravenous regimens.
Breaking Down the Mechanism: Anti-Angiogenesis and Beyond
The anti-angiogenic properties of fruquintinib are arguably its most celebrated aspect. Here are some key points that detail how the drug works:
- VEGF Pathway Inhibition: Fruquintinib selectively blocks all three VEGF receptors, leading to reduced blood vessel formation which tumors rely on for growth.
- Impact on Lymphogenesis: Beyond merely inhibiting angiogenesis, it also addresses lymph vessel formation, possibly hindering metastatic spread.
- Oral Administration: The convenience of an oral medication means fewer hospital visits and improved administration flexibility.
Such benefits are significant, especially for patients who have already undergone several lines of aggressive treatment. However, like any therapy, it is accompanied by its own set of challenging bits, including managing side effects such as hypertension and hand-foot syndrome.
Analyzing the Clinical Evidence: Insights from the FRESCO Trials
Prior to its approval, fruquintinib was evaluated in two major randomized clinical trials—the FRESCO and FRESCO-2 studies. The data from these trials provide the backbone for its regulatory approval and offer a window into its effectiveness in a treatment-refractory mCRC population.
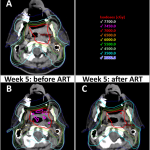
In FRESCO-2, for instance, patients who received fruquintinib had a median overall survival (OS) improvement from 4.8 months in the placebo arm to 7.4 months. This nearly 50% increase in survival is both impressive and important, particularly in a cohort full of patients with limited treatment options.
Key Findings from the FRESCO-2 and FRESCO Trials
Let’s summarize some of the main takeaways from these pivotal studies:
- Overall Survival Benefit: Fruquintinib extended median OS when compared with best supportive care alone. This finding, despite being derived from trials with patients already heavily pretreated, is a testament to the drug’s efficacy in later-line settings.
- High Disease Control Rate: Disease control rates estimated between 50% and 60% illustrate that many patients experienced stable disease, thereby preserving quality of life.
- Tolerability: Although side effects like hypertension and hand-foot syndrome were reported, the toxicities were manageable with appropriate clinical supervision.
This evidence suggests that fruquintinib can serve as a critical tool in the oncologist’s arsenal. Its ability to offer a survival benefit in a population that is both heavily pretreated and in desperate need of new options is a significant achievement. However, with every new therapy, there can be twists and turns that require careful planning and monitoring in clinical practice.
Patient Selection: Considerations in a Heavily Pretreated Population
One of the core issues in integrating fruquintinib into mCRC treatment is identifying the right patients. The drug is approved for those who have already received multiple lines of therapy, meaning its use is confined to a group of patients who are often dealing with a myriad of side effects and decreased overall fitness.
Assessing Suitability: Who Can Benefit Most?
When deciding whether a patient should receive fruquintinib, physicians weigh several factors. Here are some key points to consider:
- Treatment History: Typically, patients must have experienced progression after standard therapies, including fluoropyrimidine-, oxaliplatin-, and irinotecan-based chemotherapy, as well as anti-VEGF treatment.
- Molecular Profile: In cases where a patient is RAS wild-type, and medically appropriate, an anti-EGFR therapy may have been administered before considering fruquintinib.
- Comorbid Conditions: Patients with uncontrolled hypertension or other cardiovascular issues may not be ideal candidates given the drug’s side effect profile.
Personally Tailoring Treatment Plans
In a population where every patient’s journey is unique, treatment decisions must often be individualized. The fine points of each patient’s medical history, personal preferences, and the slight differences in their disease states all play a critical role. For instance, a patient overwhelmed by the bone marrow suppression from previous chemotherapy might benefit from the relative ease and oral administration of fruquintinib.
This level of complex decision-making requires a multidisciplinary approach where oncologists, nurses, and supportive care teams work together to find a path that minimizes additional burdens on patients while still offering hope for extended survival and quality-of-life improvements.
Managing Side Effects: Balancing Efficacy and Patient Comfort
No discussion regarding a potent anti-cancer agent is complete without addressing its safety profile. Fruquintinib is known for its predictable side effects, many of which mirror the classic toxicities of TKIs but are usually manageable with careful monitoring and preemptive action.
Common Adverse Effects and Practical Management Strategies
While the literature and clinical trials consistently highlight the effectiveness of fruquintinib, oncologists must also be vigilant about its side effects. Here are some of the common adverse events observed, along with strategies to mitigate them:
| Side Effect | Incidence | Management Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | Occurs in nearly 61% of patients (with grade 3 or 4 in about 23%) |
|
| Hand-Foot Syndrome | Any grade in approximately 49%, with 11% experiencing high-grade toxicity |
|
| Other TKI-Related Symptoms | Variable incidence |
|
Through proactive management—including frequent check-ups and timely intervention—the negative impact of these side effects on quality of life can be minimized. Patients have reported that the ease of administration and the drug’s overall tolerability often outweigh the intimidating prospect of these side effects, especially when balanced against the potential for extended survival.
Quality-of-Life Considerations in Later-Line Settings
For many patients facing mCRC, quality of life is as critical as the duration of survival. The goal in later-line therapy is not only to prolong life but also to ensure that patients maintain a reasonable level of everyday function. Researchers have noted that disease stabilization, even without significant tumor shrinkage, can contribute to a maintained or even improved quality of life.
Patients and their caregivers often express that treatment options offering a better side effect profile are particularly welcome when previous therapies have been burdensome and nerve-racking. In this context, the role of fruquintinib is especially promising, serving as a chemotherapy-free alternative that many patients find more manageable on a daily basis.
Looking Ahead: Treatment Sequencing and Combined Approaches
While the current approval for fruquintinib is for later lines of therapy, an important question remains: could this agent find a role in earlier stages of the treatment journey? Experts continue to debate the optimal sequencing of VEGF-targeted agents and the potential of combination strategies to enhance therapeutic outcomes.
The Challenge of Optimal Sequencing
One of the more tangled issues in mCRC management is determining the right order in which to administer available therapies. With several VEGF inhibitors—such as bevacizumab, ramucirumab, and regorafenib—in current use, fruquintinib’s place in the treatment sequence continues to be refined.
There are two main areas of uncertainty:
- Direct Comparisons Between Agents: There are few head-to-head trials that compare the efficacy of these different VEGF inhibitors. This lack of direct data makes it tricky for clinicians to decide which agent is best suited for which patient at a particular time.
- Predictive Biomarkers: The absence of reliable biomarkers to predict response to each available therapy further complicates decisions, making it even more challenging to figure a path in the treatment timeline.
Despite these challenges, the overriding principle remains that targeting the VEGF pathway has proven effective in mCRC. Continued research and upcoming trials aimed at evaluating combination therapies or moving fruquintinib into earlier lines of treatment will be key to refining its use.
Combination Therapies: Expanding the Therapeutic Horizon
In addition to sequencing, the interest in combining fruquintinib with other therapeutic agents is on the rise. The rationale behind such approaches is that combining drugs with complementary mechanisms may yield better outcomes by tackling cancer through multiple avenues simultaneously.
For instance, studies are currently investigating the benefits of combining fruquintinib with chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or other targeted agents. Such combinations may help in:
- Maximizing tumor control
- Reducing the risk of resistance
- Improving overall response rates
However, these strategies come with their own set of tricky parts. It requires careful design of clinical trials, vigilant monitoring for overlapping toxicities, and a clear understanding of the subtle details of drug interactions. Considering these factors, smart clinical strategies that integrate multiple agents are needed to ensure safety while pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in cancer therapy.
Expert Opinions and Perspectives on Fruquintinib
Leading experts in the field have weighed in on the potential benefits and challenges associated with fruquintinib. Many echo the sentiment of cautious optimism, pointing out that while the drug offers a much-needed option for patients with refractory mCRC, there remain several confusing bits and limiting factors that need further investigation.
Insights from Clinical Practice
From the perspective of practicing oncologists, fruquintinib is notable for its well-defined role in later-line settings. Here are some key expert opinions that have emerged:
- Ease of Use: The oral formulation simplifies treatment regimens and reduces the need for frequent hospital visits—an important consideration for patient comfort and convenience.
- Manageable Side Effects: The predictable side effect profile, although not without its challenges, appears to be manageable with proper patient selection and proactive measures.
- Plausibility for Future Use: Many experts are enthusiastic about exploring fruquintinib further—in both combination therapies and potentially in earlier lines of treatment. The evolving data in this space is something both clinicians and researchers are keenly watching.
While these expert insights are encouraging, they also highlight the fact that the treatment journey for mCRC is far from straightforward. It is a process laden with challenging twists and turns that require flexible and adaptive treatment plans customized to each patient’s evolving condition.
Patient and Caregiver Perspectives: Balancing Hope with Realism
An often underexplored aspect of new cancer therapies is the patient and caregiver experience. For many families, the promise of a new drug like fruquintinib offers hope when traditional options have been exhausted. However, there is also a need to manage expectations realistically.
Real-World Experiences and Expectations
Patients and caregivers are frequently faced with a confusing mix of optimism and apprehension when considering a new treatment avenue. Here are a few points that encapsulate their experience:
- Hope for Improved Quality of Life: With previous treatments sometimes resulting in overwhelming side effects or severe quality-of-life reductions, the prospect of a more tolerable option is enticing.
- Realistic Appraisal of Benefits: It is critical that both patients and their families understand that while fruquintinib may help stabilize disease and extend survival, it is not a cure. Setting realistic goals helps maintain a practical outlook amid the tension and challenges of advanced cancer care.
- Active Participation in Decision-Making: Most experts advocate for a shared decision-making process, where patients are informed about the potential benefits and the various side effects so they feel empowered to take a more active role in their treatment planning.
This balanced approach not only fosters a therapeutic alliance between the healthcare team and the patient but also ensures that treatment choices are aligned with the patient’s values and preferences.
Policy and Healthcare System Considerations
Expanding access to promising treatments such as fruquintinib does not occur in isolation. It requires the alignment of various stakeholders including pharmaceutical companies, insurance providers, and regulatory agencies. Recent moves, such as fruquintinib’s inclusion on the CVS Caremark National Template Formularies, signify important policy shifts that can lead to broader access for patients.
Coverage and Reimbursement: Implications for Patient Access
The decision by Takeda Oncology to ensure that fruquintinib is covered by a large network of insurers means that more patients may benefit from this therapeutic option. This is particularly crucial in the later-line setting where every available treatment option matters. However, the following factors remain essential:
- Insurance Coverage: Widespread coverage reduces the financial burden on patients and makes newer therapies accessible to a broader demographic.
- Reimbursement Policies: Streamlined and fair reimbursement can help ensure that patients from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds are not left behind.
- Real-World Data Collection: Continued collection and sharing of efficacy and safety data will help refine reimbursement models and inform future policy decisions.
Overall, enabling broader access to fruquintinib highlights the interconnected nature of clinical innovation and healthcare policy. It is a reminder that improving patient outcomes requires not only scientific breakthroughs but also supportive policy frameworks.
The Road Ahead: Future Research and Clinical Trials
The journey of fruquintinib in the treatment of mCRC is still unfolding. As new trials are launched and ongoing studies mature, clinicians and researchers alike are excited about the potential for this drug to further change the treatment landscape, including exploring its role in first-line maintenance or second-line settings when combined with chemotherapy.
Ongoing Research: What’s Next for Fruquintinib?
Current research efforts are aimed at answering several key questions that remain on the minds of healthcare providers:
- Early-Line Use: Can fruquintinib be safely and effectively incorporated into treatment protocols earlier in the disease course?
- Combination Regimens: What are the best partner therapies to combine with fruquintinib to enhance outcomes, and how can we minimize overlapping toxicities?
- Individualizing Treatment: Are there biomarkers or clinical factors that could help predict which patients will benefit most, thereby fine-tuning treatment personalization?
Further research in these areas holds promise for unlocking even greater potential from fruquintinib. As more data become available, we anticipate that treatment guidelines will be updated to reflect these new insights, ensuring that patients continue to receive state-of-the-art care based on the latest evidence.
Collaboration and Multi-Disciplinary Input
Future clinical trials will benefit from the active involvement of multidisciplinary teams. Collaboration between oncologists, pharmacologists, and clinical researchers is key to understanding the subtle details of drug interactions and to develop strategies that streamline the treatment process. Through such cooperative efforts, the oncology community can tackle the hidden complexities and tangled issues that come with integrating new therapies into routine care.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective on Fruquintinib’s Role in mCRC
The introduction of fruquintinib as a treatment option for metastatic colorectal cancer represents a significant step forward in the challenging field of oncology. For patients who have run out of standard therapeutic options, this agent offers not only an opportunity for prolonged survival but also a chance to maintain a reasonable quality of life with an oral, manageable regimen.
It is clear that while fruquintinib carries promise, its integration into clinical practice requires careful consideration of patient selection, side effect management, and treatment sequencing. Ongoing research, supportive policy changes, and the collaborative efforts of the healthcare community will play a critical role in defining its future. By addressing the nerve-racking challenges with practical strategies and continuously learning from real-world applications, clinicians can better steer through the evolving landscape of mCRC treatment.
In today’s complex healthcare environment, every new tool is both a beacon of hope and a call to action. Fruquintinib stands as a super important addition to our therapeutic toolkit—but like every therapy, its success depends on how well we manage its tricky parts, gauge its benefits, and integrate it into personalized treatment plans for each patient. As we continue to figure a path forward, the combined efforts of clinicians, researchers, and policymakers will be essential in ensuring that advancements in cancer care translate into tangible, positive outcomes for patients facing this daunting disease.
As we reflect on the progress made so far and look ahead to ongoing advancements, one thing is certain: the field of oncology is continuously evolving. With agents like fruquintinib, the promise of longer survival and improved quality of life is within reach for many mCRC patients—a promise that, with careful application and relentless research, may soon transform into a new standard of care.
In summary, while there remain confusing bits and challenges still to be unraveled in the domain of targeted cancer therapy, fruquintinib offers a constructive and hopeful avenue. By continuing to work through the fine points and subtle parts of its clinical application, we can better serve patients who are in desperate need of new options. The journey ahead might be full of twists and turns, but with a thoughtful, evidence-based approach, the horizon of mCRC treatment looks brighter than ever before.
Originally Post From https://www.onclive.com/view/fruquintinib-represents-viable-later-line-option-for-mcrc-as-access-expands-for-patients
Read more about this topic at
Optimizing Treatment Sequence for Late-line Metastatic …
optimizing targeted biological therapies to improve outcomes