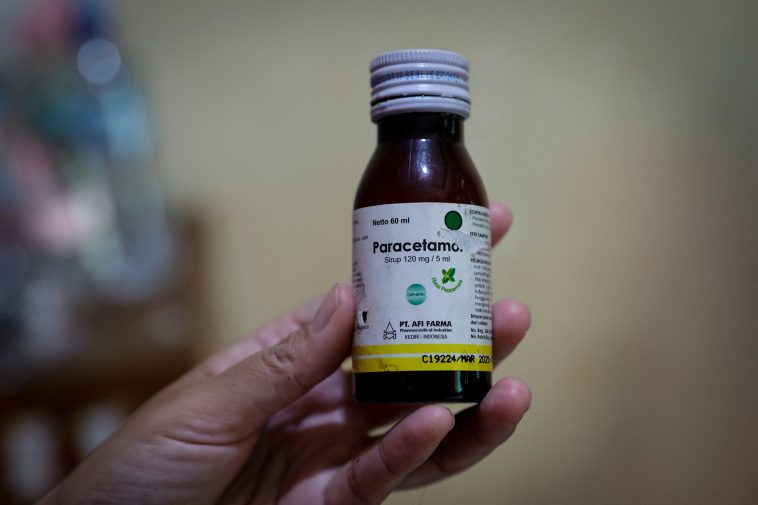
Introduction: A Crisis in Cough Syrup Safety
India has long been known as the “pharmacy of the world,” a title earned through decades of providing affordable and life-saving medicines to countries across the globe. Yet, recent events have cast a shadow over this reputation. A series of tragic incidents involving contaminated cough syrups have not only resulted in the premature loss of innocent lives but have also exposed several tangled issues within the nation’s drug testing and regulatory systems. In this opinion piece, we take a closer look at how a lapse in quality standards turned everyday medicine into a potential poison and discuss the key measures required to restore global trust in Indian pharmaceuticals.
The Silent Crisis of Contaminated Cough Syrups
The story of tainted cough syrups is not entirely new, but its persistent occurrence has left many puzzled over the confusing bits of drug regulation and quality control. Recent events in Madhya Pradesh and Rajasthan, where dozens of children lost their lives after consuming syrup products laced with dangerous chemicals such as diethylene glycol (DEG), have triggered both national and international concern. These tragedies remind us that even when a system appears robust, hidden complexities can undermine the safety of medicines at a fundamental level.
Tracing the Emergence of Tainted Medicines
Historically, India’s pharmaceutical industry has built a solid reputation for efficiency and affordability. Yet, sporadic cases of peripheral negligence have gradually widened the gap between high production standards and everyday practice. By digging into the history of these issues, one can identify several key factors that have contributed to today’s crisis:
- Lapses in Quality Assurance: There have been several instances where drugmakers failed to test essential raw materials or final products with the rigor required by national laws.
- Insufficient Regulatory Oversight: With regulatory systems that sometimes appear to be too relaxed, there are dozens of tricky parts in the screening process that allow contaminants to slip through.
- Pressure from International Markets: With billions of dollars at stake in exports, some manufacturers might feel pressured to cut corners to meet global demand quickly.
- Lack of Transparent Testing Protocols: Without reliable third-party verification, it becomes challenging to ensure that every batch of medicine meets the highest standards of safety.
The History of Pharmaceutical Excellence and Recent Troubles
For decades, India’s pharmaceutical prowess has been a source of pride. The nation has successfully supplied critical medications—from HIV antiretrovirals to COVID-19 vaccines—to countries with varying levels of healthcare infrastructure. However, this history of excellence now stands at a crossroads as repeated tragedies have revealed some of the more complicated pieces of the system:
- Historical Success: Indian manufacturers have been recognized globally for making essential medications widely available and affordable.
- Emergence of Quality Concerns: Reports of contaminated cough syrups and other medicines, particularly those used for children, have highlighted significant oversights.
- Recurring Incidents: From the tragic case in Jammu in December 2019 to multiple child deaths in recent months, the pattern points to recurring negligence and oversight failures.
- International Criticism: Global news agencies and regulatory bodies like the World Health Organization have increasingly noted the dangerous twists and turns within India’s drug regulation system.
Challenges in Drug Testing and Quality Assurance
At the heart of these tragedies lies a failure to spot the hidden complexities of drug manufacturing. Even as governments enforce laws that mandate the testing of raw materials and final products, loopholes in these procedures continue to cause problems. Whether it is the mislabeling of ingredients or insufficient toxicity tests, the system is often left vulnerable to exploitation.
Key challenges include:
- Independent Testing Limitations: Most manufacturers rely on in-house testing rather than verified third-party labs, which can lead to a conflict of interest and missed detections of harmful substances.
- Inadequate Screening Processes: The testing protocols are sometimes too nerve-racking in their complexity, causing delays and potential oversights when dealing with a mass production environment.
- Regulatory Compliance Gaps: Despite laws that detail mandatory tests, some companies continue to bypass or falsify these records. This failure to manage the hidden complexities of drug formulation is a major contributor to recurring incidents.
- Technological Shortcomings: Traditional inspection methods, reliant on manual review and incomplete digital records, make it challenging to trace the subtle details of each drug’s production journey.
One useful way to visualize these challenges is through a summary table that outlines the main obstacles in quality assurance:
| Area | Issues |
|---|---|
| Testing Protocols | Overreliance on internal testing, limited third-party oversight |
| Regulatory Environment | Loopholes in law enforcement, inconsistent labelling, non-transparency |
| Technology Adoption | Outdated tracing practices, slow adoption of digital systems |
| Accountability | Lack of strict penalties and legal consequences for violators |
The Impact on Child Health and Global Trust
The heart-wrenching loss of young lives is the most immediate and devastating consequence of unsafe cough syrups. When children fall victim to contaminated products, the ripple effects extend far beyond the tragic loss of life—they also erode the trust that countless international partners have placed in India’s pharmaceutical industry.
Here are some of the pressing concerns regarding this impact:
- Child Safety at Risk: Unsafe medicines, particularly those containing toxic chemicals like DEG, have led to kidney failure, neurological complications, and other life-threatening issues among children.
- Eroded Global Confidence: International buyers, already wary of quality lapses, may begin questioning the safety of other Indian pharmaceutical exports, from vaccines to generic drugs.
- Public Distrust: With domestic incidents making headlines, patients and caregivers are increasingly skeptical of over-the-counter cough syrups and other liquid formulations, often leading them to seek alternative treatments.
- Regulatory Backlash: Notifications from global organizations like the World Health Organization have sparked fears that India’s reputation as a reliable supplier might be compromised if these issues continue unchecked.
Regulatory Gaps in the Indian Pharmaceutical Sector
Despite strict national laws that mandate extensive testing and quality checks, there are several tangled issues within the regulatory framework that have allowed these tragedies to persist. The existing system sometimes appears to be working through glaring gaps in transparency and accountability.
Some of the most critical regulatory gaps include:
- Inefficient Enforcement: Although laws allow for severe penalties, including life imprisonment for those culpable in child deaths, enforcement is weak. A loose regulatory framework may embolden companies to skirt safety measures in their rush to meet high demands.
- Inconsistent Monitoring: Often, the same manufacturers operate with minimal oversight for decades, easily slipping into routines that reduce the intensity of quality controls. The lack of diversified, independent monitoring creates room for quality shortcuts.
- Limited International Oversight: The absence of collaborative international audits means that some dangerous batches might never be caught by local regulators before reaching the market.
- Delayed Response Mechanisms: In many cases, public alerts and recalls are issued only after the damage is done. The system is slow to react once the first signs of trouble have appeared, putting more lives in jeopardy.
Ensuring Safety Through Strict Accountability Measures
Restoring global trust in Indian medicines requires a hard look at accountability measures. It is clear that the current state of affairs—from inadequate testing protocols to inefficient regulatory systems—demands a comprehensive overhaul. A child’s life lost to tainted medication represents not only a personal tragedy but also a significant public health crisis.
To address these issues, several steps should be considered:
- Independent Quality Control: Mandate that every batch of medicine undergoes toxicity testing by accredited, impartial third-party laboratories. This approach could reduce the risk of conflicts of interest and ensure consistent quality.
- Stricter Legal Penalties: Current laws already allow for severe punishments, but these must be applied rigorously. Consistent, law-based accountability should act as a deterrent against cutting corners in quality control.
- Regular Audits and Transparent Reporting: Frequent audits of manufacturing processes, conducted by both domestic and international agencies, can improve transparency, ensuring that no hidden complexities slip through the safety net.
- Investment in New Technology: Upgrading to modern digital traceability systems—from raw material sourcing through to final shipment—can help identify any deviations early in the process, providing a clearer picture of potential toxic exposures.
Economic and Global Implications of Reputational Damage
The quality issues surrounding cough syrups extend their influence well beyond public health, casting a long shadow over India’s standing in the international pharmaceutical market. With exports valued at more than $25 billion annually, even a minor lapse in safety protocols threatens to have nerve-racking economic consequences.
Key economic and global implications include:
- Reduced Market Confidence: International buyers and humanitarian organizations that depend on Indian generics might begin to reassess their procurement policies, leading to a potential decline in export orders.
- Increased Legal and Financial Liabilities: As class-action lawsuits and global penalties loom on the horizon, companies might face significant financial and reputational losses, further destabilizing the market.
- Strained International Relations: Some importing nations may start to question India’s ability to supply safe medications, prompting them to tighten import regulations or source alternatives from other countries.
- Long-term Economic Impact: A prolonged crisis in quality control could affect the overall economic health of the pharmaceutical sector, leading to reduced investments in research, development, and production capabilities.
To provide a clear breakdown of the economic risks, consider the following table outlining key factors:
| Risk Factor | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Global Buyer Confidence | Reduction in orders, shift to alternative suppliers |
| Legal and Financial Costs | Increased litigation, fines, and compensation claims |
| Market Share | Loss of market share in critical regions, especially in developing countries |
| Export Earnings | Potential decrease in earnings, affecting the broader economy |
Building Confidence: A Way Forward for Drug Regulation
Given the current problems, it is essential to figure a path that rebuilds the regulatory framework and aligns it with international best practices. The challenge is to manage your way through the complicated pieces of modern drug regulation by implementing steps that simultaneously address safety, accountability, and technology.
The following recommendations could serve as a roadmap for effective reforms:
- Mandatory Third-Party Certification: Introduce strict laws that require independent certification for each batch of pharmaceuticals. Not only would this ensure a higher level of safety, but it would also restore public confidence in the drugs available in the market.
- Enhanced Digital Traceability: Adopt digital systems that provide end-to-end traceability from raw materials to finished products. This technological upgrade would allow regulators and auditors alike to take a closer look at every subtle detail involved in the manufacturing process.
- International Collaboration: Invite oversight from global organizations, aligning Indian regulatory practices with internationally recognized standards. Joint inspection frameworks can be a super important tool in ensuring that exported medicines meet the high safety demands of importing nations.
- Consistent Enforcement of Penalties: Ensure the law is applied equally and strictly to all entities found in violation of drug safety norms. This will send a strong signal that negligence or fraudulent practices will have severe consequences.
- Regular Training and Upgrading Skills: Invest in ongoing training programs for regulators and quality inspectors so they remain aware of the fine points of evolving pharmaceutical technology and modern hazards. Improved training can help officials better detect batch inconsistencies and other subtle issues before they spiral out of control.
Understanding the Public Health and Policy Dimensions
The public health implications of contaminated medicines are far-reaching. Apart from immediate health hazards, repeated incidents of tainted products stress the healthcare system, compel massive recalls, and lead policymakers to revisit and tighten regulations. It is imperative for both government bodies and pharmaceutical companies to get into a continuous cycle of review and improvement.
Some critical public health and policy dimensions that need attention include:
- Public Awareness: Developing large-scale public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the importance of safe medication practices, and how to recognize certified brands.
- Transparent Reporting: Initiating a system of regular public reports on drug safety that detail incidents, corrective measures, and improvements made over a specified period.
- Collaboration with Health Experts: Engaging with experts from alternative medicine, nutrition, and modern medicine to develop a holistic approach to drug safety will provide diverse perspectives and innovative solutions to long-standing problems.
- Legislative Reforms: Encouraging lawmakers to focus on the nitty-gritty of drug safety regulations, including periodic revision of permissible levels for toxins such as DEG and EG, to match evolving international standards.
Examining the Root Causes: A Closer Look at Production Practices
An essential part of finding your way through this crisis involves analyzing the production practices that have allowed adulterated medicines to reach market shelves. The failure to adequately inspect every step of the manufacturing process has led to repeated oversights in quality control. A thorough review of these practices reveals several problematic areas:
- Overlooked Raw Material Sourcing: Often, manufacturers prioritize cost over quality, sourcing raw materials without sufficient screening. Such shortcuts can introduce harmful contaminants into the final product.
- Inadequate Process Controls: Many pharmaceutical production facilities lack sufficient automated systems to monitor production parameters, leaving a gap in tracking minor yet critical changes in the formulation process.
- Failure in Batch-Level Testing: With batch-testing sometimes being rushed or improperly documented, regulators have a tough time pinpointing exactly where in the chain the contamination took place.
- Lack of Standardization Across Facilities: Different production sites may follow varying protocols, making it difficult to enforce a uniform standard of quality across the industry.
These issues underscore the need for significant improvements not only in regulatory oversight but also in the internal quality control practices adopted by manufacturers. More robust and technologically integrated manufacturing practices could help reduce the chances of these hidden complexities escalating into public health disasters.
The Role of International Bodies in Enhancing Drug Safety
International organizations like the World Health Organization play a key role in setting benchmarks for drug safety. By providing guidelines and frameworks for regulatory practices, they offer a pathway to align domestic practices with global standards. However, recent statements from the WHO have highlighted that even when contaminated batches are identified and not officially exported, the potential for unofficial shipments remains a worrying possibility.
Key aspects of international collaboration include:
- Adopting Global Benchmarking Tools: India could align its domestic regulatory systems with WHO’s Global Benchmarking Tool for regulatory systems. This approach would provide critical oversight and comparability of safety standards.
- Developing Joint Inspection Frameworks: Inviting joint inspections with representatives from major importing countries could provide additional layers of accountability and ensure compliance with the highest safety standards.
- Regular Information Exchange: Establishing a robust dialogue with international regulatory agencies can help adopt best practices and respond proactively to emerging threats in pharmaceutical quality.
- Collaborative Research and Development: Working together on research into safer, more efficient testing methodologies could lead to innovations that would be mutually beneficial for both domestic industries and international markets.
Implementing Long-Term Strategic Reforms
The current series of tragedies demands not only a short-term response but a long-term strategic overhaul of the drug manufacturing and regulation system. Embracing systematic reforms is essential to ensure that every dose of medicine—especially those meant for vulnerable populations—meets uncompromising safety standards.
Strategic reforms should include:
- Policy Overhaul: A comprehensive review of existing drug safety policies with a focus on addressing the confusing bits and subtle details that have allowed these tragedies to occur.
- Enhanced Infrastructure Investment: Allocating significant budgets to upgrade testing facilities and digital traceability systems. This investment will be key in managing your way through the demanding parts of modern drug production oversight.
- Collaboration with Academia: Engaging experts from academic institutions can foster innovative research in toxicology, quality control, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Such collaborations can also help craft more effective training modules for regulatory inspectors.
- Public and Private Sector Partnerships: Encouraging a synergistic relationship between government agencies and manufacturers to foster transparency. Bullet-proof partnership models could include shared responsibilities in quality assurance, leading to better overall outcomes in public health.
Conclusion: Restoring Trust in Indian Medicines
The contamination of cough syrups is a wake-up call—a reminder that even the most celebrated institutions can falter when the hidden complexities of quality control and regulation are not managed with the utmost care. Every incident of a contaminated product is a profound loss, especially when it involves the life of a child. The emergency to figure a path that incorporates independent testing, stringent legal penalties, and digital traceability systems cannot be overstated.
India’s status as a global pharmaceutical powerhouse is built on decades of hard work and meticulous research. It is super important that the current challenges be addressed head-on, with actionable reforms that restore both domestic and international confidence. Only then can India ensure that a spoonful of medicine remains a symbol of healing—and not a byproduct of hidden, dangerous shortcuts.
This transformation will require coordination across multiple fronts: from government policymakers, regulatory bodies, and manufacturers to international organizations and healthcare professionals. We must all work through the tangled issues of our present system in order to build a safer, more transparent future where public health is never compromised by oversight lapses again.
Let us pledge to not rest until every child, every patient, and every global partner can be assured that when they receive an Indian medicine, they are getting a product that meets the most exacting standards of safety and quality. The journey ahead is complicated and perhaps even overwhelming at times, but the moral imperative—to safeguard life and health—demands nothing less.
In the coming years, with the right policies, technological upgrades, and unwavering accountability, India’s pharmaceutical industry can overcome these hidden complexities. It can reclaim its reputation and continue to be a beacon for affordable, quality medicines worldwide. The road to recovery might be filled with twists and turns, but it is a path we must take, for every child lost to unsafe medicine is a loss to humanity itself.
Originally Post From https://www.greaterkashmir.com/opinion/deadly-doses-how-cough-syrups-turned-into-poison/
Read more about this topic at
The deadly dose: Inside India’s cough syrup obsession
Toxic Cough Syrup, Deadly Fallout: Here’s How The Public …